- Home
- Anatomy Models
- Head & Neck Anatomy Models
- 3D Printed Superficial Dissection of Facial Nerves and Parotid Gland
Description
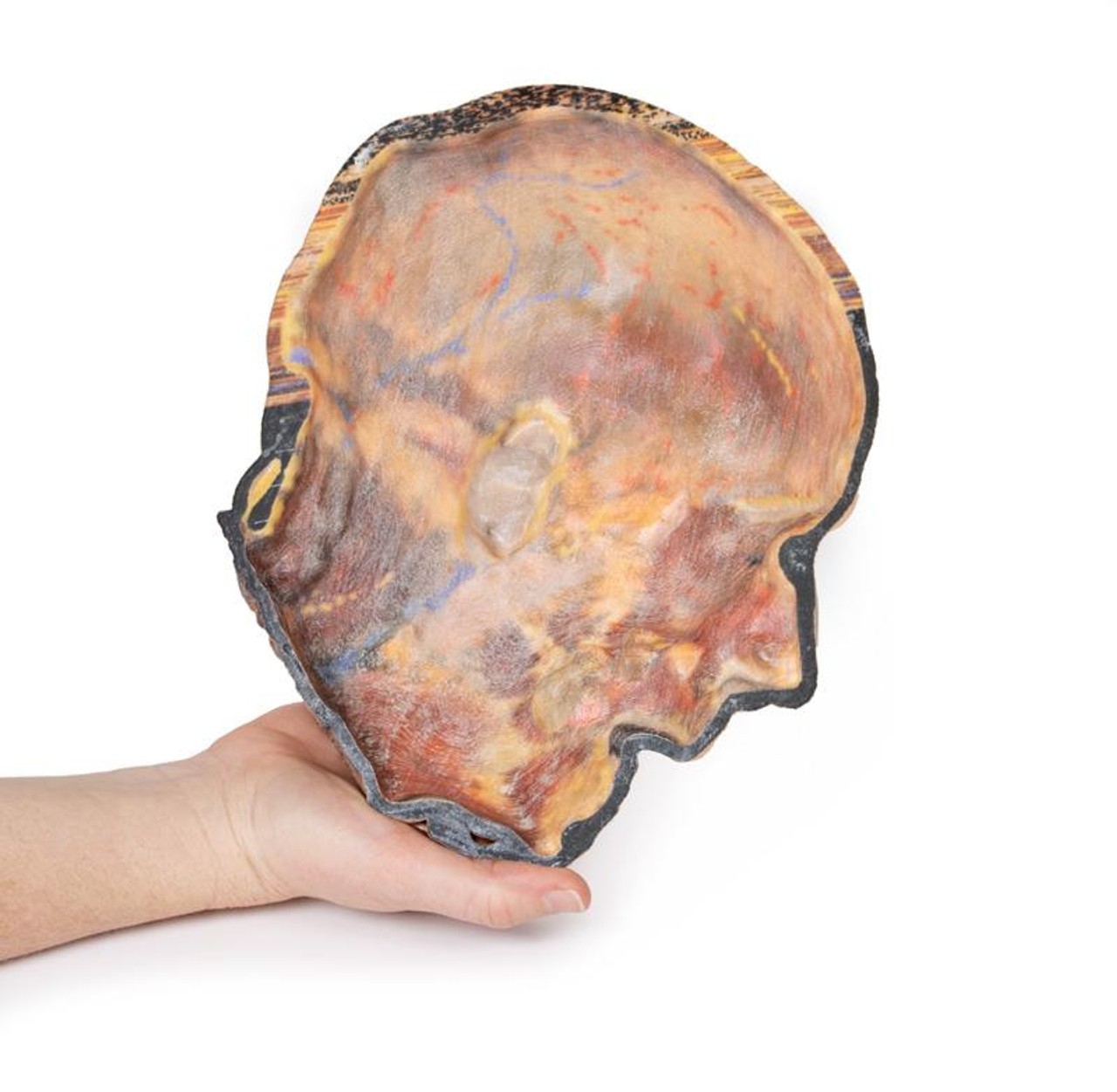
