Description
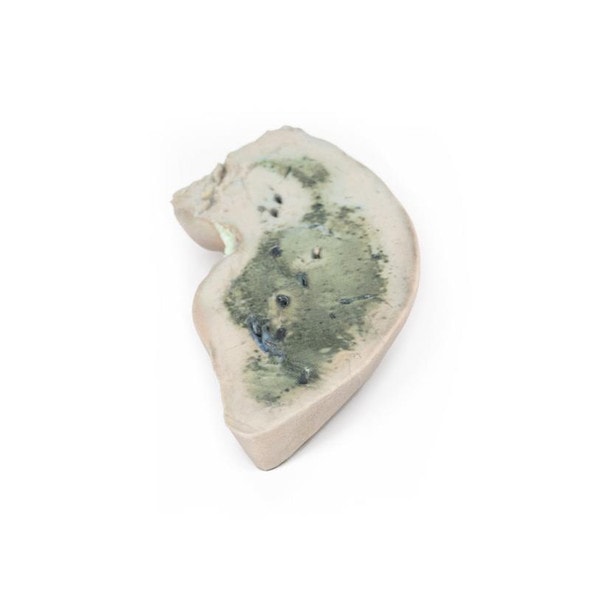
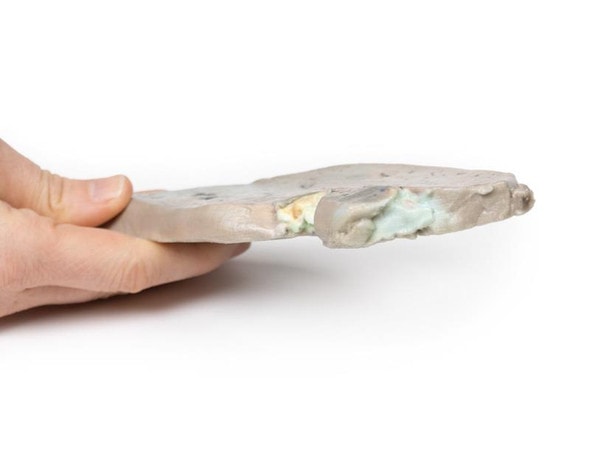
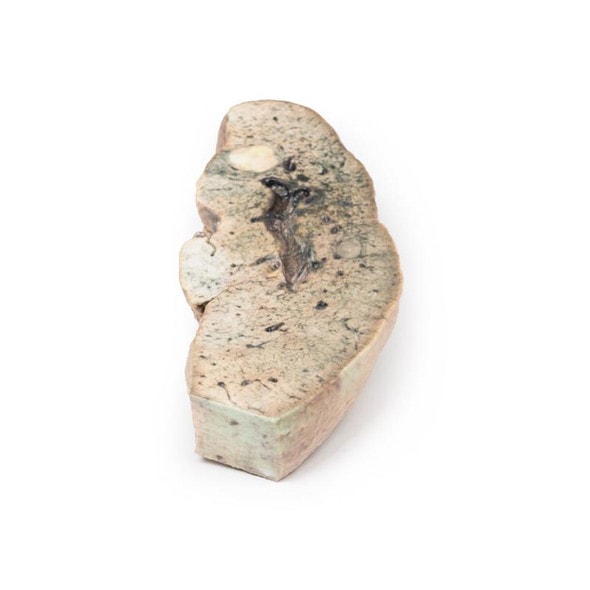
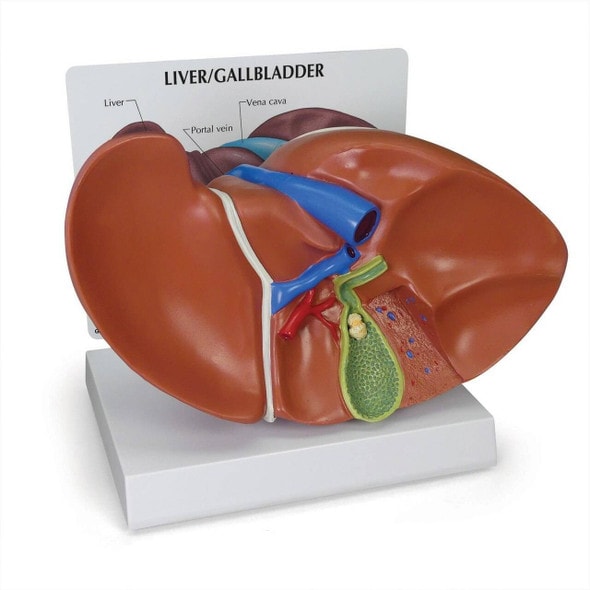
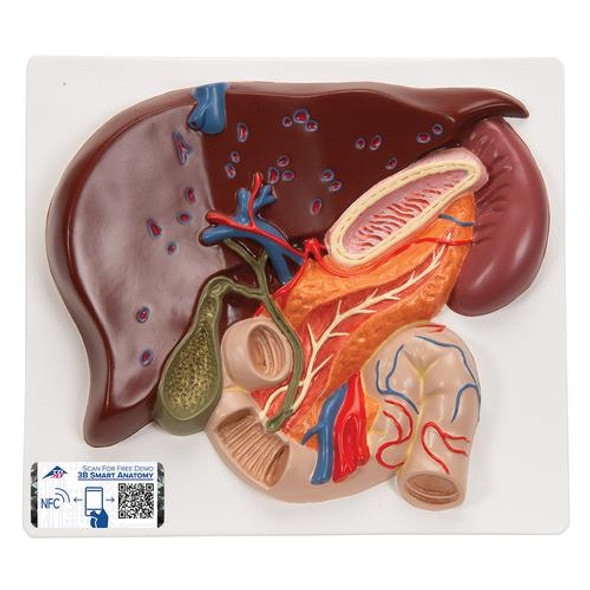
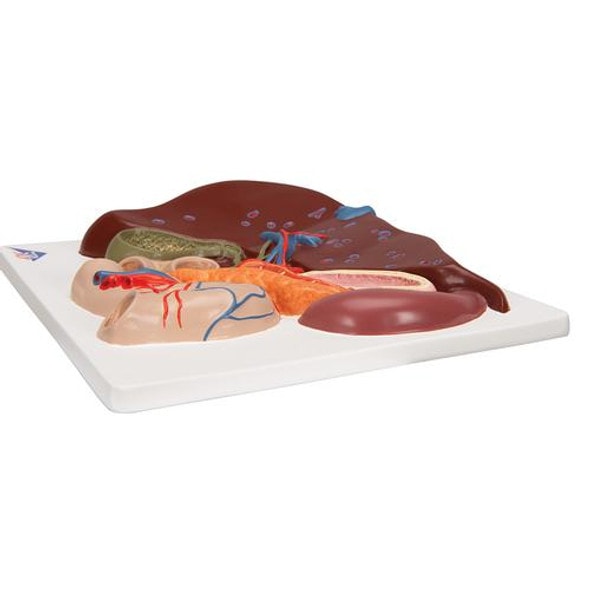
The size and shape of this specimen varies somewhat from a typical liver. It is less wedge-shaped and longer in the superoinferior dimension (on the posterior view this would translate to a greater vertical height). Normally, a liver is less than 16cm in the midclavicular line.1 This specimen measures approximately 18cm in the midclavicular line, suggesting some degree of hepatomegaly. However, it is worth mentioning that some measurement distortion may have occurred based on the fixing and curation of the specimen and it must be noted that the accuracy of estimating liver size using a single parameter is limited. Liver measurements diagnostic of hepatomegaly vary depending on normal anatomical variation in liver size and morphology, the method of measurement, and patient features such as sex and BMI.
An alternative explanation could be normal anatomical variation. However, this specimen does not fit the description of the most common anatomical variations confused with hepatomegaly Riedel's lobe (a downward projection of the right lobe), beaver tail liver (an elongated left lobe), or a papillary process projecting from the caudate lobe.
Advantages of 3D Printed Anatomical Models
- 3D printed anatomical models are the most anatomically accurate examples of human anatomy because they are based on real human specimens.
- Avoid the ethical complications and complex handling, storage, and documentation requirements with 3D printed models when compared to human cadaveric specimens.
- 3D printed anatomy models are far less expensive than real human cadaveric specimens.
- Reproducibility and consistency allow for standardization of education and faster availability of models when you need them.
