Description
Developed from real patient case study specimens, the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series introduces an unmatched level of realism in human anatomy models. Each 3D printed anatomy model is a high-fidelity replica of a human cadaveric specimen, focusing on the key morbidity presentations that led to the deceasement of the patient. With advances in 3D printing materials and techniques, these stories can come to life in an ethical, consistently reproduceable, and easy to handle format. Ideal for the most advanced anatomical and pathological study, and backed by authentic case study details, students, instructors, and experts alike will discover a new level of anatomical study with the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series.
Clinical History
A 73-year-old female was admitted with new left-sided hemiplegia. On further questioning she revealed a 3-month history of headaches, nausea and deteriorating balance. CT brain revealed an inoperable brain tumor. She died 1 week after being admitted.
Pathology
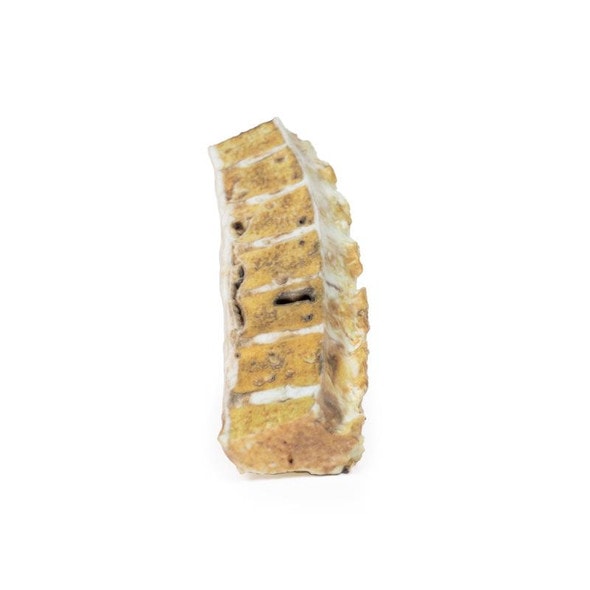
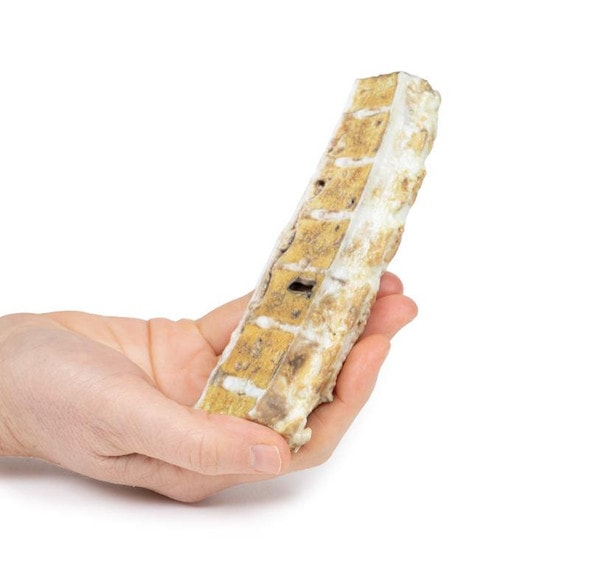
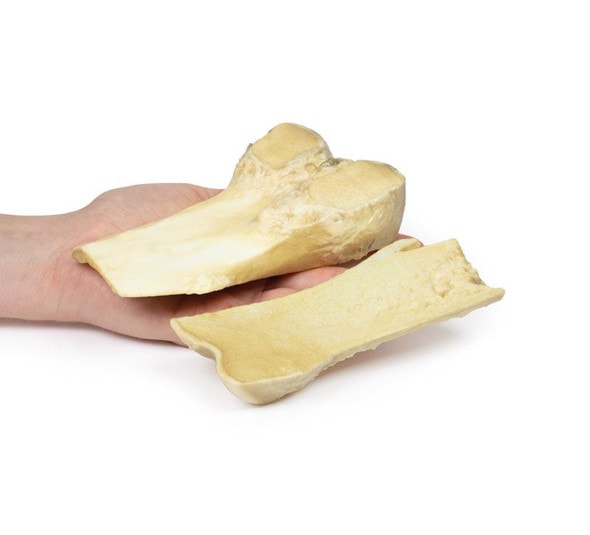
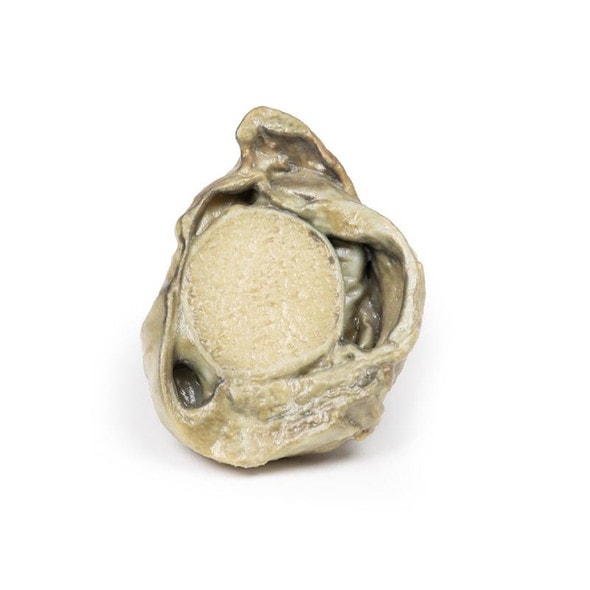
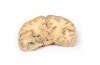
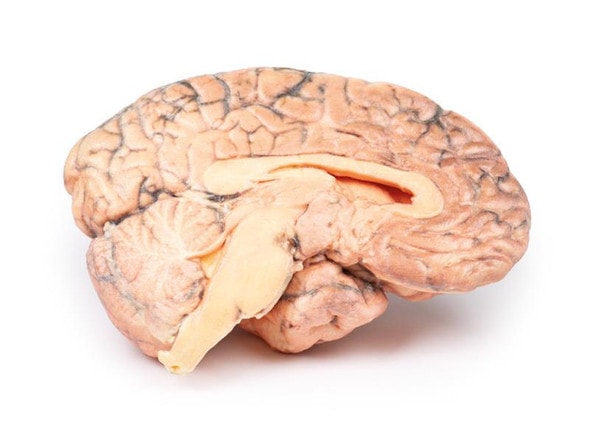
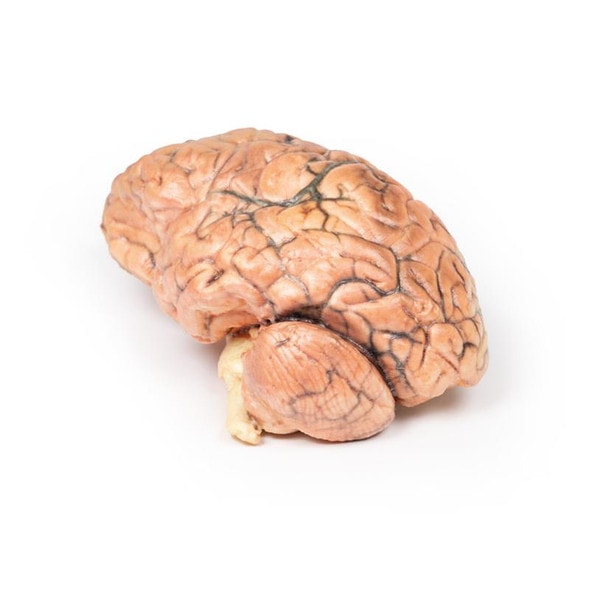
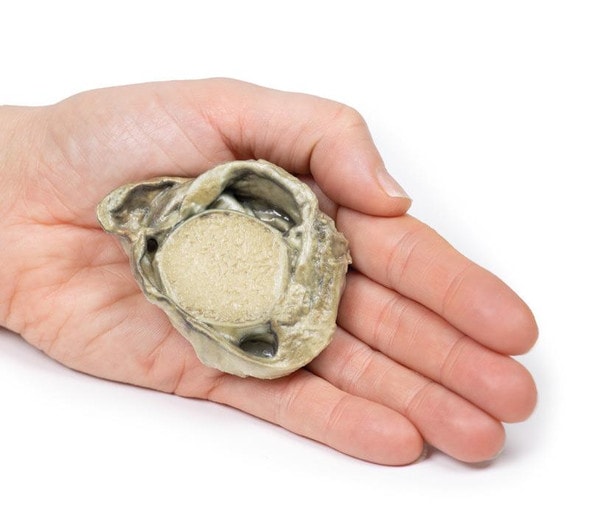
This brain specimen is a coronal section. In the right temporal lobe, a poorly demarcated tumor is present. There is enlargement of the hemispheres and flattening of the gyral pattern. From the posterior aspect of the specimen subfalcine herniation is appreciated and the tumor appear less well differentiated with hemorrhagic and necrotic foci. Histology of this tumor showed an astrocytoma, Grade III/IV.
