Description
Developed from real patient case study specimens, the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series introduces an unmatched level of realism in human anatomy models. Each 3D printed anatomy model is a high-fidelity replica of a human cadaveric specimen, focusing on the key morbidity presentations that led to the deceasement of the patient. With advances in 3D printing materials and techniques, these stories can come to life in an ethical, consistently reproduceable, and easy to handle format. Ideal for the most advanced anatomical and pathological study, and backed by authentic case study details, students, instructors, and experts alike will discover a new level of anatomical study with the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series.
Clinical History
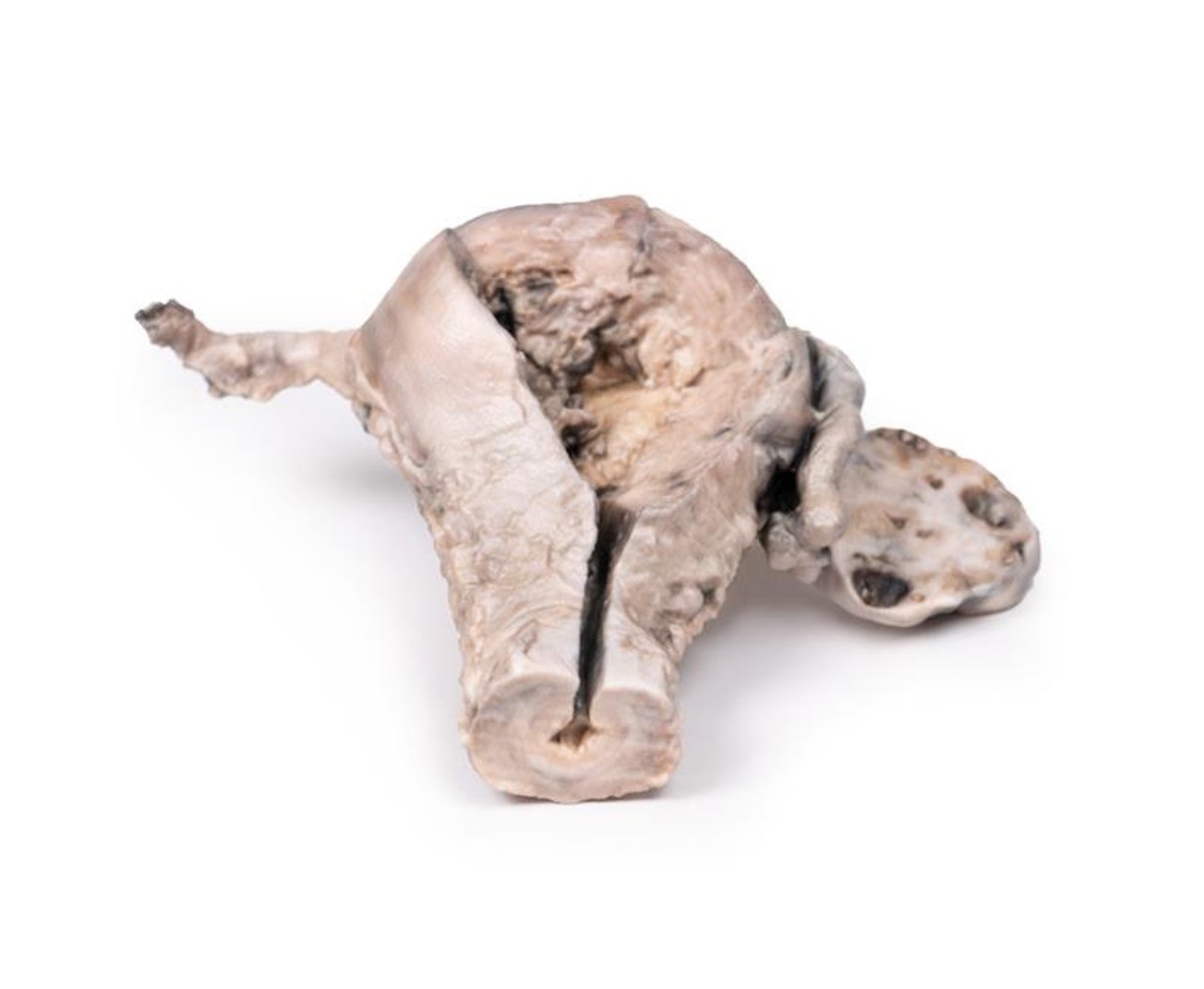
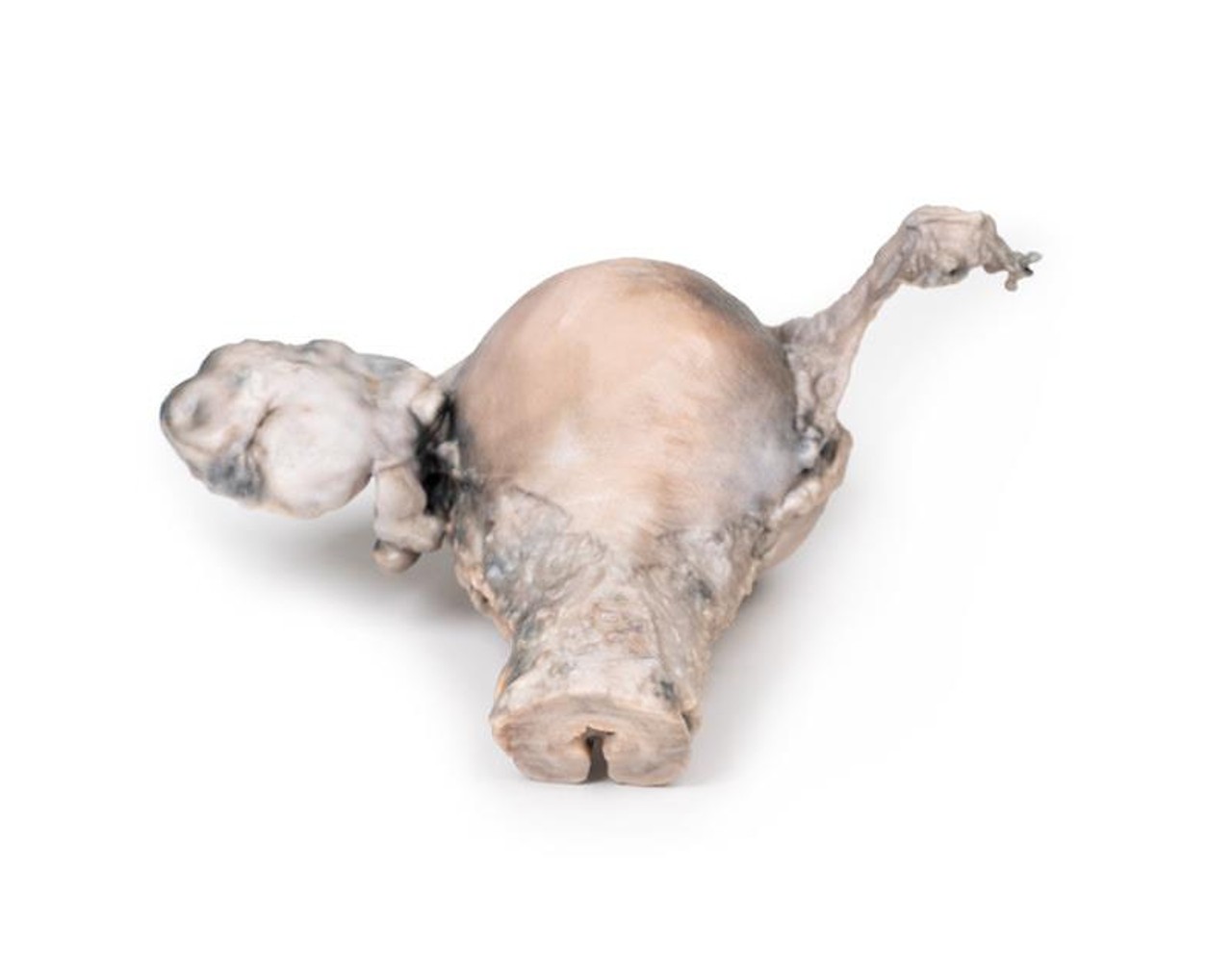
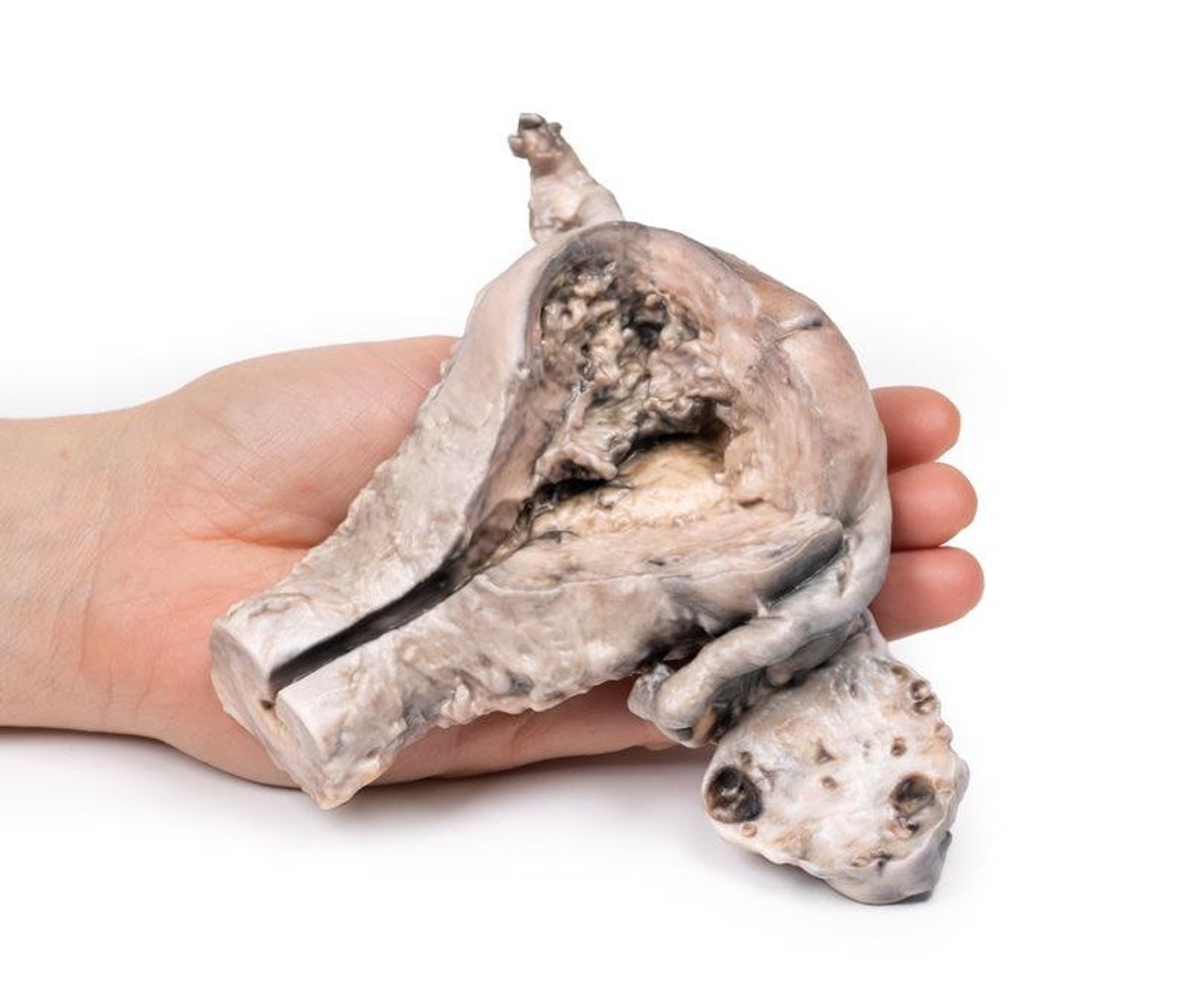
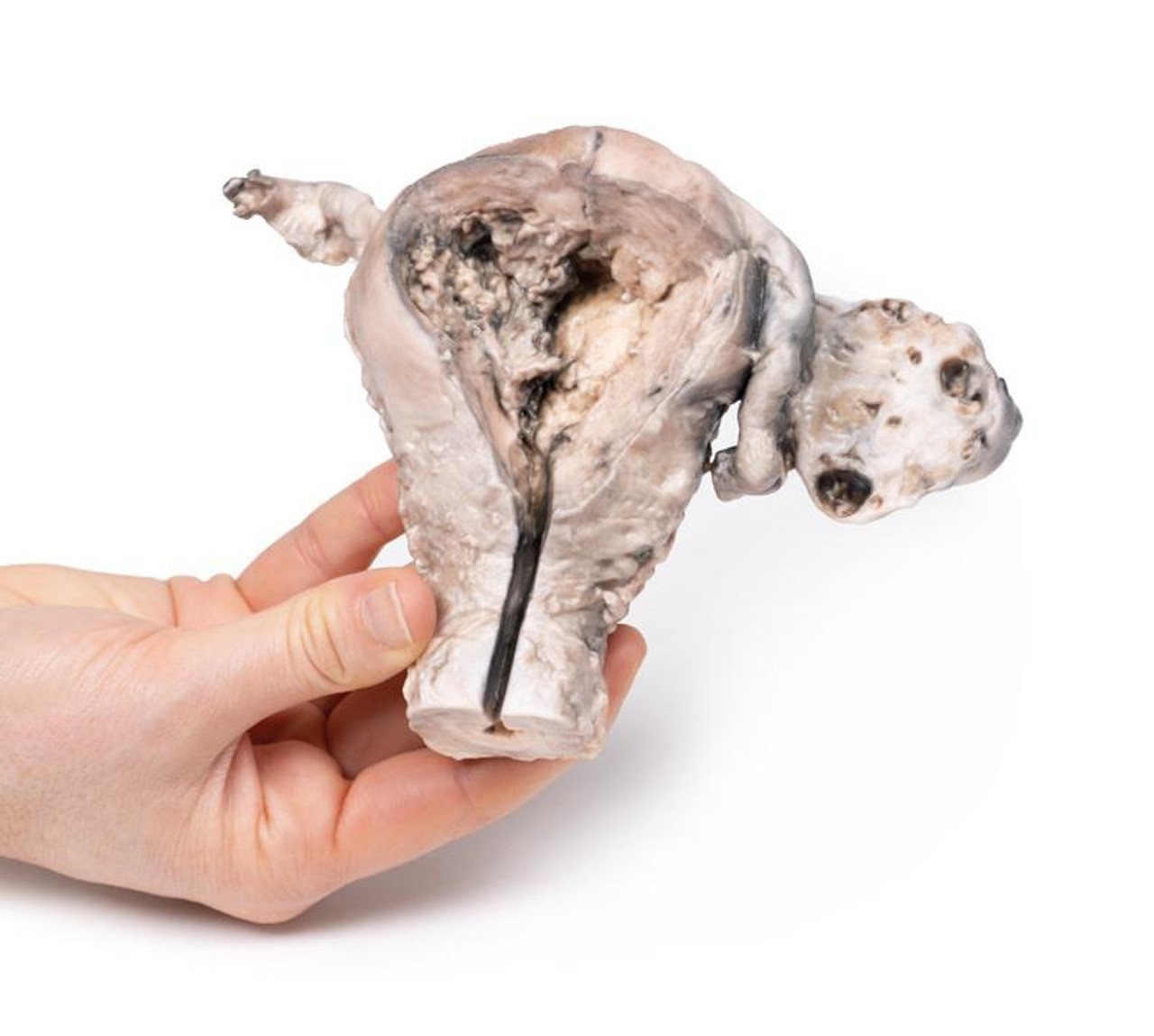
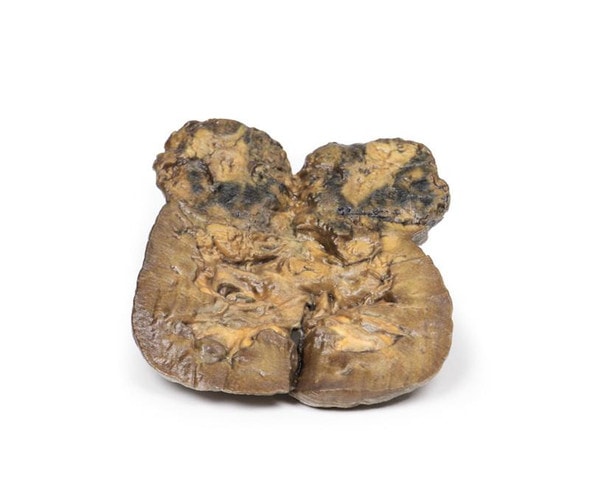
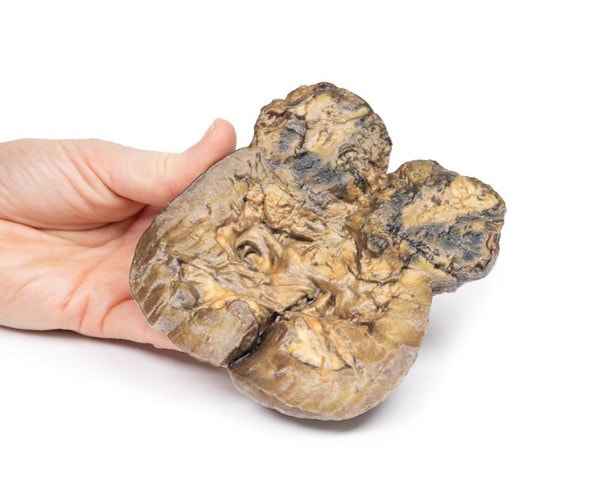
A 63-year old woman presented with a history of dull lower abdominal pain for 2 months and heavy persistent vaginal bleeding for 1 week. The menopause had occurred 13 years previously. Radical abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy were commonly performed for the treatment of endometrial cancer following confirmation of endometrial carcinoma in biopsy.