- Customization options are available for specific applications or educational needs. Enlargement, highlighting of specific anatomical structures, cutaway views, and more are just some of the customizations available.
Disadvantages of Human Cadavers
- Access to cadavers can be problematic and ethical complications are hard to avoid. Many countries cannot access cadavers for cultural and religious reasons.
- Human cadavers are costly to procure and require expensive storage facilities and dedicated staff to maintain them. Maintenance of the facility alone is costly.
- The cost to develop a cadaver lab or plastination technique is extremely high. Those funds could purchase hundreds of easy to handle, realistic 3D printed anatomical replicas.
- Wet specimens cannot be used in uncertified labs. Certification is expensive and time-consuming.
- Exposure to preservation fluids and chemicals is known to cause long-term health problems for lab workers and students. 3D printed anatomical replicas are safe to handle without any special equipment.
- Lack of reuse and reproducibility. If a dissection mistake is made, a new specimen has to be used and students have to start all over again.
Disadvantages of Plastinated Specimens
- Like real human cadaveric specimens, plastinated models are extremely expensive.
- Plastinated specimens still require real human samples and pose the same ethical issues as real human cadavers.
- The plastination process is extensive and takes months or longer to complete. 3D printed human anatomical models are available in a fraction of the time.
- Plastinated models, like human cadavers, are one of a kind and can only showcase one presentation of human anatomy.
Advanced 3D Printing Techniques for Superior Results
- Vibrant color offering with 10 million colors
- UV-curable inkjet printing
- High quality 3D printing that can create products that are delicate, extremely precise, and incredibly realistic
- To improve durability of fragile, thin, and delicate arteries, veins or vessels, a clear support material is printed in key areas. This makes the models robust so they can be handled by students easily.