In subfalcine (or cingulate) herniation, the most common type of brain herniation, the innermost part of the frontal lobe is pushed under part of the falx cerebri, between the two hemispheres of the brain.
Further Information
Gliomas are the second most common cancer of the central nervous system after meningiomas. The term glioma refers to tumors that are histologically similar to normal glial cells i.e. astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and ependymal cells. They arise from a progenitor cell that differentiates down one of the cell lines. Astrocytomas develop from the astrocyte lineage of glial cells. Tumors are staged according to histological differentiation and range from diffuse astrocytoma (Grade II/IV) to anaplastic astrocytoma (Grade III/IV) to glioblastoma (Grade IV). Histological features include the prominent eosinophilic cytoplasm in some astrocytic tumor cells (gemistocytes) as well as a fibrillary background.
Astrocytomas occur most commonly between the fourth and sixth decades of life. Tumors usually occur in the cerebral hemispheres but may also occur in the cerebellum, brainstem or spinal cord. They most commonly present with seizures, headaches, nausea and focal neurological deficits depending on area involved. Without treatment Grade III median survival is 18 months. Treatment includes surgical resection, radiotherapy, chemotherapy or a combination thereof, depending on the clinical context.
Advantages of 3D Printed Anatomical Models
- 3D printed anatomical models are the most anatomically accurate examples of human anatomy because they are based on real human specimens.
- Avoid the ethical complications and complex handling, storage, and documentation requirements with 3D printed models when compared to human cadaveric specimens.
- 3D printed anatomy models are far less expensive than real human cadaveric specimens.
- Reproducibility and consistency allow for standardization of education and faster availability of models when you need them.
- Customization options are available for specific applications or educational needs. Enlargement, highlighting of specific anatomical structures, cutaway views, and more are just some of the customizations available.
Disadvantages of Human Cadavers
- Access to cadavers can be problematic and ethical complications are hard to avoid. Many countries cannot access cadavers for cultural and religious reasons.
- Human cadavers are costly to procure and require expensive storage facilities and dedicated staff to maintain them. Maintenance of the facility alone is costly.
- The cost to develop a cadaver lab or plastination technique is extremely high. Those funds could purchase hundreds of easy to handle, realistic 3D printed anatomical replicas.
- Wet specimens cannot be used in uncertified labs. Certification is expensive and time-consuming.
- Exposure to preservation fluids and chemicals is known to cause long-term health problems for lab workers and students. 3D printed anatomical replicas are safe to handle without any special equipment.
- Lack of reuse and reproducibility. If a dissection mistake is made, a new specimen has to be used and students have to start all over again.
Disadvantages of Plastinated Specimens
- Like real human cadaveric specimens, plastinated models are extremely expensive.
- Plastinated specimens still require real human samples and pose the same ethical issues as real human cadavers.
- The plastination process is extensive and takes months or longer to complete. 3D printed human anatomical models are available in a fraction of the time.
- Plastinated models, like human cadavers, are one of a kind and can only showcase one presentation of human anatomy.
Advanced 3D Printing Techniques for Superior Results
- Vibrant color offering with 10 million colors
- UV-curable inkjet printing
- High quality 3D printing that can create products that are delicate, extremely precise, and incredibly realistic
- To improve durability of fragile, thin, and delicate arteries, veins or vessels, a clear support material is printed in key areas. This makes the models robust so they can be handled by students easily.