- Home
- Anatomy Models
- Respiratory System Anatomy Models
- 3D Printed Lobar Pneumonia - Grey Hepatisation Phase
Description
Developed from real patient case study specimens, the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series introduces an unmatched level of realism in human anatomy models. Each 3D printed anatomy model is a high-fidelity replica of a human cadaveric specimen, focusing on the key morbidity presentations that led to the deceasement of the patient. With advances in 3D printing materials and techniques, these stories can come to life in an ethical, consistently reproduceable, and easy to handle format. Ideal for the most advanced anatomical and pathological study, and backed by authentic case study details, students, instructors, and experts alike will discover a new level of anatomical study with the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series.
Clinical History
There is no clinical history for this specimen.
Pathology
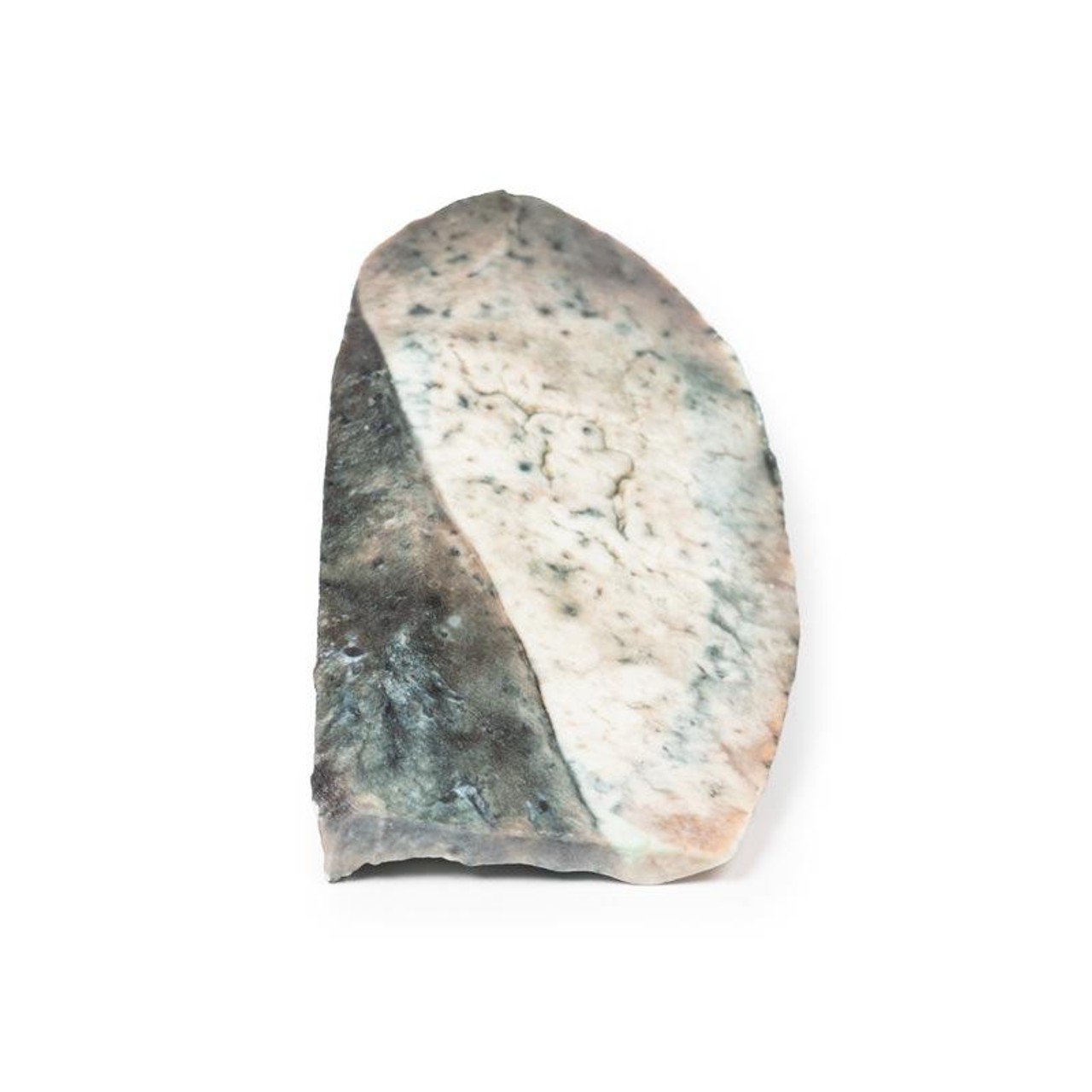
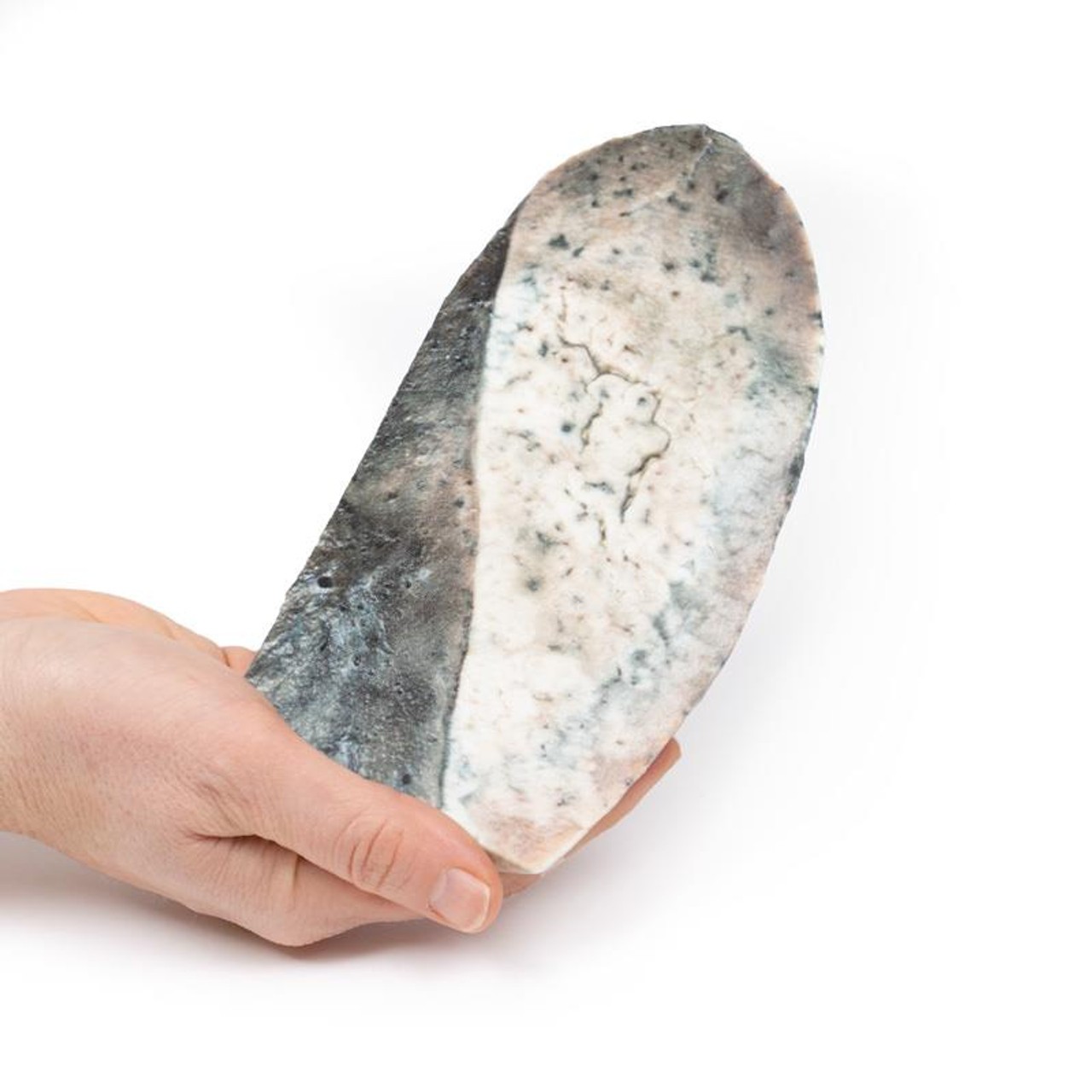