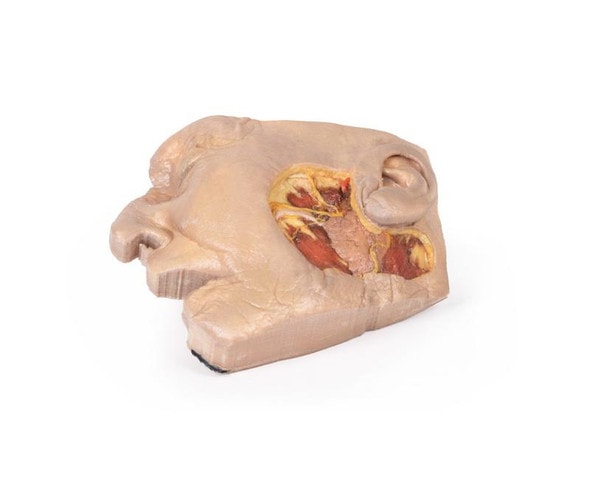
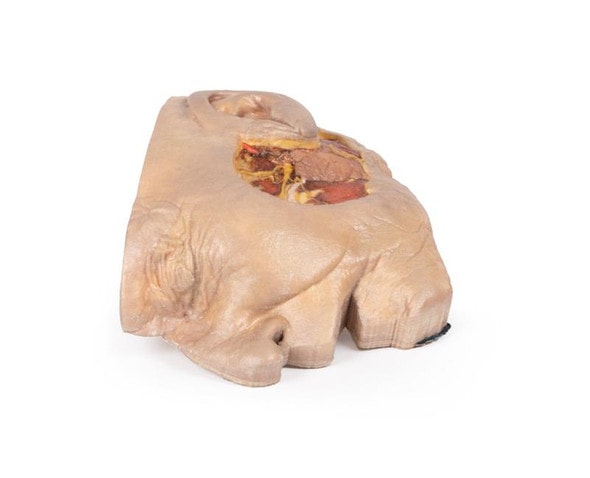
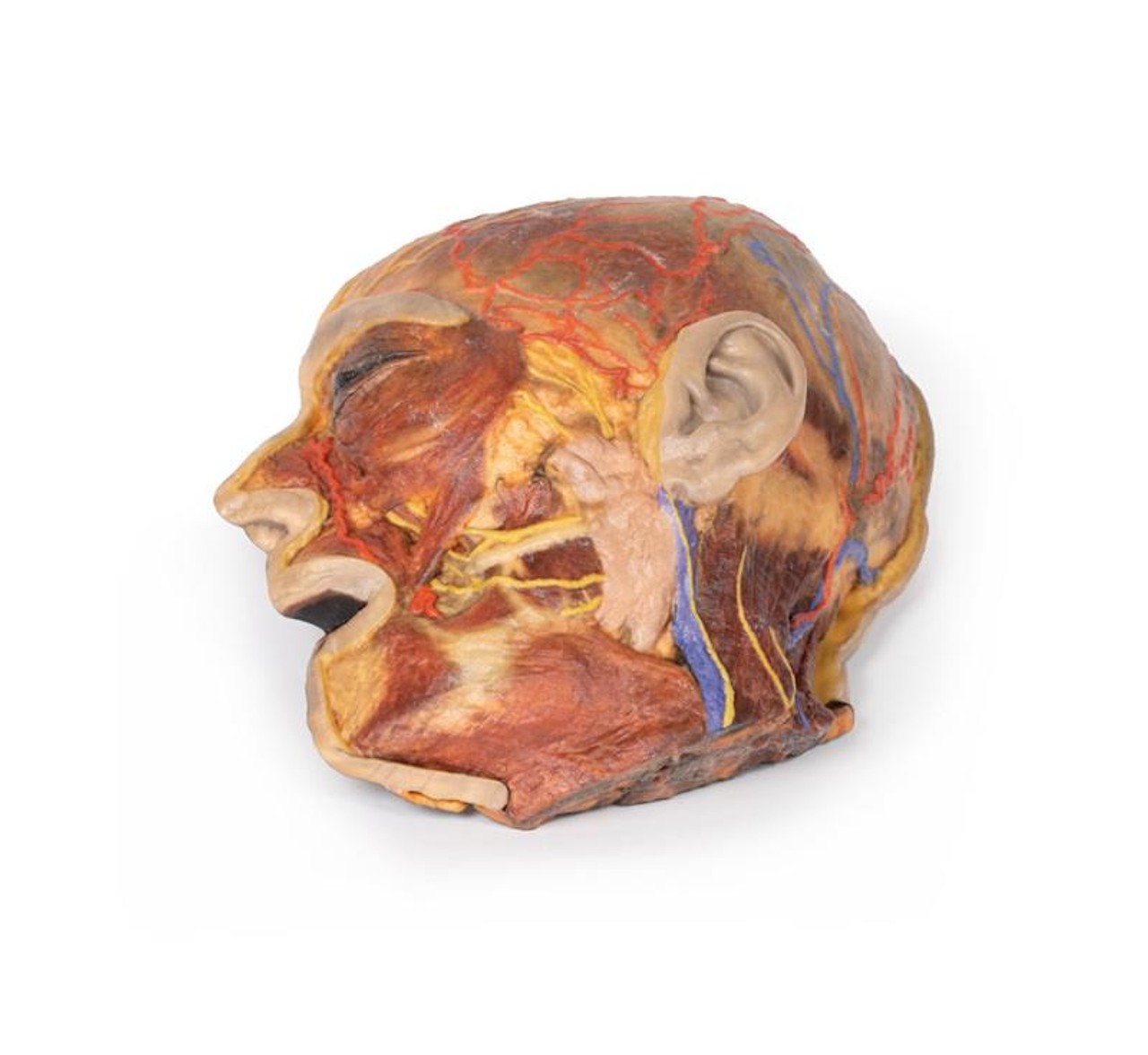
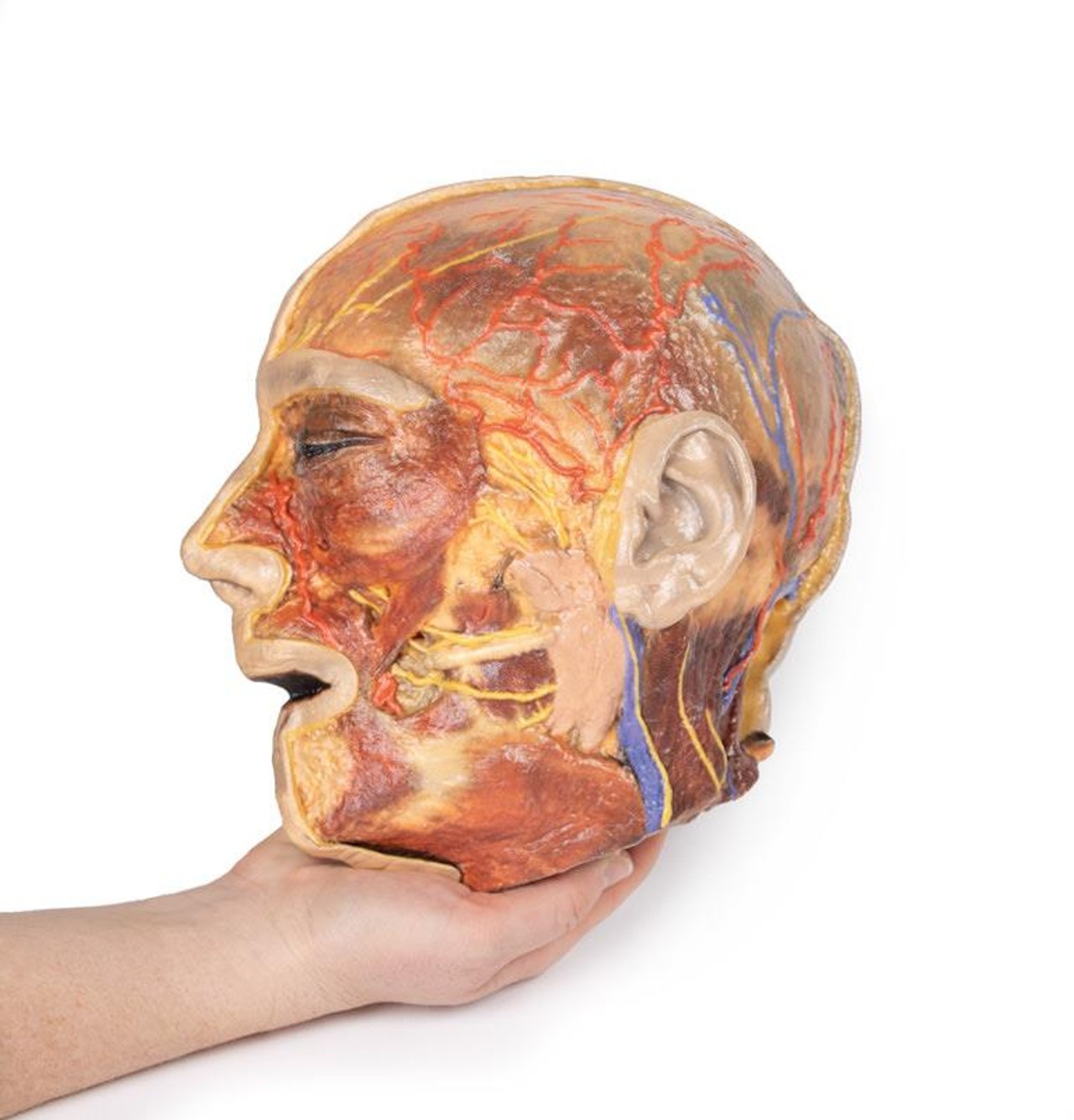
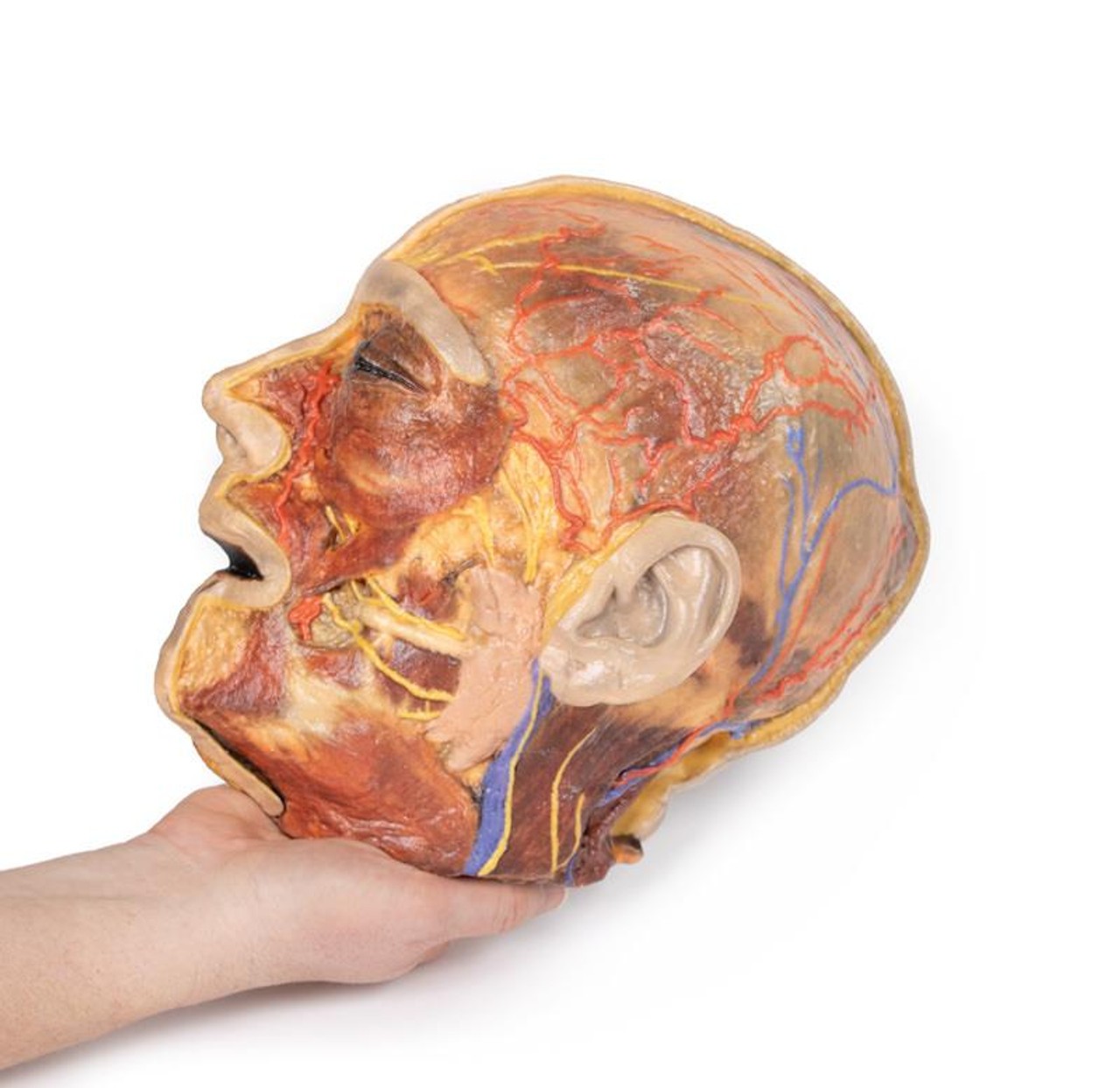
