Description
Developed from real patient case study specimens, the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series introduces an unmatched level of realism in human anatomy models. Each 3D printed anatomy model is a high-fidelity replica of a human cadaveric specimen, focusing on the key morbidity presentations that led to the deceasement of the patient. With advances in 3D printing materials and techniques, these stories can come to life in an ethical, consistently reproduceable, and easy to handle format. Ideal for the most advanced anatomical and pathological study, and backed by authentic case study details, students, instructors, and experts alike will discover a new level of anatomical study with the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series.
Clinical History
A 40-year old male presents with shortness of breath and swelling of his lower limbs. He is a smoker with a history of diabetes and previous myocardial infarctions. On examination bilateral pleural effusion, peripheral pitting oedema and a swollen scrotum were noted. Transillumination of the swelling transmitted red light. Chest x-ray showed radiological features of congestive cardiac failure. He was commenced on appropriate treatment for heart failure but later died during this admission.
Pathology
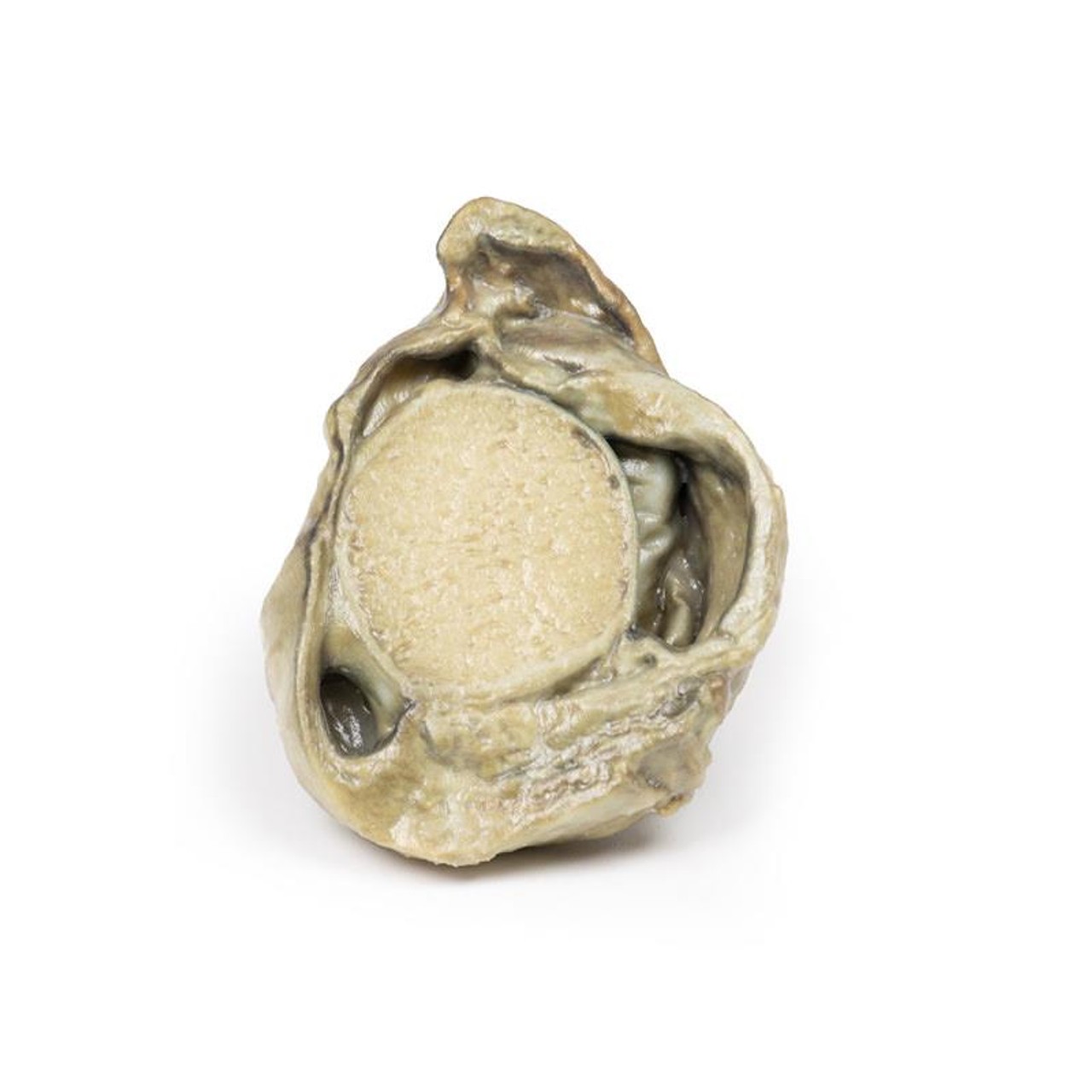
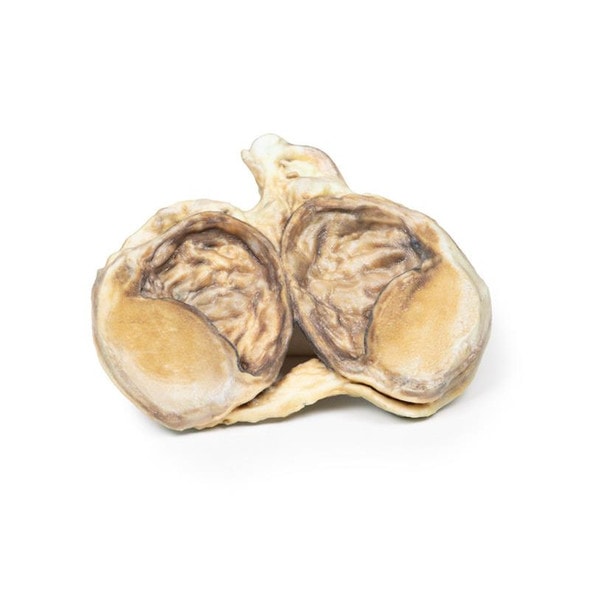