Pathology
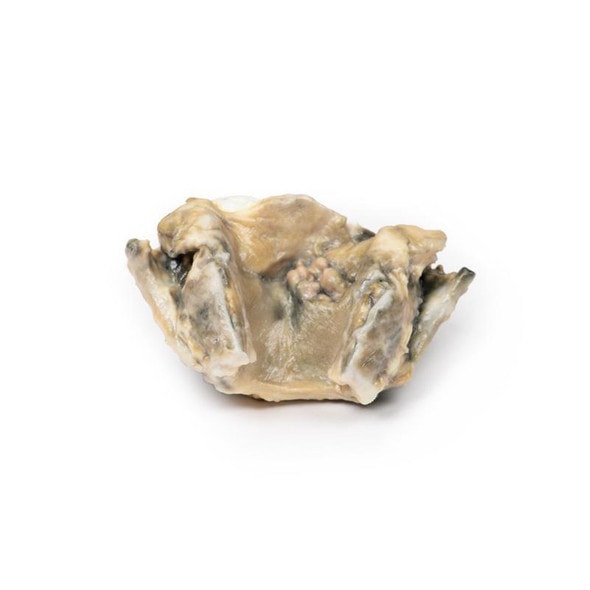
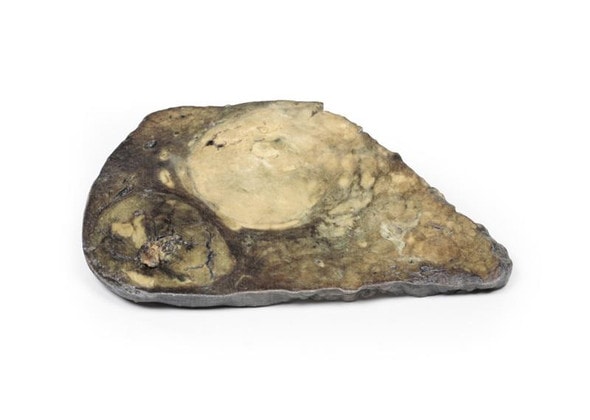
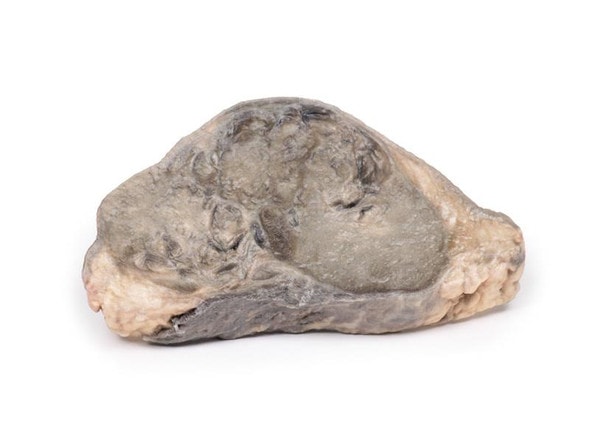
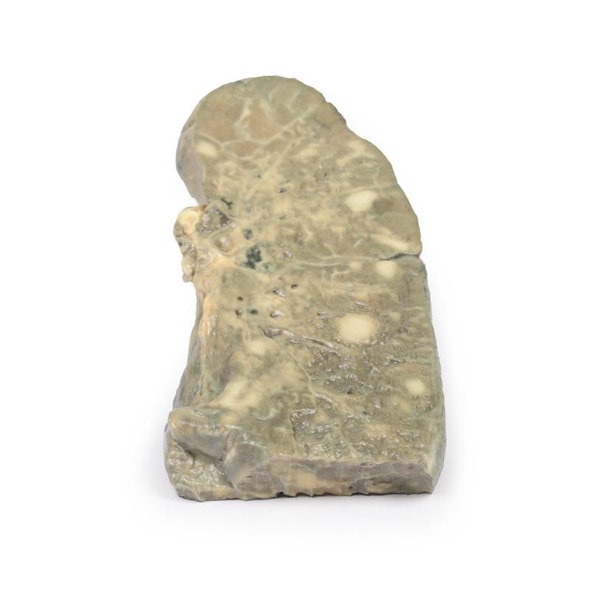
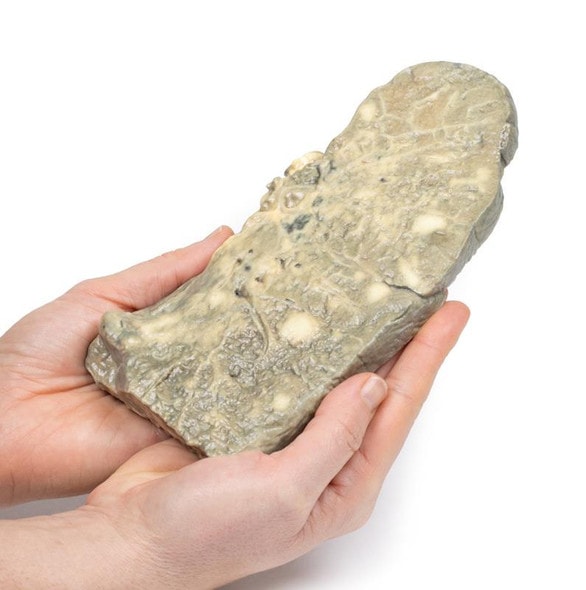
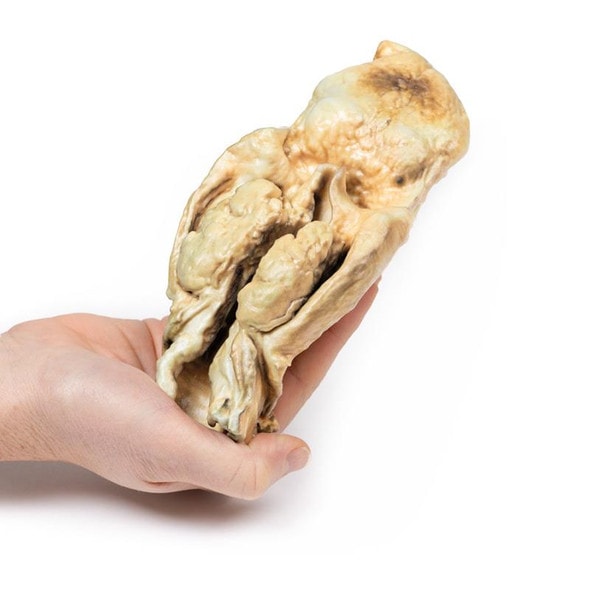
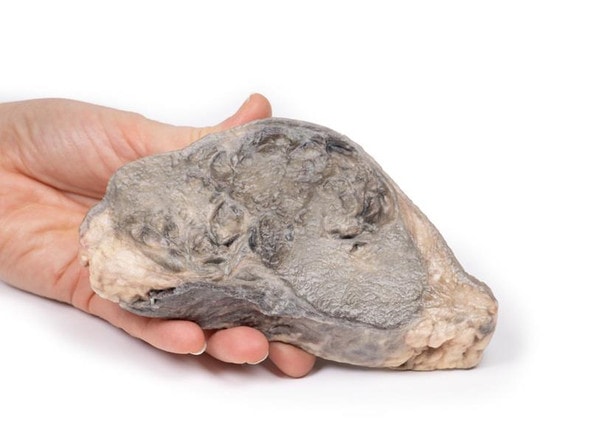
The specimen consists of uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries. The endometrial cavity and endocervical canal have been opened on the anterior aspect. The endometrial lining is grossly abnormal especially on the right side and a brown polypoid tumor has invaded the myometrium and extends inferiorly into the cervical canal. Histologically this was a well-differentiated adenocarcinoma of the endometrium. The left ovary, which has been sectioned in the coronal plane, is enlarged and has several large follicular cysts/cavities.
