Description
At the forefront of medicine and technology, we are proud to offer these incredible, uncompromised replicas of human anatomy. Using the latest 3D printing technology and materials available, this model is an exact replica of a human cadaver, brought to "life" by extensive medical scanning and manufacturing technologies. Over are the days of using ethically questionable cadavers, the mess of hazardous preservation chemicals, and the inaccuracies of plastinated models that often over-enhance anatomy for display, not realism. See the future, and the beauty, of real human anatomy with these incredible anatomical replicas!
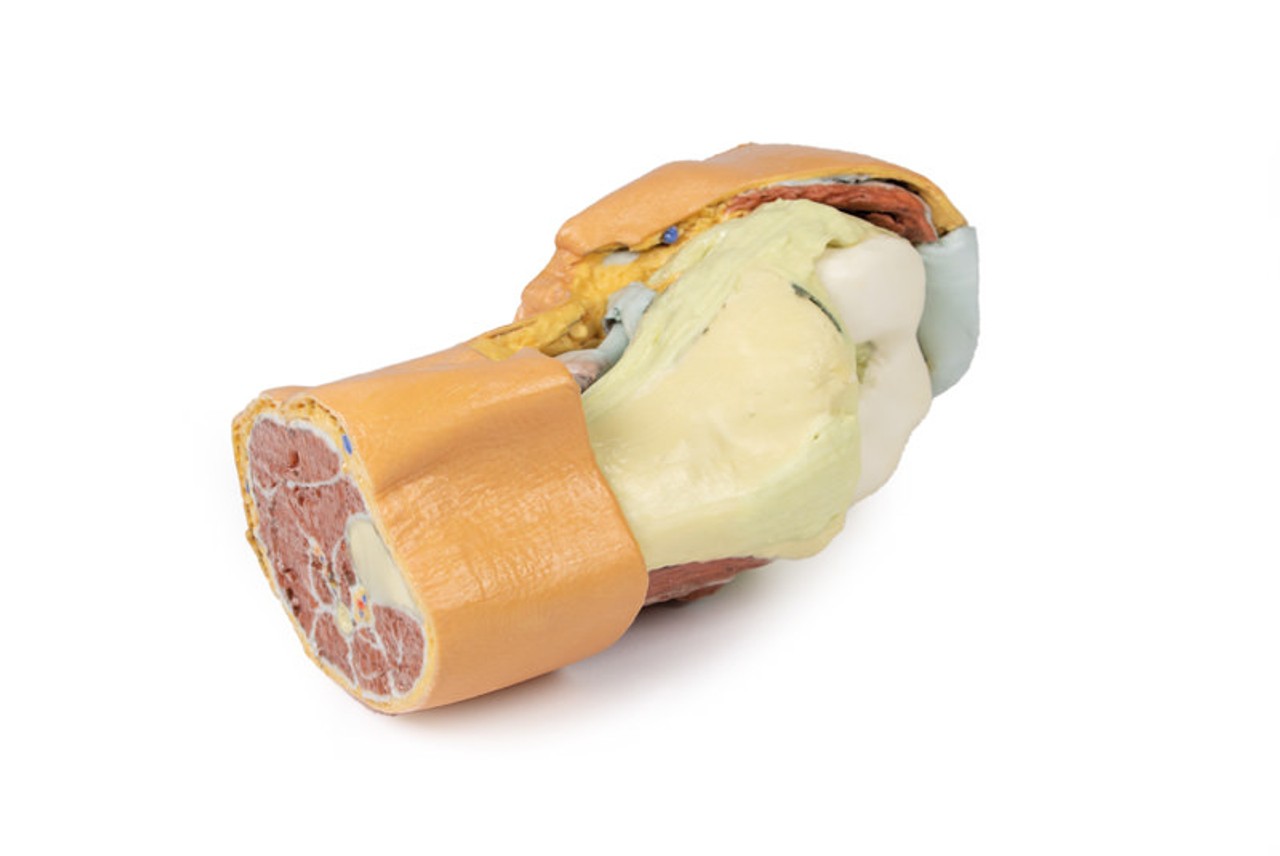
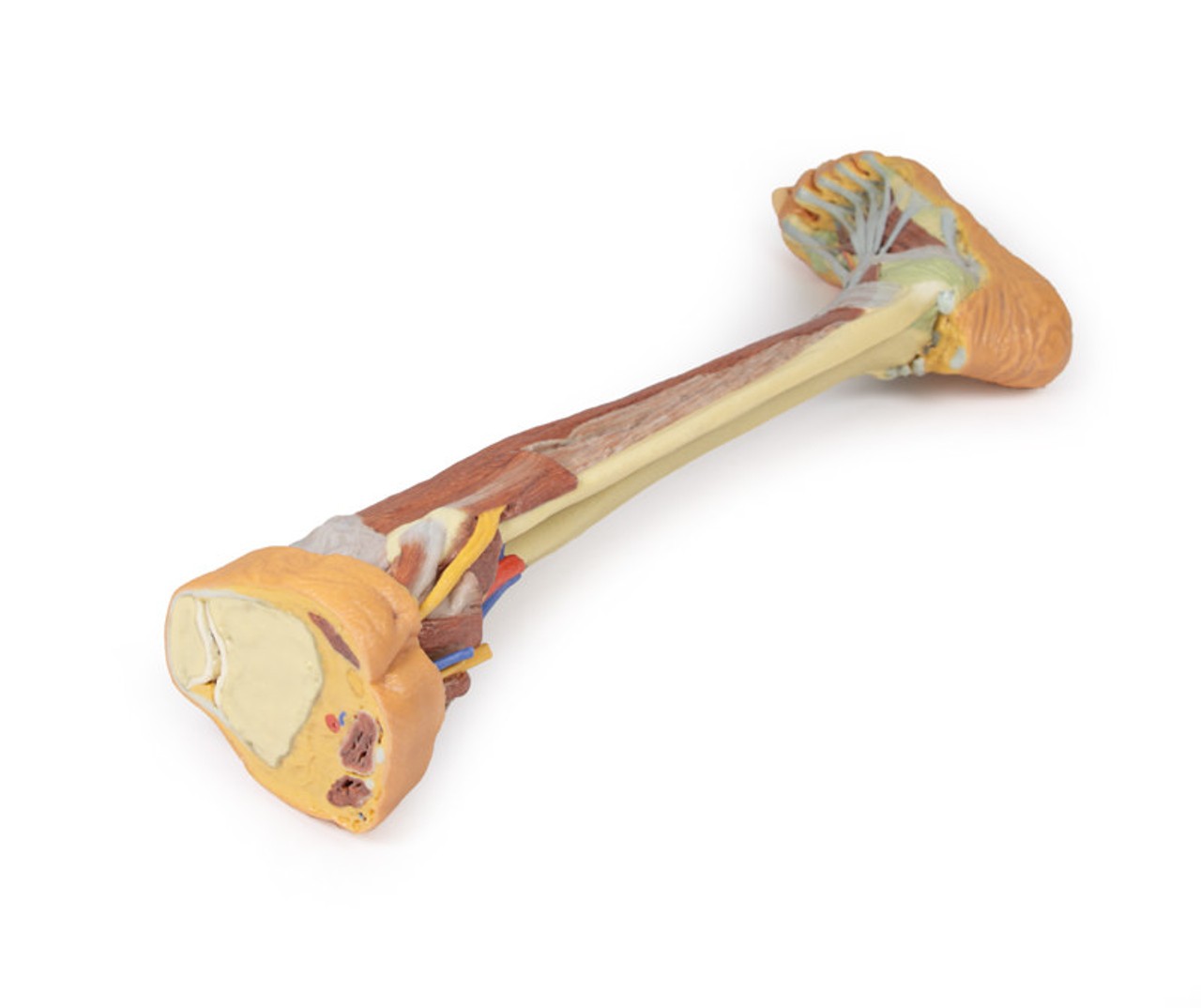
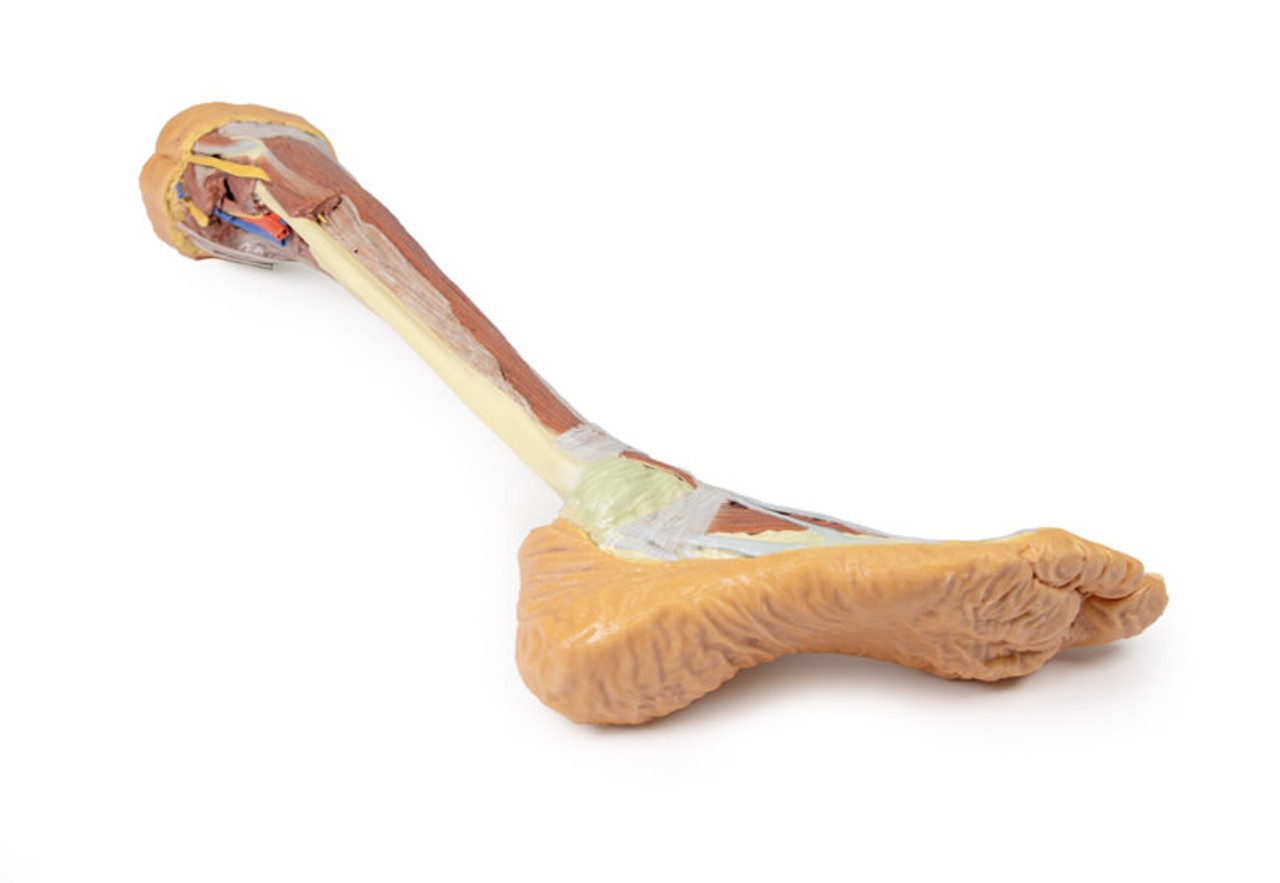
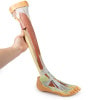
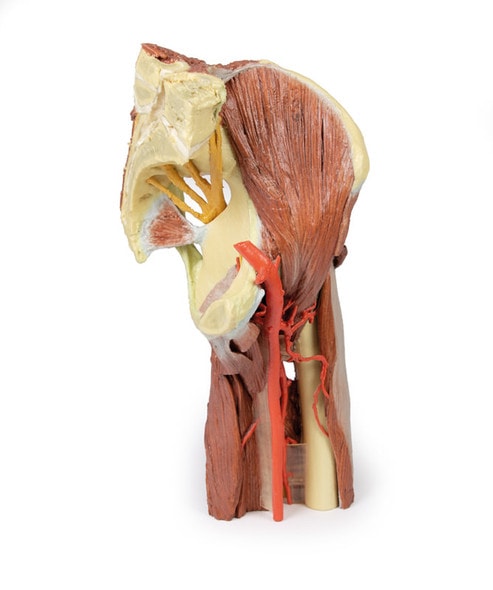
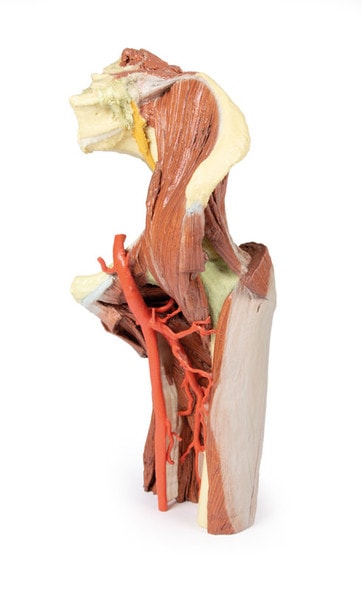
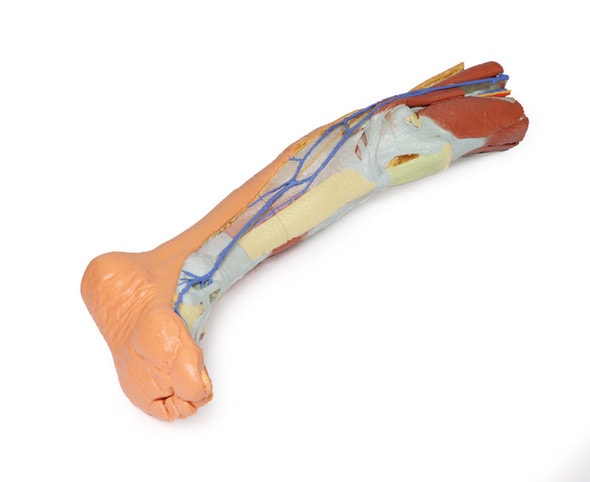