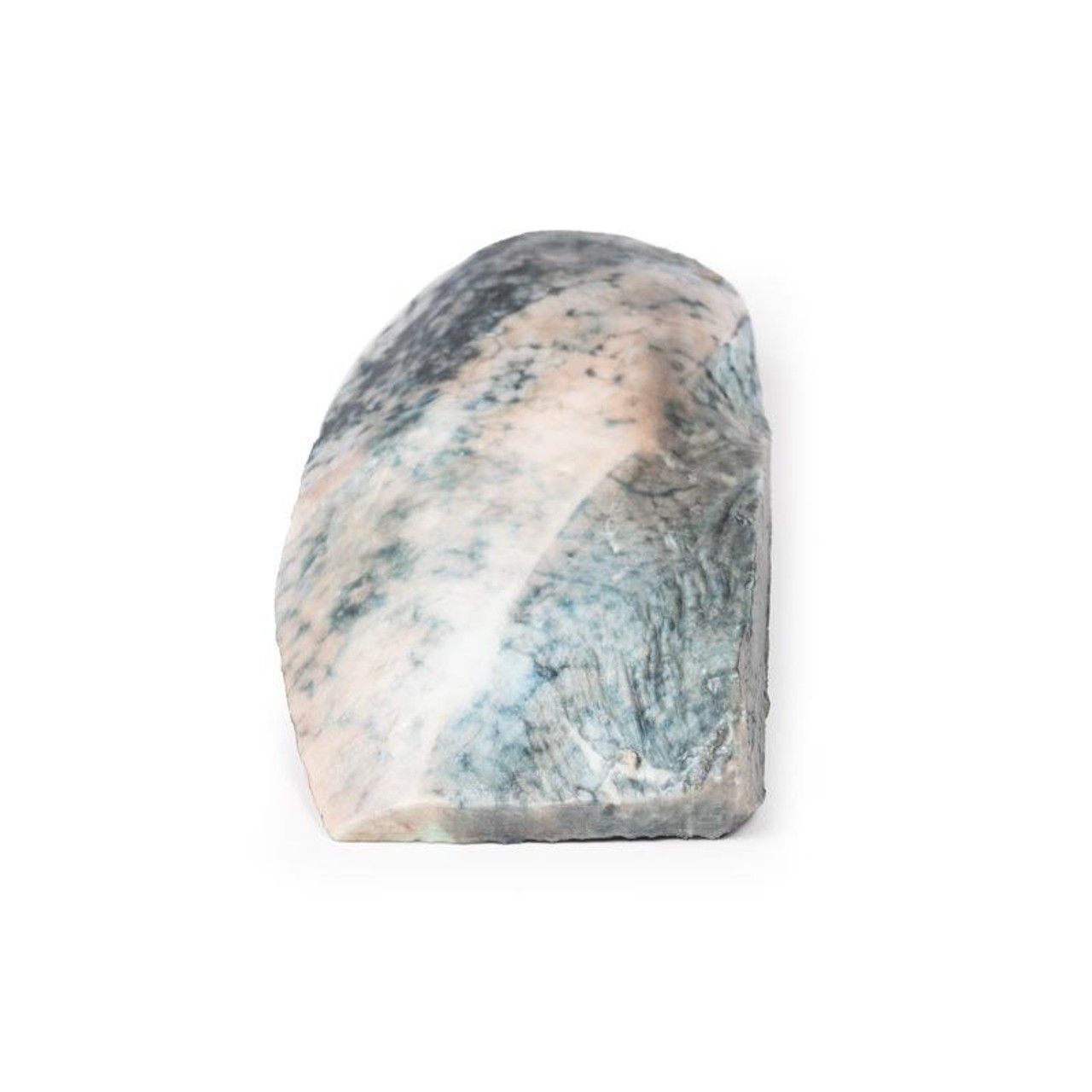
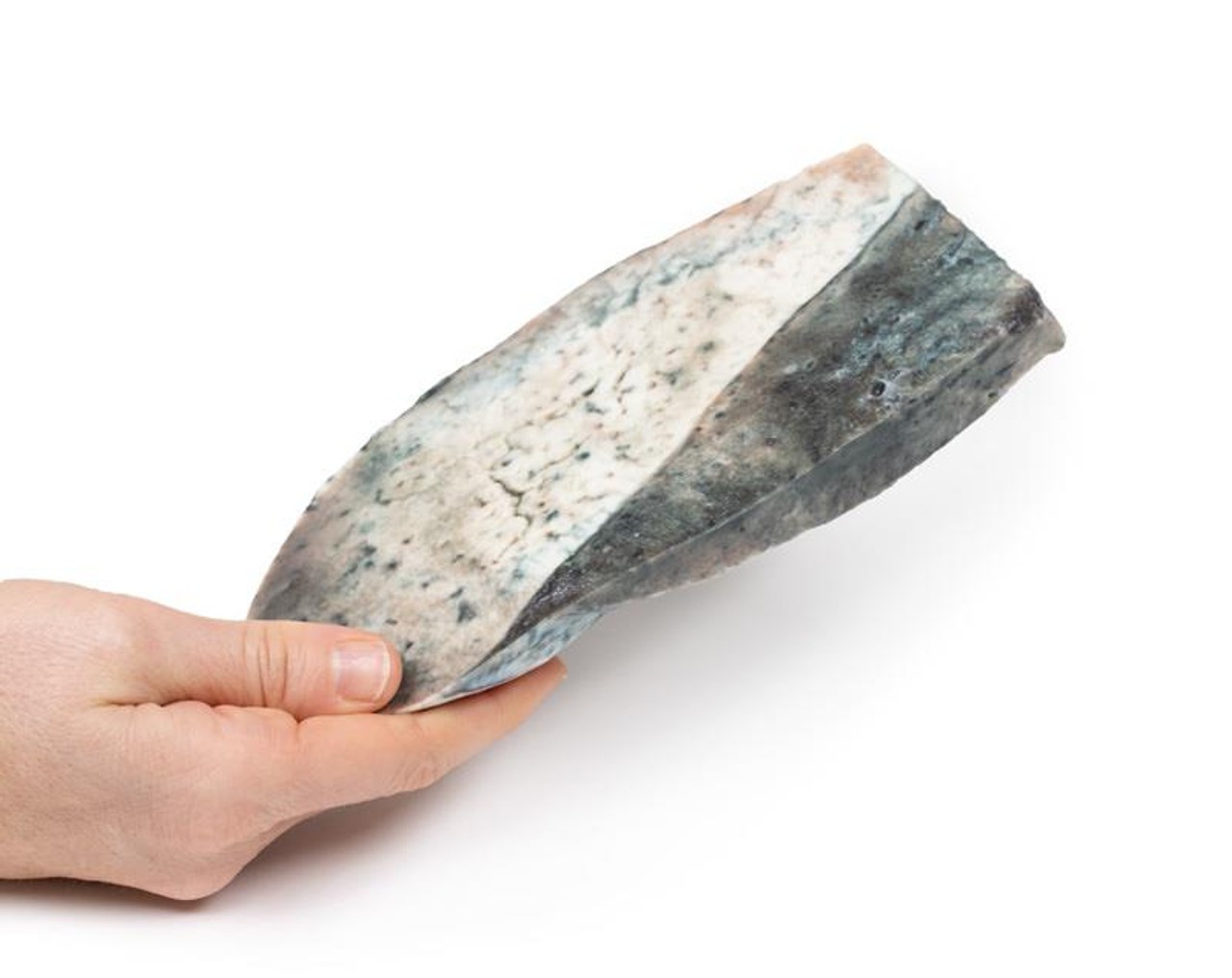
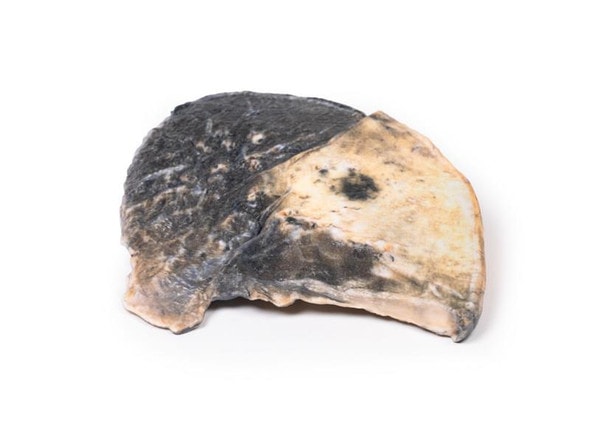
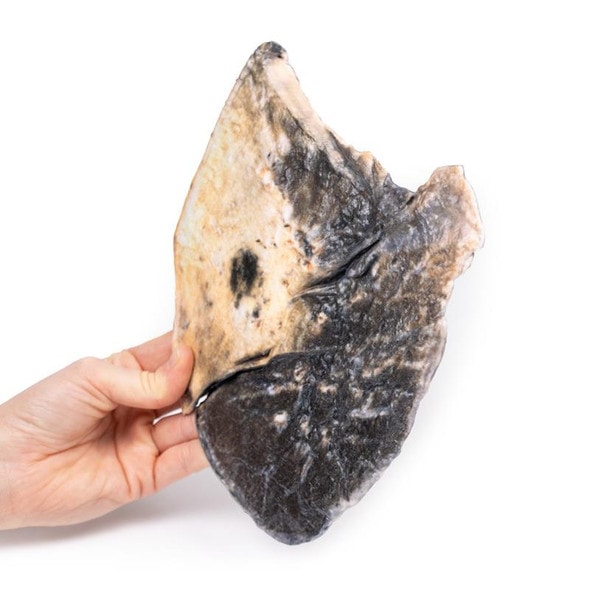
The specimen is a parasagittal section of the right lung and the boundaries between the upper and lower lobes is clearly visible. The entire upper lobe is congested and pale grey in color.