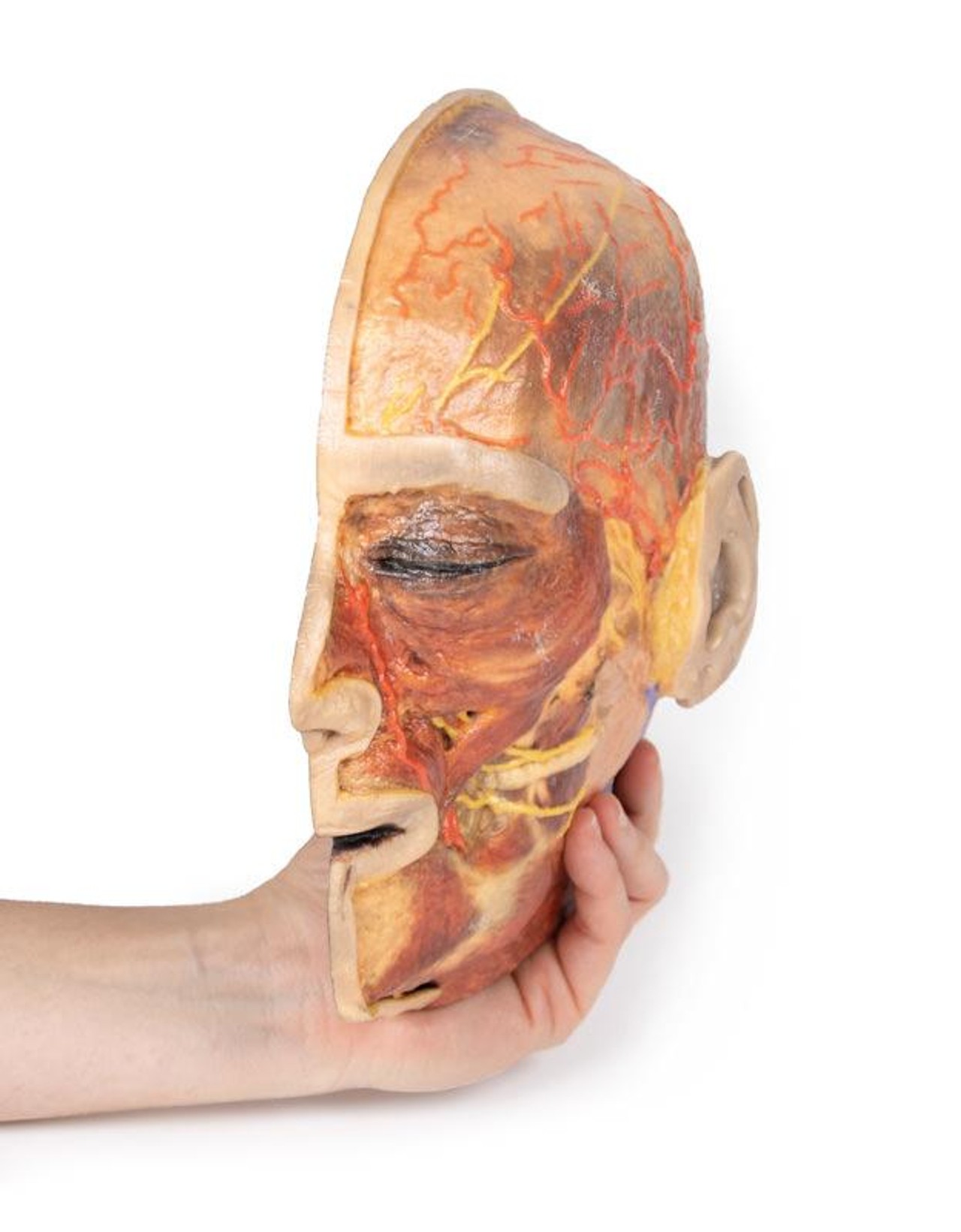
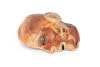
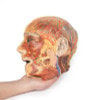
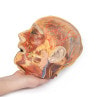