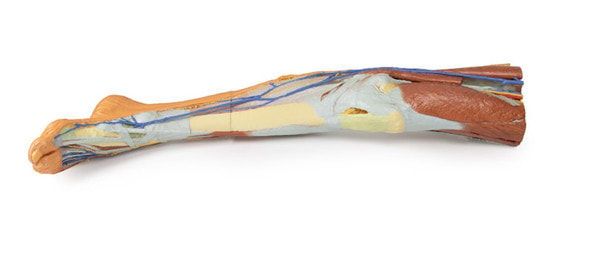
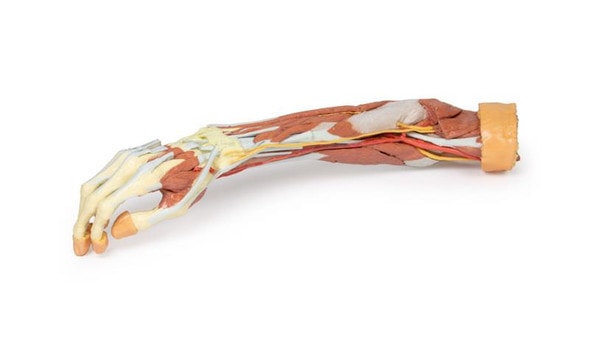
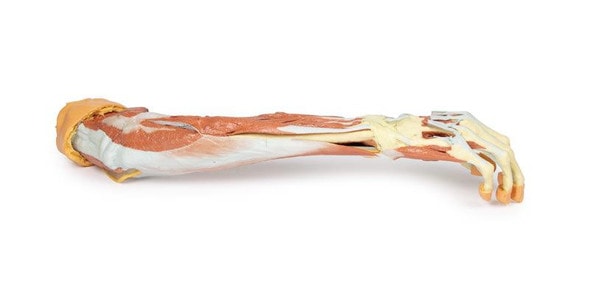
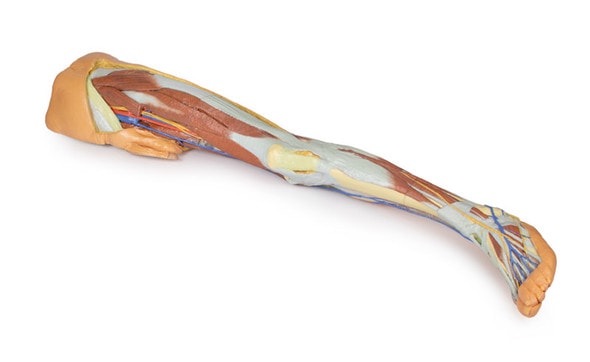
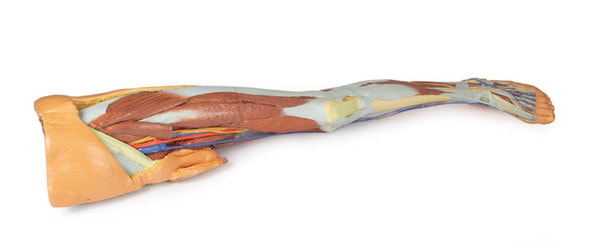
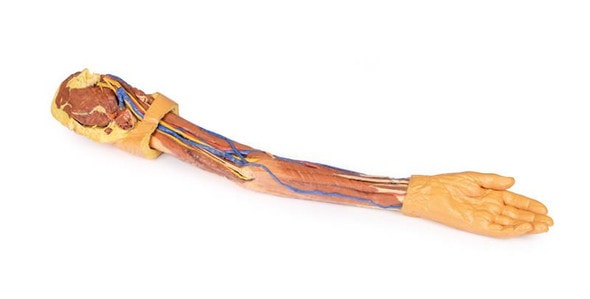
This 3D printed specimen consists of a right partial lower limb sectioned just proximal to the knee joint and complete through a partially dissected foot exposing the structures on the dorsum. In the proximal cross section, the patella