Further Information
Endometrial carcinoma is the most common gynecological malignancy in developed countries and the second most common in developing countries after cervical cancer. There are two major types of endometrial carcinoma. Endometroid carcinoma account for almost 80% of endometrial carcinoma. They usually present early and so have a more favorable outcome. These tumors may arise from atypical endometrial hyperplasia. Common genetic abnormalities seen in endometrioid tumors are mutations in the PTEN, PIK3Ca and ARID1A genes. Serous carcinoma are a less common form of endometrial carcinoma. These tumors are associated with mutations in TP53 gene and carry a poorer prognosis. Endometrioid tumors tend to affect women aged 55 to 65 years. Risk factors for developing endometrioid endometrial cancer include obesity, impaired glucose tolerance, infertility, unopposed estrogen therapy (e.g. early menarche, late menopause or exogenous sources). Serous neoplasms affect older women aged 65 to 75 years with other risk factors for development include having a lower BMI and an atrophic uterus. Women with Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer (Lynch Syndrome) have a significantly higher risk of developing endometrial cancer.
The most common symptom of endometrial cancer is abnormal vaginal bleeding. Most frequently it presents as post-menopausal bleeding, which often allows early presentation. Others may be asymptomatic or an incidental finding of an abnormal endometrium on abdominopelvic imaging. The main radiological sign of endometrial cancer is abnormally thickened endometrium on pelvic ultrasound or CT scan. Diagnosis is made on endometrial biopsy, endometrial curettage or hysterectomy. Treatment depends on the stage of the cancer and includes local radiotherapy, systemic chemotherapy and surgical hysterectomy +/- salpingo-oophorectomy.
Advantages of 3D Printed Anatomical Models
- 3D printed anatomical models are the most anatomically accurate examples of human anatomy because they are based on real human specimens.
- Avoid the ethical complications and complex handling, storage, and documentation requirements with 3D printed models when compared to human cadaveric specimens.
- 3D printed anatomy models are far less expensive than real human cadaveric specimens.
- Reproducibility and consistency allow for standardization of education and faster availability of models when you need them.
- Customization options are available for specific applications or educational needs. Enlargement, highlighting of specific anatomical structures, cutaway views, and more are just some of the customizations available.
Disadvantages of Human Cadavers
- Access to cadavers can be problematic and ethical complications are hard to avoid. Many countries cannot access cadavers for cultural and religious reasons.
- Human cadavers are costly to procure and require expensive storage facilities and dedicated staff to maintain them. Maintenance of the facility alone is costly.
- The cost to develop a cadaver lab or plastination technique is extremely high. Those funds could purchase hundreds of easy to handle, realistic 3D printed anatomical replicas.
- Wet specimens cannot be used in uncertified labs. Certification is expensive and time-consuming.
- Exposure to preservation fluids and chemicals is known to cause long-term health problems for lab workers and students. 3D printed anatomical replicas are safe to handle without any special equipment.
- Lack of reuse and reproducibility. If a dissection mistake is made, a new specimen has to be used and students have to start all over again.
Disadvantages of Plastinated Specimens
- Like real human cadaveric specimens, plastinated models are extremely expensive.
- Plastinated specimens still require real human samples and pose the same ethical issues as real human cadavers.
- The plastination process is extensive and takes months or longer to complete. 3D printed human anatomical models are available in a fraction of the time.
- Plastinated models, like human cadavers, are one of a kind and can only showcase one presentation of human anatomy.
Advanced 3D Printing Techniques for Superior Results
- Vibrant color offering with 10 million colors
- UV-curable inkjet printing
- High quality 3D printing that can create products that are delicate, extremely precise, and incredibly realistic
- To improve durability of fragile, thin, and delicate arteries, veins or vessels, a clear support material is printed in key areas. This makes the models robust so they can be handled by students easily.