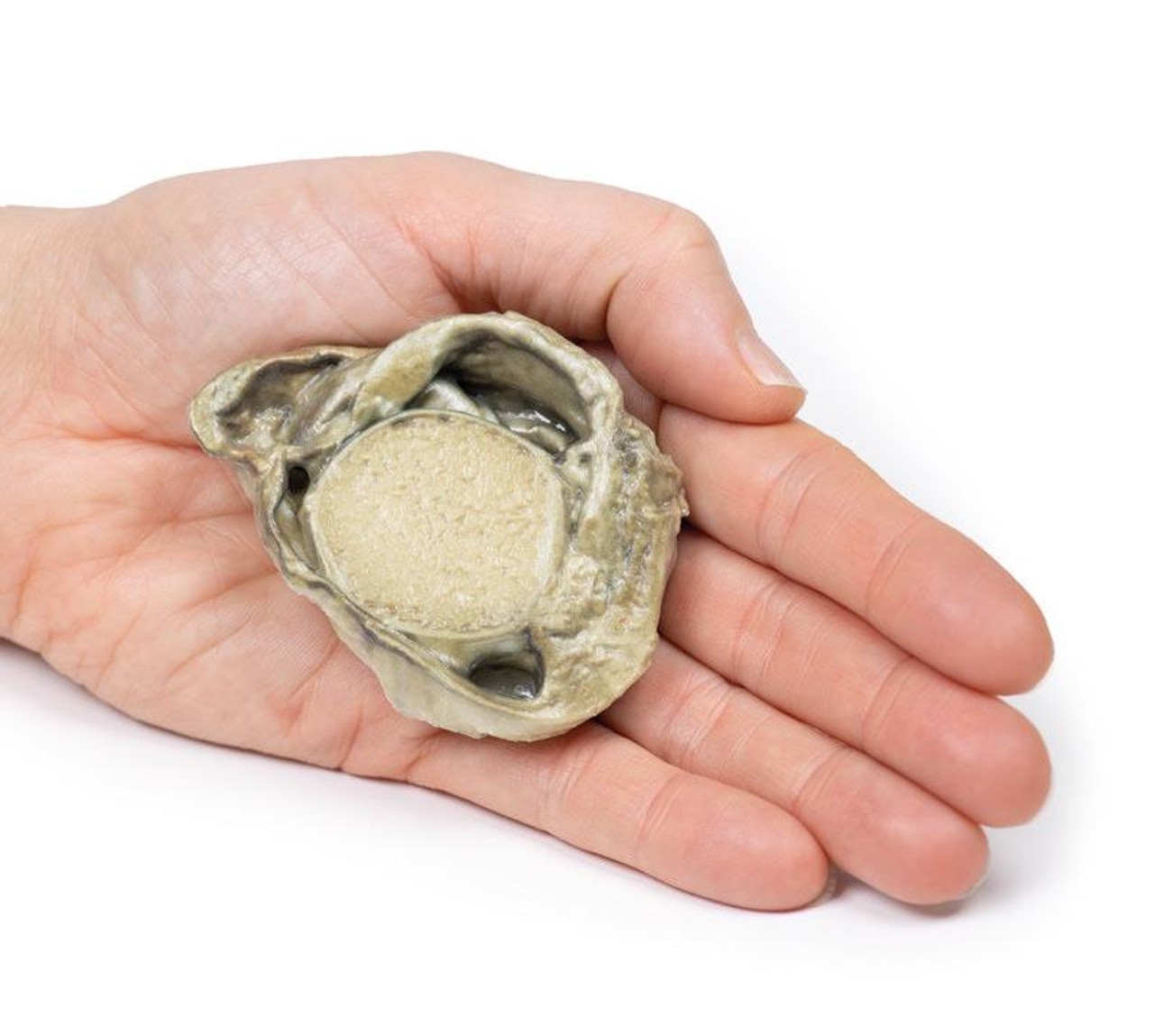
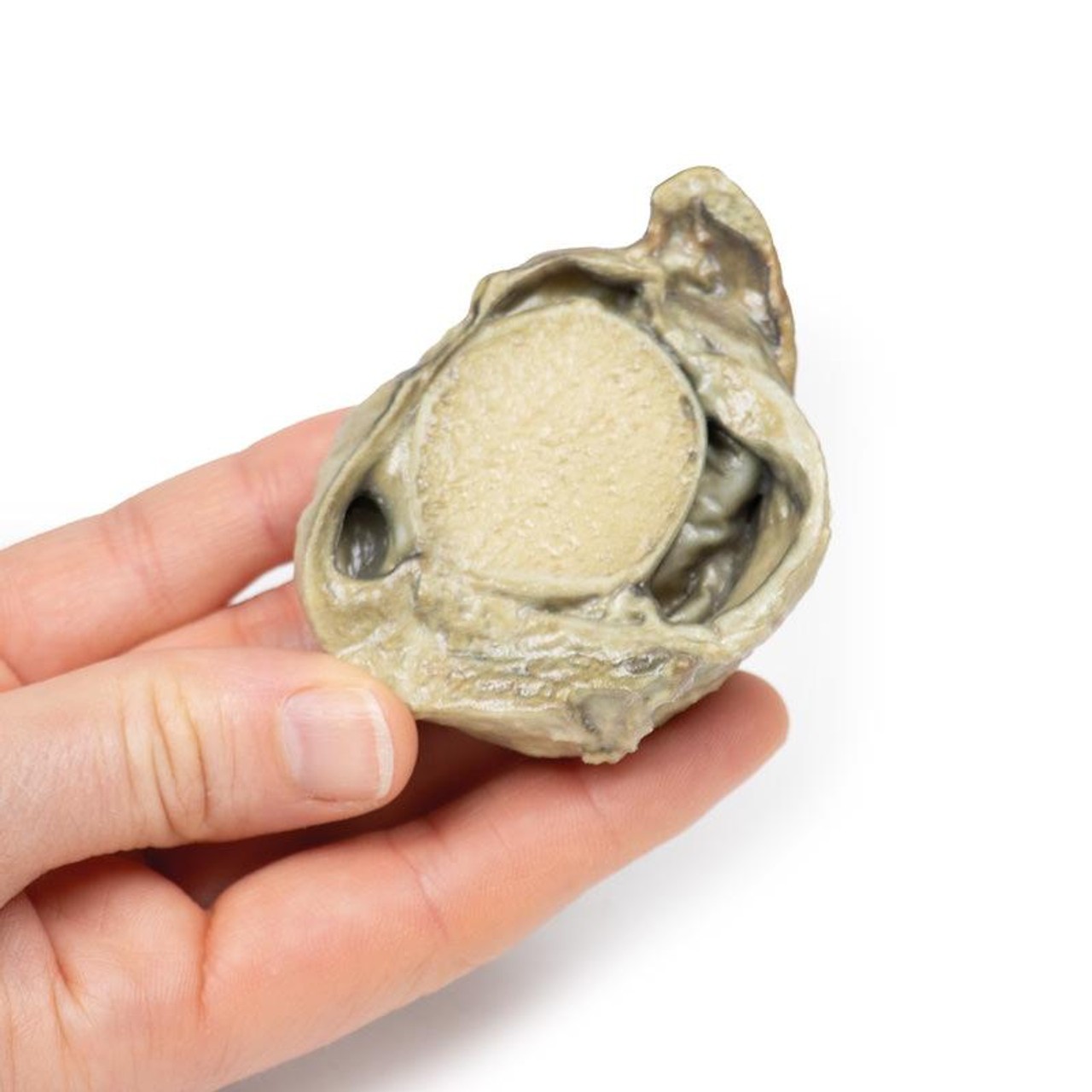
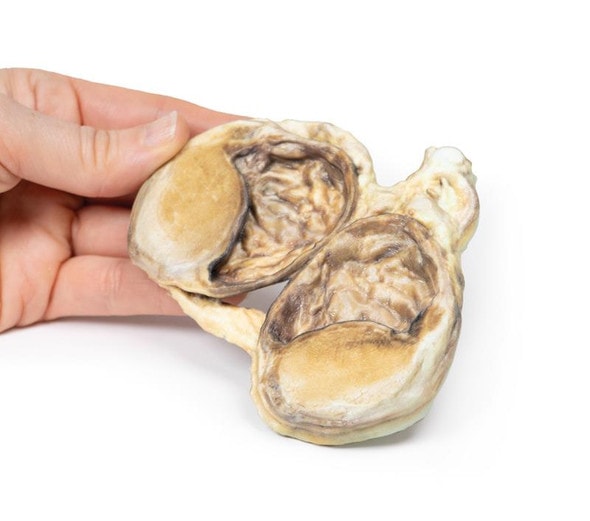
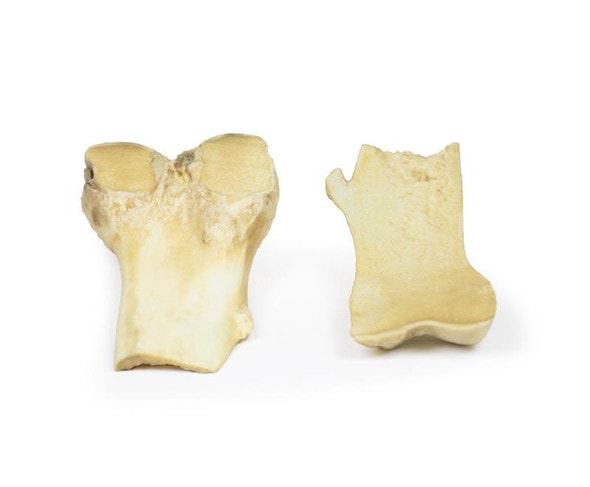
The specimen is a testis and its coverings, sliced to display the cut surface. The cavity bounded by the visceral and parietal layers of the tunica vaginalis is distended due to the accumulation of serous fluid. This is an example of a hydrocoele, secondary to generalized oedema due to congestive cardiac failure.