articulates with the distal femur anteriorly, while the posterior portion of the specimen preserves structures within the superior portion of the popliteal fossa (including the popliteal artery, vein, and terminal portion of the sciatic nerve).
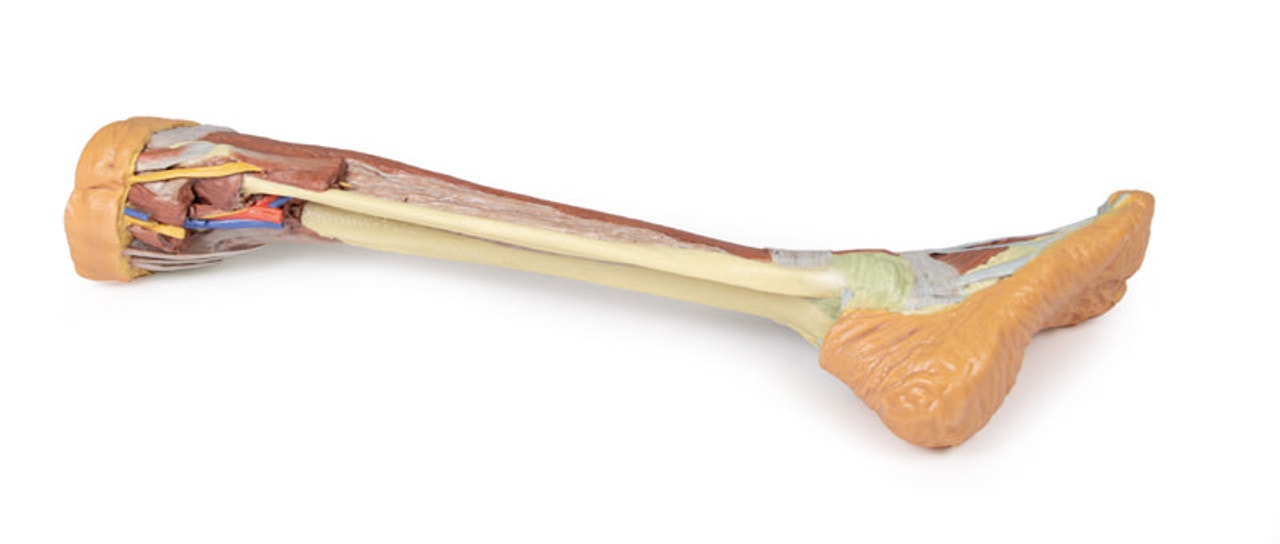
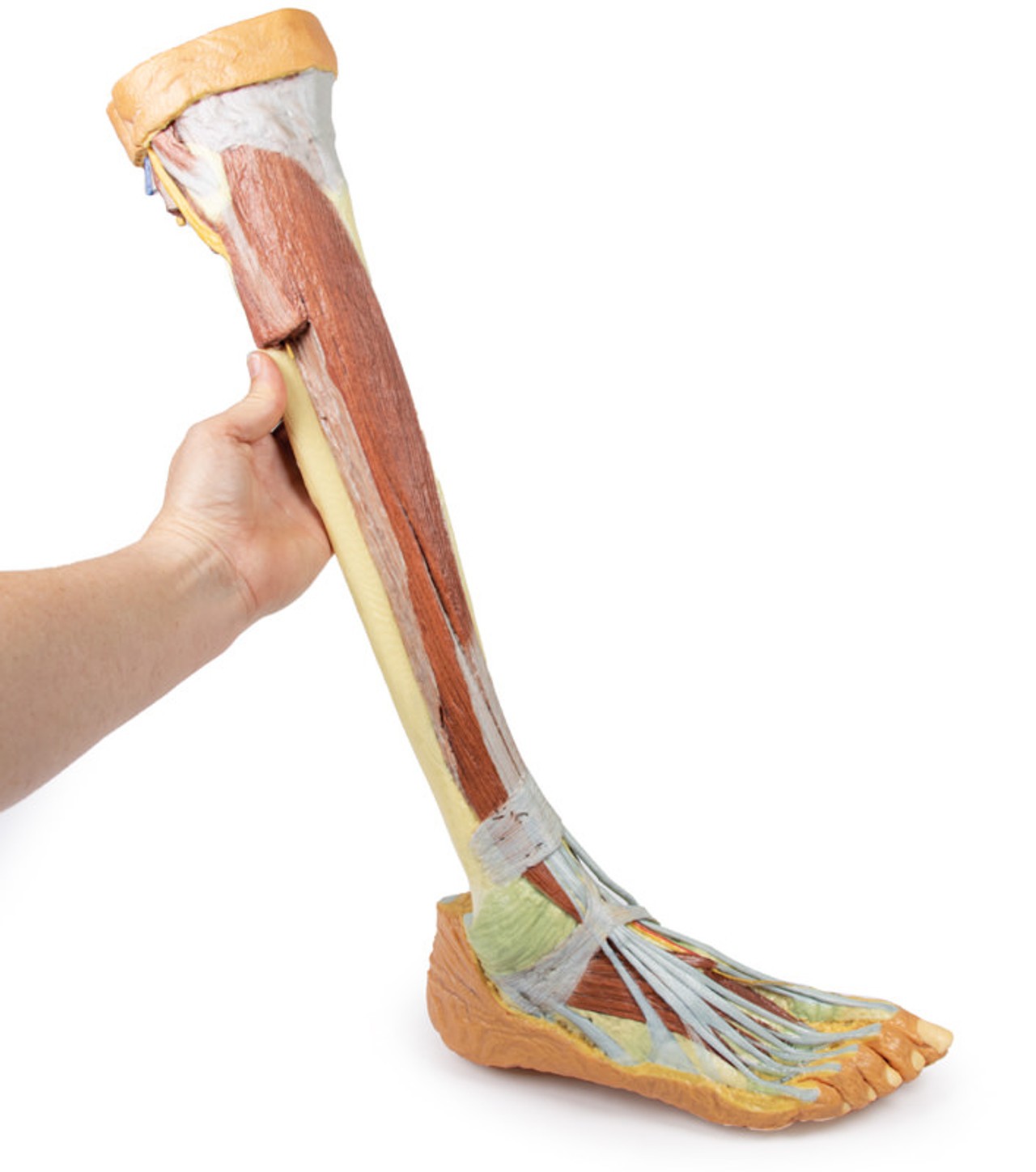
On the posterior aspect of the specimen distal to the knee joint, most of the musculature has been removed to demonstrate the passage of the neurovascular structures (common peroneal nerve, tibial nerve, posterior tibial artery, anterior tibial artery) relative to the deep musculature (e.g., popliteus muscle) and the interosseous membrane between the exposed posterior surfaces of the tibia and fibula. Medially the pes anserinus is visible inserting onto the medial aspect of the proximal tibia, while laterally the biceps femoris is seen inserting into the head of the fibula adjacent to the common peroneal nerve.
