Description
Developed from real patient case study specimens, the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series introduces an unmatched level of realism in human anatomy models. Each 3D printed anatomy model is a high-fidelity replica of a human cadaveric specimen, focusing on the key morbidity presentations that led to the deceasement of the patient. With advances in 3D printing materials and techniques, these stories can come to life in an ethical, consistently reproduceable, and easy to handle format. Ideal for the most advanced anatomical and pathological study, and backed by authentic case study details, students, instructors, and experts alike will discover a new level of anatomical study with the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series.
Clinical History
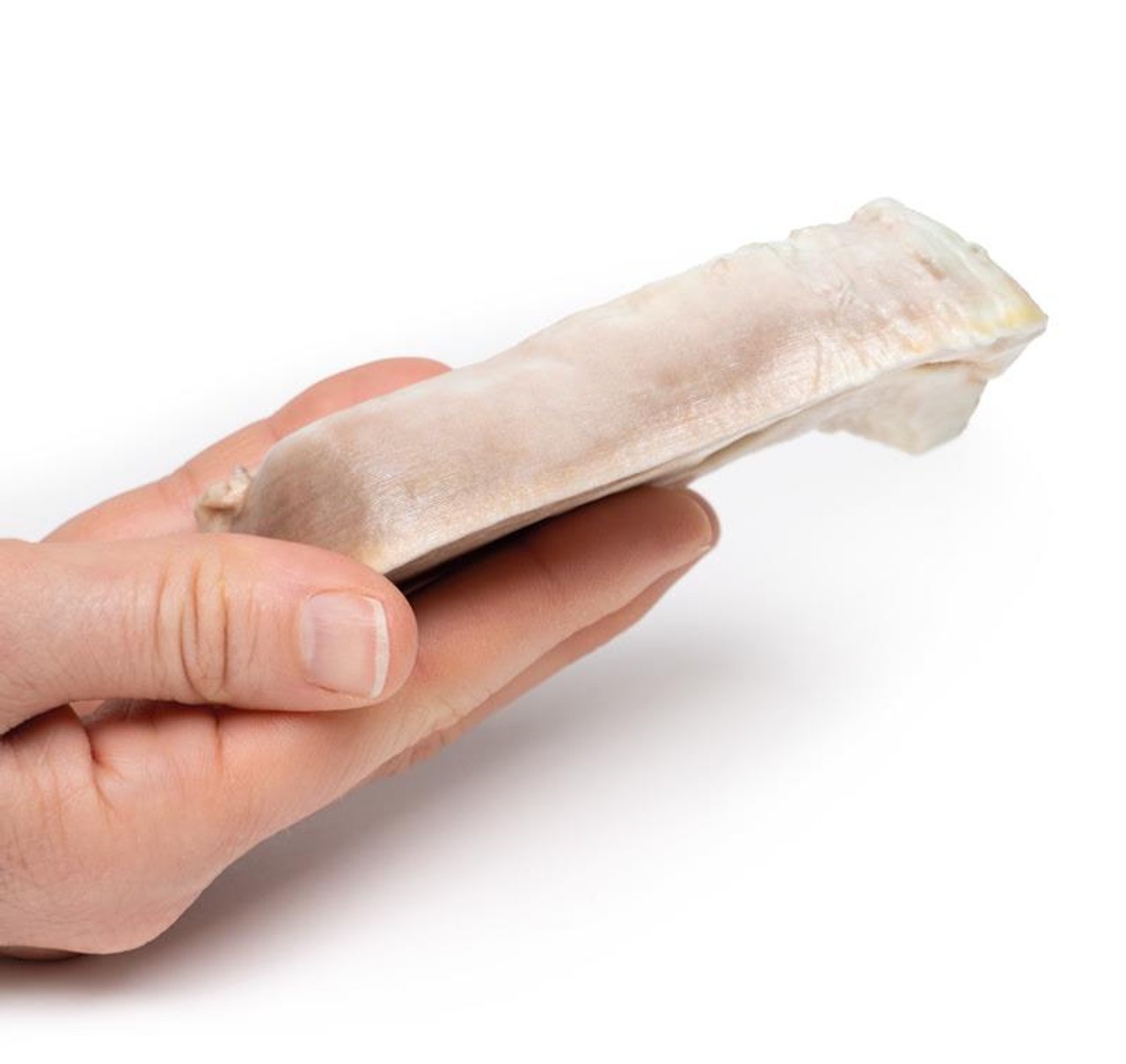
A 30-year old female presents with inability to conceive. She also reports a history of intermittent pelvic discomfort, menorrhagia and painful periods. On examination a pelvic mass was palpable. All of her blood tests were within normal ranges. A pelvic ultrasound showed a hypoechoic mass within the myometrium of her uterus. She went for hysteroscopic myomectomy but unfortunately complications meant her surgery was converted to an emergency hysterectomy. She made a full recovery post-op.