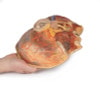
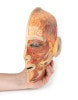
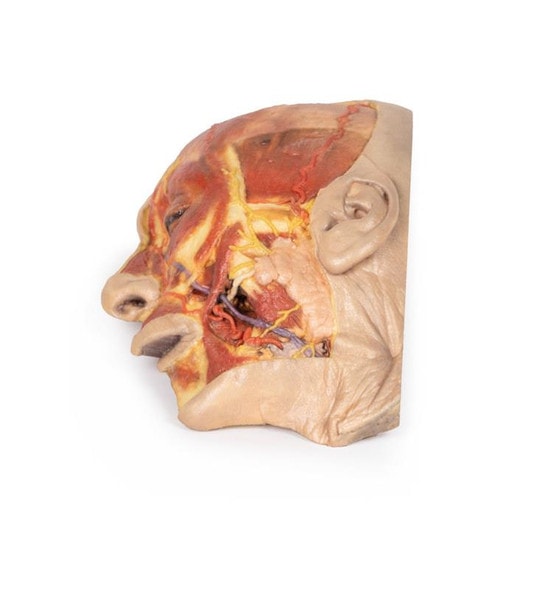
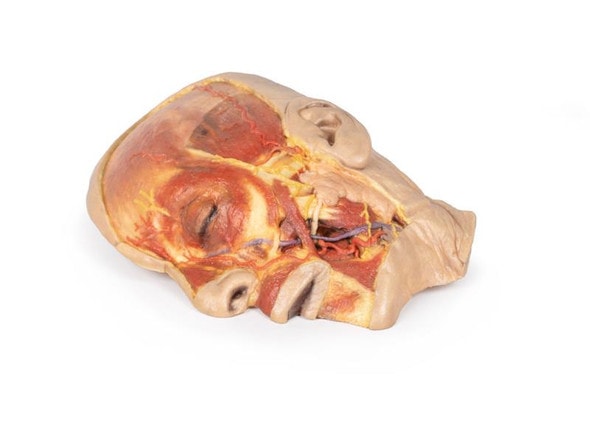
This 3D model presents the superficial anatomy of the face and head, and compliments the superficial facial anatomy of our HW 44 model with a more expanded dissection across the scalp and occipital regions.