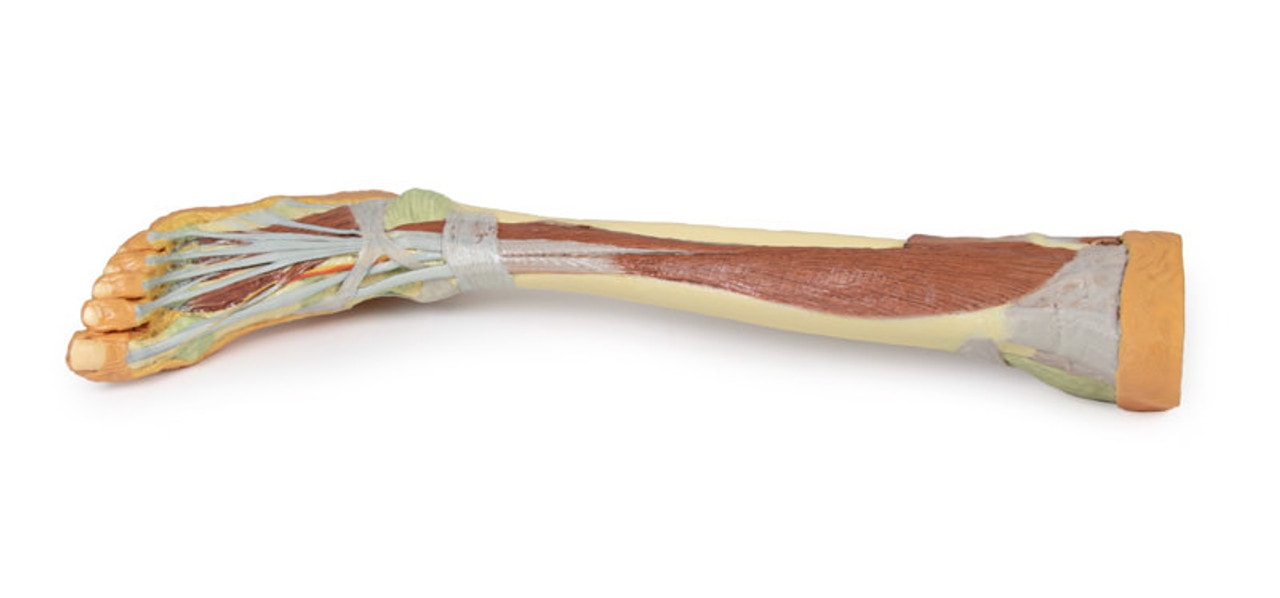
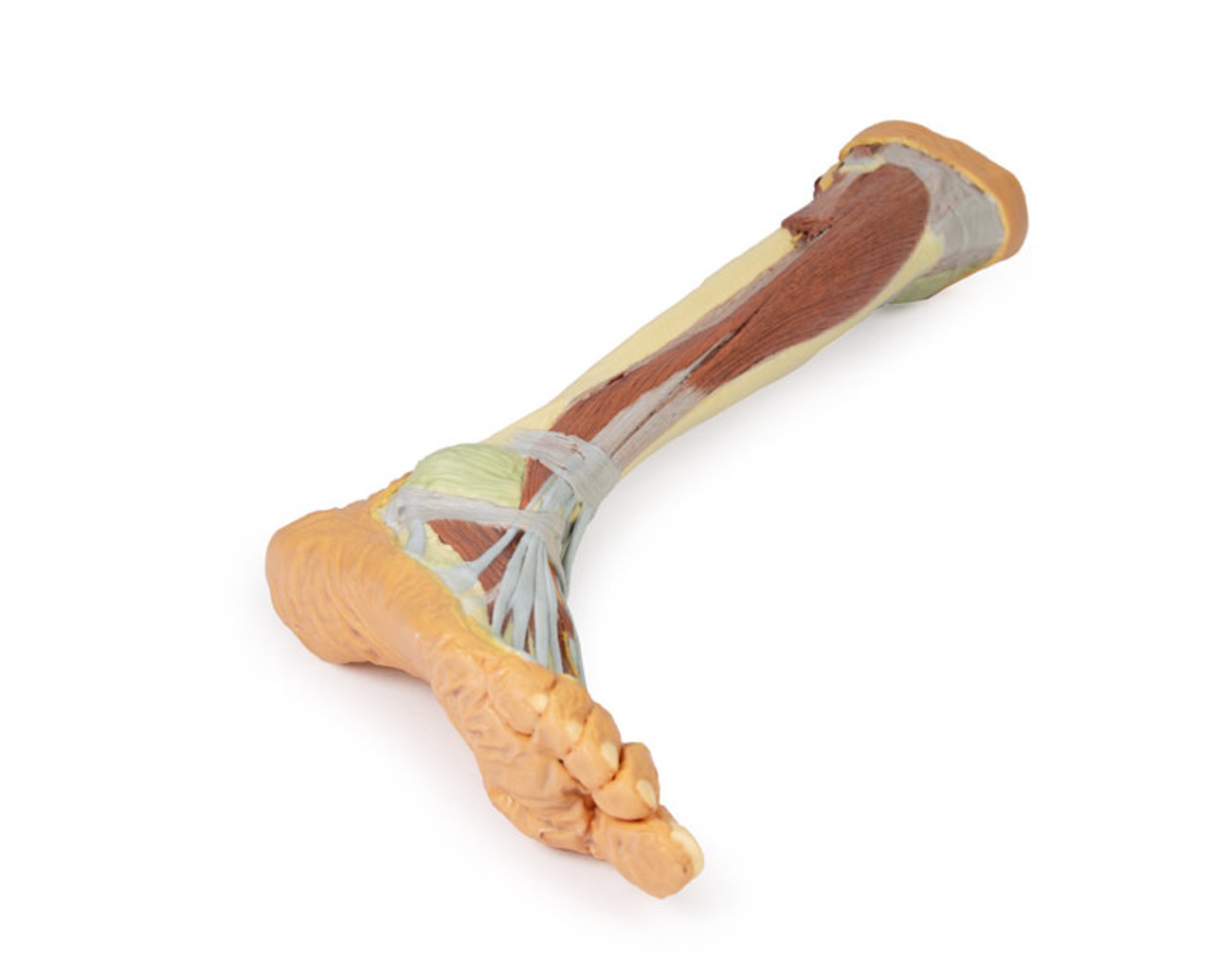
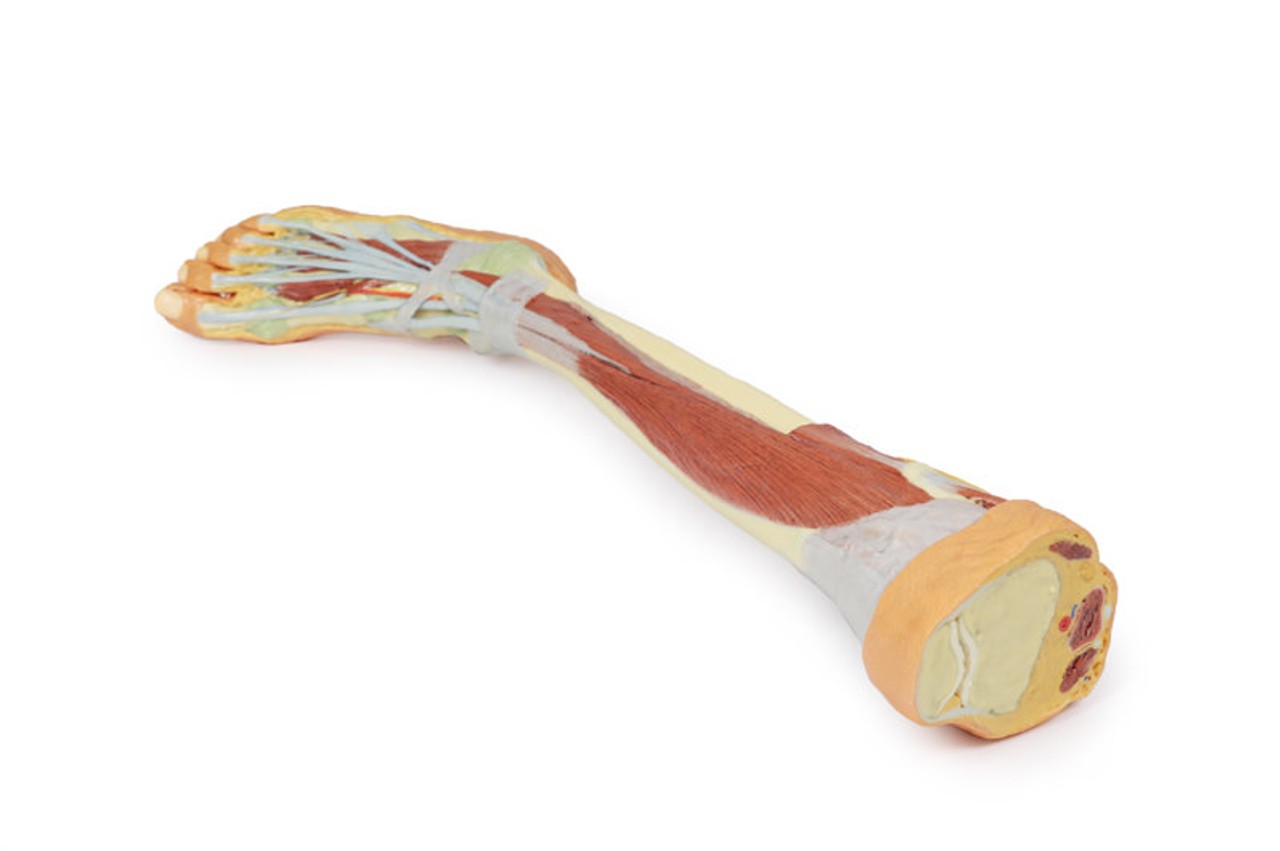
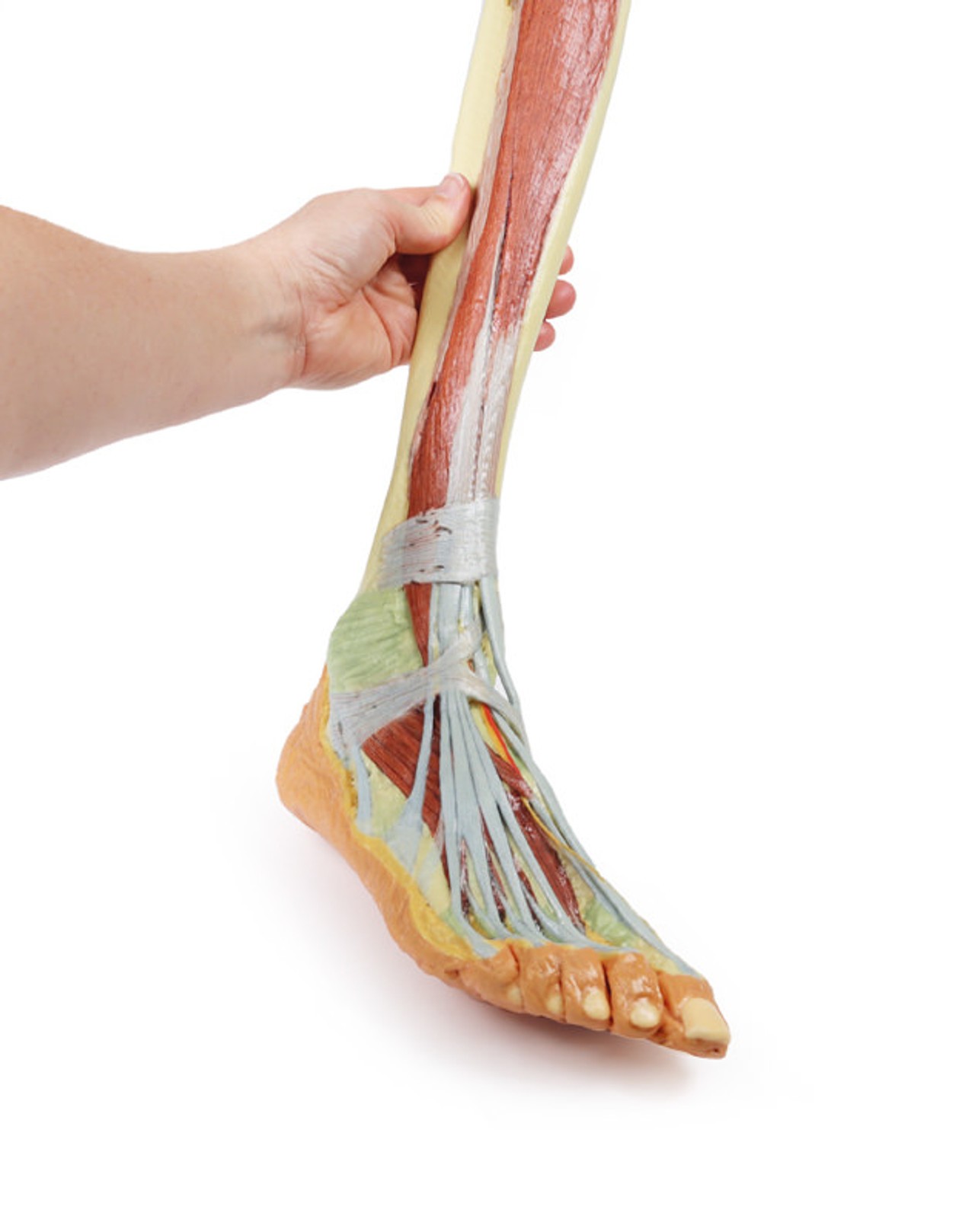
The bulk of the posterior compartment musculature (excepting the proximal deep posterior muscular origins and insertions and the distal tendons of the tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus and flexor hallucis longus) and the lateral compartment musculature (excepting the proximal portion of the fibularis longus muscle) have been removed to the ankle joint, while the anterior compartment musculature has been maintained and exposed deep to the crural fascia. Deep to the exposed posterior surface of the interosseous membrane the anterior tibial artery and vein can be seen passing distally through the anterior compartment. On the anterior and distal aspect of the specimen the tendons of the anterior musculature pass deep to the extensor and peroneal retinaculae and are visible passing to their respective insertions. The dorsalis pedis and the terminal portion of the deep peroneal nerve is visible lateral to the extensor hallucis longus tendon and medial to the extensor hallucis brevis tendons, and a well-developed extensor digitorum brevis is visible deep to the extensor digitorum longus and peroneus tertius tendons.