Further Information
This is an example of a stage of lobar pneumonia in which the inflammatory exudates within the intra-alveolar space resulting in consolidation that affects a large and continuous area of the lobe of a lung. The affected lobe in this case shows grey hepatization or late consolidation. This usually occurs 2 to 3 days following red hepatization, and lasts for 4 to 8 days. The lung appears grey with liver-like solid consistency, due to a fibrinopurulent exudate, progressive disintegration of red blood cells, and hemosiderin. Large numbers of macrophages begin to appear in the interstitial tissue. They are the dominant cells, which attempt to clear away the cellular debris and acute inflammation through phagocytosis. The macrophages may contain iron due to consumption of erythrocytes, and are thus termed siderophages. Following grey hepatization, resolution and restoration of the pulmonary architecture start by the eighth day. The enzymatic action begins centrally and spreads peripherally, which liquefies the previous solid fibrinous content and eventually restores aeration.
The most common organisms that cause lobar pneumonia are Streptococcus pneumoniae, also called pneumococcus, Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis. Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the tubercle bacillus, may also cause lobar pneumonia if pulmonary tuberculosis is not treated promptly. Other organisms causing lobar pneumonia are Legionella pneumophila and Klebsiella pneumoniae.[2]On a posteroanterior and lateral chest radiograph, an entire lobe will be radiopaque, which is indicative of lobar pneumonia.
Advantages of 3D Printed Anatomical Models
- 3D printed anatomical models are the most anatomically accurate examples of human anatomy because they are based on real human specimens.
- Avoid the ethical complications and complex handling, storage, and documentation requirements with 3D printed models when compared to human cadaveric specimens.
- 3D printed anatomy models are far less expensive than real human cadaveric specimens.
- Reproducibility and consistency allow for standardization of education and faster availability of models when you need them.
- Customization options are available for specific applications or educational needs. Enlargement, highlighting of specific anatomical structures, cutaway views, and more are just some of the customizations available.
Disadvantages of Human Cadavers
- Access to cadavers can be problematic and ethical complications are hard to avoid. Many countries cannot access cadavers for cultural and religious reasons.
- Human cadavers are costly to procure and require expensive storage facilities and dedicated staff to maintain them. Maintenance of the facility alone is costly.
- The cost to develop a cadaver lab or plastination technique is extremely high. Those funds could purchase hundreds of easy to handle, realistic 3D printed anatomical replicas.
- Wet specimens cannot be used in uncertified labs. Certification is expensive and time-consuming.
- Exposure to preservation fluids and chemicals is known to cause long-term health problems for lab workers and students. 3D printed anatomical replicas are safe to handle without any special equipment.
- Lack of reuse and reproducibility. If a dissection mistake is made, a new specimen has to be used and students have to start all over again.
Disadvantages of Plastinated Specimens
- Like real human cadaveric specimens, plastinated models are extremely expensive.
- Plastinated specimens still require real human samples and pose the same ethical issues as real human cadavers.
- The plastination process is extensive and takes months or longer to complete. 3D printed human anatomical models are available in a fraction of the time.
- Plastinated models, like human cadavers, are one of a kind and can only showcase one presentation of human anatomy.
Advanced 3D Printing Techniques for Superior Results
- Vibrant color offering with 10 million colors
- UV-curable inkjet printing
- High quality 3D printing that can create products that are delicate, extremely precise, and incredibly realistic
- To improve durability of fragile, thin, and delicate arteries, veins or vessels, a clear support material is printed in key areas. This makes the models robust so they can be handled by students easily.