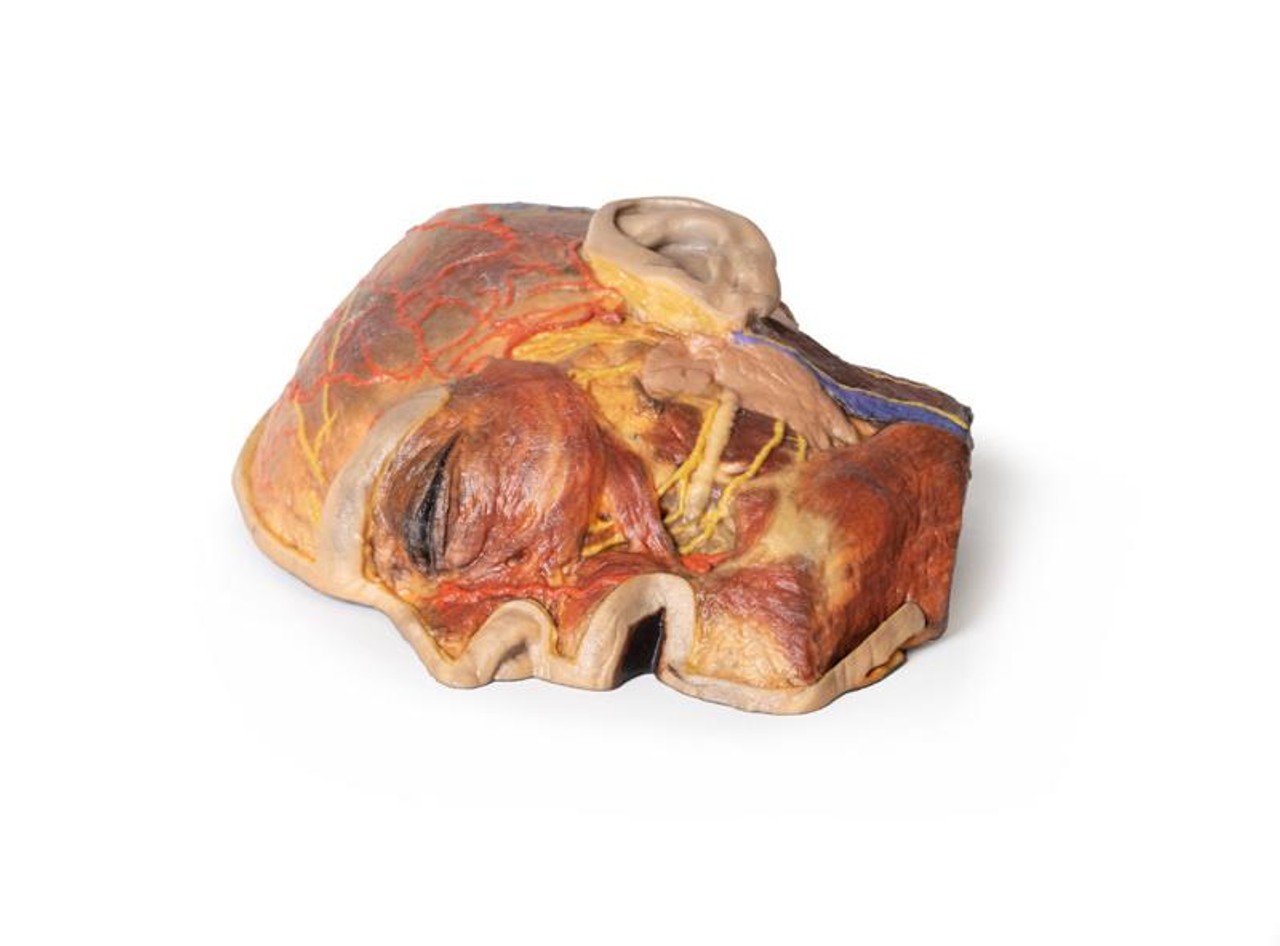
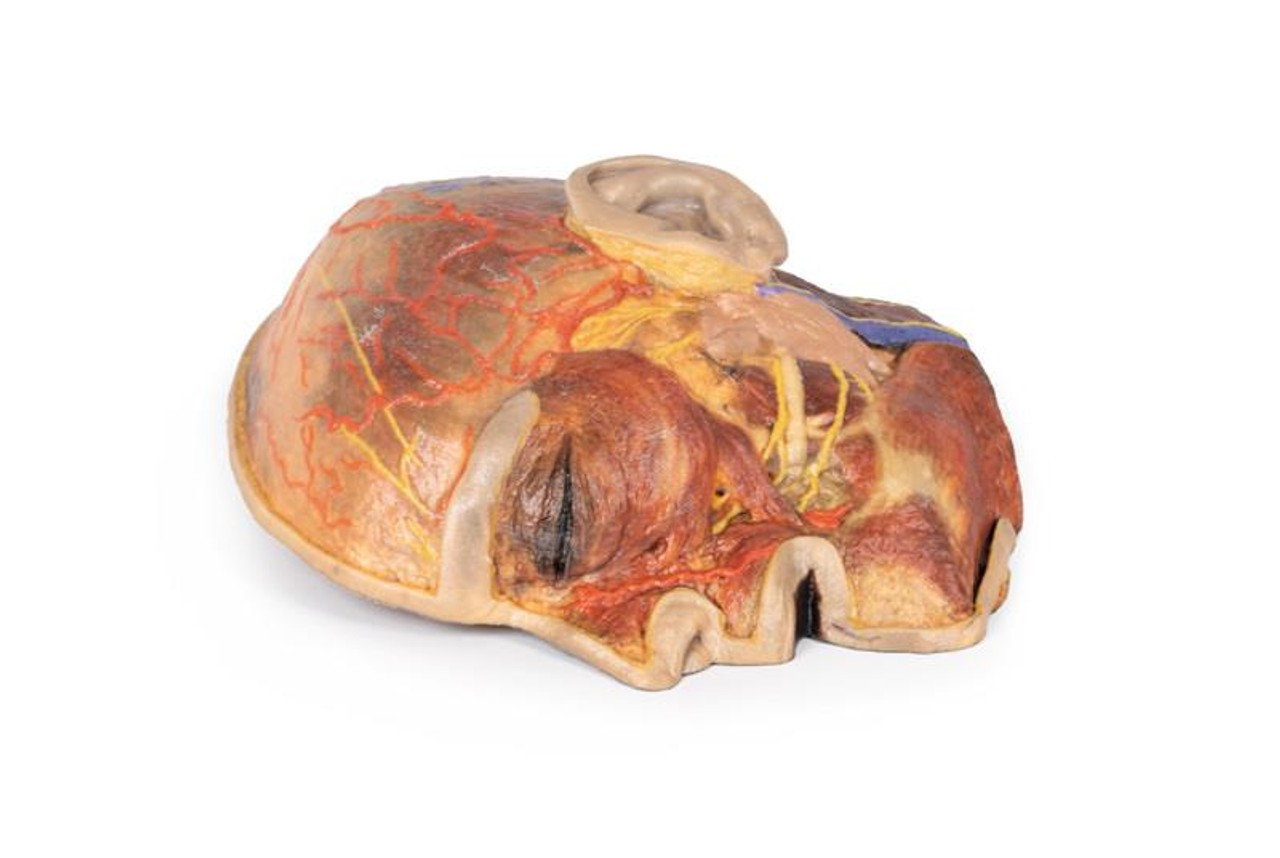
The superficial neurovascular and muscular structures in the face largely mirror the structures described in reference to our HW 44 specimen (see description), although the terminal branches of the facial nerve (CNVII) can be largely followed across a longer course from the parotid gland and the platysma muscle has been retained superficial to the mandible and extends towards the neck.
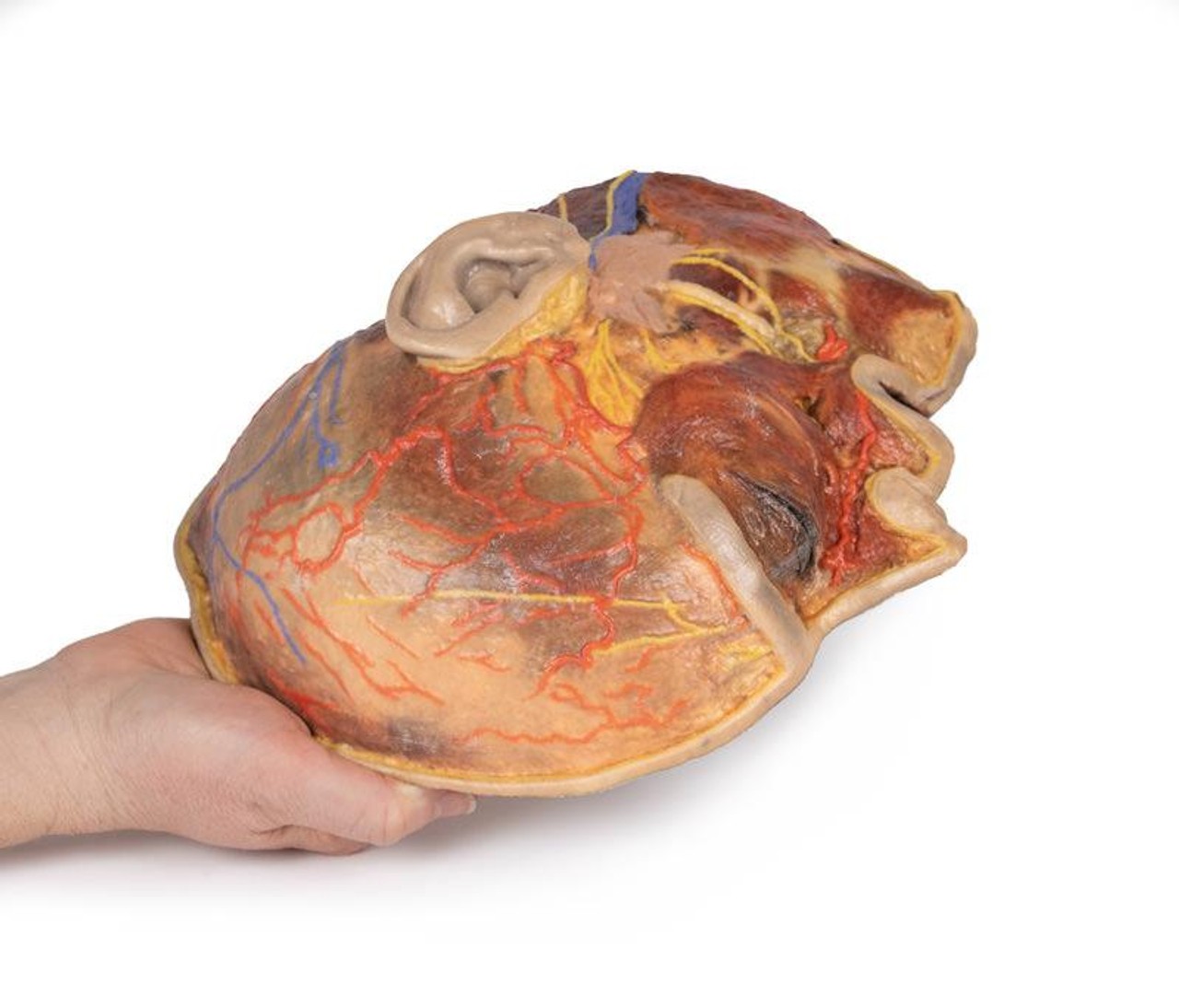
In contrast to the HW 44 specimen, this model has a more expansive superficial dissection inferior to the external ear and across the posterior scalp and occipital region. This allows for an expanded appreciation of the neurovascular distribution of the supraorbital and supratrochlear nerves and arties with the superficial temporal artery. Inferior to the ear, the retromandibular vein has been exposed with the ascending fibers of the great auricular nerve on its superficial surface (and further branches of this nerve on the surface of the sternocleidomastoid muscle). At the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle the lesser occipital nerve is just preserved, near the exiting and ascension of the occipital artery and vein near the trapezius muscle towards the posterior scalp. Surrounding the external ear are fibers of the auricularis superior and posterior muscles. Near the margin of the dissection window posteriorly the deep fibers of the occipitalis muscle can be seen integrated into the epicranius (occipitofrontalis) muscle.