Further Information
A hydrocele is an accumulation of serous fluid between the parietal and visceral layers of the tunica vaginalis around the testes. Hydroceles can be described as communicating with the peritoneal cavity or non-communicating with the peritoneal cavity.
Communicating hydroceles develop as a result of failure of the processus vaginalis to close after the descent of the testes into the scrotum. These may present after birth as a congenital hydrocele or may present later in life due to increase in intra-abdominal pressure, such a cardiac failure in this case. Non-communicating hydroceles are caused by imbalances in fluid secretion and reabsorption e.g. orchitis, epididymitis, testicular tumor, physical trauma (e.g. hernia, testicular torsion) or defective lymphatic drainage (e.g. filariasis, elephantiasis).
Patients present with a scrotal mass. The mass may be uni- or bilateral. Communicating hydroceles may be reducible and increase in size with raised intra-abdominal pressure. Non-communicating are usually non-reducible swellings. The swelling is usually non tender unless there is an underlying infection or torsion causing the hydrocele. Larger hydroceles may be cumbersome and cause erosion and skin infections on the scrotum. Diagnosis can be made on physical examination. Serous fluid allows the passage of light shined through the scrotum when examined: this is called transillumination. Ultrasound may be used to consolidate diagnosis and exclude other testicular pathology. Testicular cancer serum markers, such as alpha fetoprotein and B-HCG, may be taken to exclude testicular cancer.
Many congenital hydroceles resolve spontaneously before the age of 2. If communicating hydroceles persist beyond 2 year they are surgically repaired in order to reduce the risk of developing incarcerated hernias. Surgical repair of communicating hydroceles in older patients may be offered if they are symptomatic. Treatment of the underlying etiology of reactive hydrocele may cause them to resolve.
Advantages of 3D Printed Anatomical Models
- 3D printed anatomical models are the most anatomically accurate examples of human anatomy because they are based on real human specimens.
- Avoid the ethical complications and complex handling, storage, and documentation requirements with 3D printed models when compared to human cadaveric specimens.
- 3D printed anatomy models are far less expensive than real human cadaveric specimens.
- Reproducibility and consistency allow for standardization of education and faster availability of models when you need them.
- Customization options are available for specific applications or educational needs. Enlargement, highlighting of specific anatomical structures, cutaway views, and more are just some of the customizations available.
Disadvantages of Human Cadavers
- Access to cadavers can be problematic and ethical complications are hard to avoid. Many countries cannot access cadavers for cultural and religious reasons.
- Human cadavers are costly to procure and require expensive storage facilities and dedicated staff to maintain them. Maintenance of the facility alone is costly.
- The cost to develop a cadaver lab or plastination technique is extremely high. Those funds could purchase hundreds of easy to handle, realistic 3D printed anatomical replicas.
- Wet specimens cannot be used in uncertified labs. Certification is expensive and time-consuming.
- Exposure to preservation fluids and chemicals is known to cause long-term health problems for lab workers and students. 3D printed anatomical replicas are safe to handle without any special equipment.
- Lack of reuse and reproducibility. If a dissection mistake is made, a new specimen has to be used and students have to start all over again.
Disadvantages of Plastinated Specimens
- Like real human cadaveric specimens, plastinated models are extremely expensive.
- Plastinated specimens still require real human samples and pose the same ethical issues as real human cadavers.
- The plastination process is extensive and takes months or longer to complete. 3D printed human anatomical models are available in a fraction of the time.
- Plastinated models, like human cadavers, are one of a kind and can only showcase one presentation of human anatomy.
Advanced 3D Printing Techniques for Superior Results
- Vibrant color offering with 10 million colors
- UV-curable inkjet printing
- High quality 3D printing that can create products that are delicate, extremely precise, and incredibly realistic
- To improve durability of fragile, thin, and delicate arteries, veins or vessels, a clear support material is printed in key areas. This makes the models robust so they can be handled by students easily.