Please Note: Thanks to the flexibility of manufacturing that 3D Printing offers, this model is "printed to order", and is not typically available for immediate shipment. Most models are printed within 15 working days and arrive within 3-5 weeks of ordering, and once an order is submitted to us, it cannot be canceled or altered. Please contact us if you have specific a specific delivery date requirement, and we will do our best to deliver the model by your target date.
Advantages of 3D Printed Anatomical Models
- 3D printed anatomical models are the most anatomically accurate examples of human anatomy because they are based on real human specimens.
- Avoid the ethical complications and complex handling, storage, and documentation requirements with 3D printed models when compared to human cadaveric specimens.
- 3D printed anatomy models are far less expensive than real human cadaveric specimens.
- Reproducibility and consistency allow for standardization of education and faster availability of models when you need them.
- Customization options are available for specific applications or educational needs. Enlargement, highlighting of specific anatomical structures, cutaway views, and more are just some of the customizations available.
Disadvantages of Human Cadavers
- Access to cadavers can be problematic and ethical complications are hard to avoid. Many countries cannot access cadavers for cultural and religious reasons.
- Human cadavers are costly to procure and require expensive storage facilities and dedicated staff to maintain them. Maintenance of the facility alone is costly.
- The cost to develop a cadaver lab or plastination technique is extremely high. Those funds could purchase hundreds of easy to handle, realistic 3D printed anatomical replicas.
- Wet specimens cannot be used in uncertified labs. Certification is expensive and time-consuming.
- Exposure to preservation fluids and chemicals is known to cause long-term health problems for lab workers and students. 3D printed anatomical replicas are safe to handle without any special equipment.
- Lack of reuse and reproducibility. If a dissection mistake is made, a new specimen has to be used and students have to start all over again.
Disadvantages of Plastinated Specimens
- Like real human cadaveric specimens, plastinated models are extremely expensive.
- Plastinated specimens still require real human samples and pose the same ethical issues as real human cadavers.
- The plastination process is extensive and takes months or longer to complete. 3D printed human anatomical models are available in a fraction of the time.
- Plastinated models, like human cadavers, are one of a kind and can only showcase one presentation of human anatomy.
Advanced 3D Printing Techniques for Superior Results
- Vibrant color offering with 10 million colors
- UV-curable inkjet printing
- High quality 3D printing that can create products that are delicate, extremely precise, and incredibly realistic
- To improve durability of fragile, thin, and delicate arteries, veins or vessels, a clear support material is printed in key areas. This makes the models robust so they can be handled by students easily.