Advantages of 3D Printed Anatomical Models
- 3D printed anatomical models are the most anatomically accurate examples of human anatomy because they are based on real human specimens.
- Avoid the ethical complications and complex handling, storage, and documentation requirements with 3D printed models when compared to human cadaveric specimens.
- 3D printed anatomy models are far less expensive than real human cadaveric specimens.
- Reproducibility and consistency allow for standardization of education and faster availability of models when you need them.
- Customization options are available for specific applications or educational needs. Enlargement, highlighting of specific anatomical structures, cutaway views, and more are just some of the customizations available.
Disadvantages of Human Cadavers
- Access to cadavers can be problematic and ethical complications are hard to avoid. Many countries cannot access cadavers for cultural and religious reasons.
- Human cadavers are costly to procure and require expensive storage facilities and dedicated staff to maintain them. Maintenance of the facility alone is costly.
- The cost to develop a cadaver lab or plastination technique is extremely high. Those funds could purchase hundreds of easy to handle, realistic 3D printed anatomical replicas.
- Wet specimens cannot be used in uncertified labs. Certification is expensive and time-consuming.
- Exposure to preservation fluids and chemicals is known to cause long-term health problems for lab workers and students. 3D printed anatomical replicas are safe to handle without any special equipment.
- Lack of reuse and reproducibility. If a dissection mistake is made, a new specimen has to be used and students have to start all over again.
Disadvantages of Plastinated Specimens
- Like real human cadaveric specimens, plastinated models are extremely expensive.
- Plastinated specimens still require real human samples and pose the same ethical issues as real human cadavers.
- The plastination process is extensive and takes months or longer to complete. 3D printed human anatomical models are available in a fraction of the time.
- Plastinated models, like human cadavers, are one of a kind and can only showcase one presentation of human anatomy.
Advanced 3D Printing Techniques for Superior Results
- Vibrant color offering with 10 million colors
- UV-curable inkjet printing
- High quality 3D printing that can create products that are delicate, extremely precise, and incredibly realistic
- To improve durability of fragile, thin, and delicate arteries, veins or vessels, a clear support material is printed in key areas. This makes the models robust so they can be handled by students easily.