Pathology
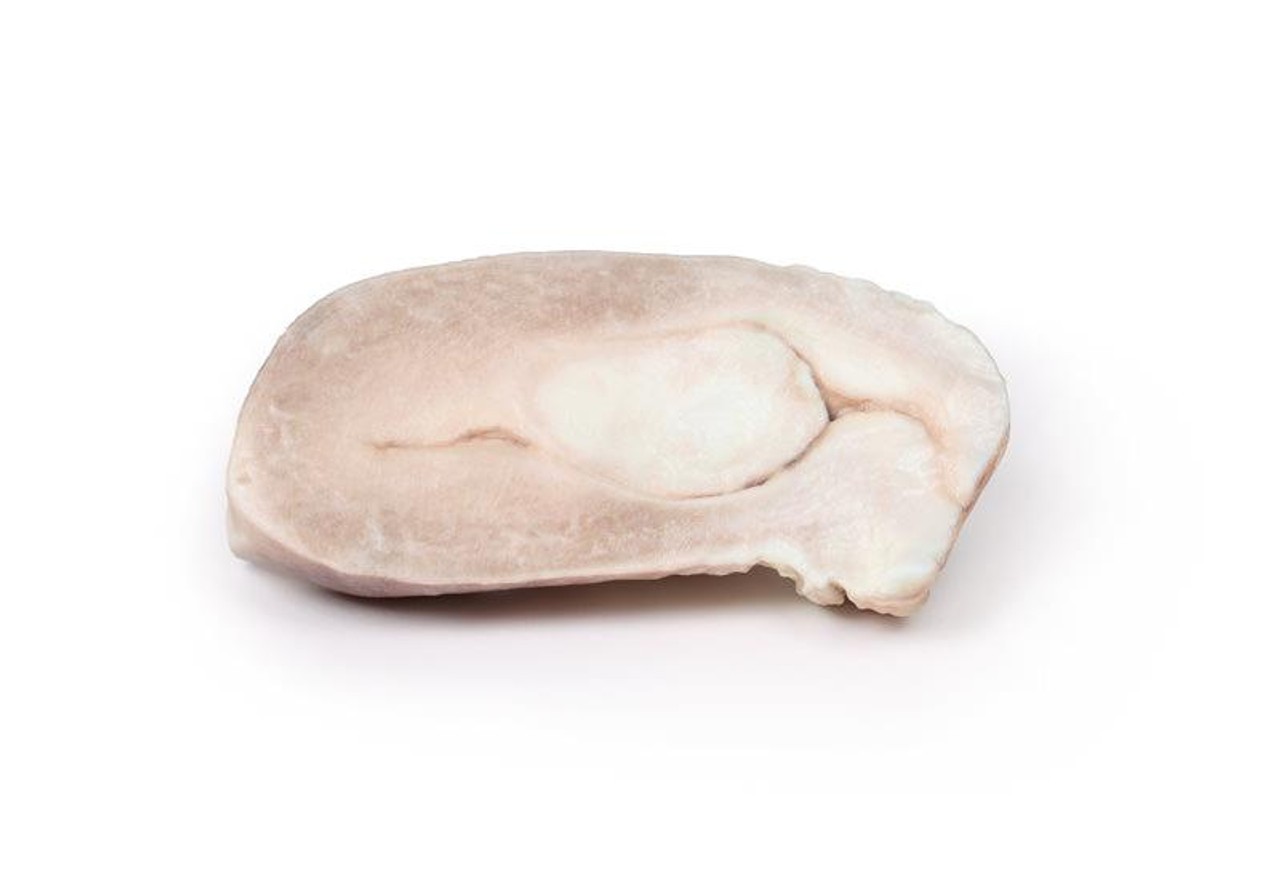
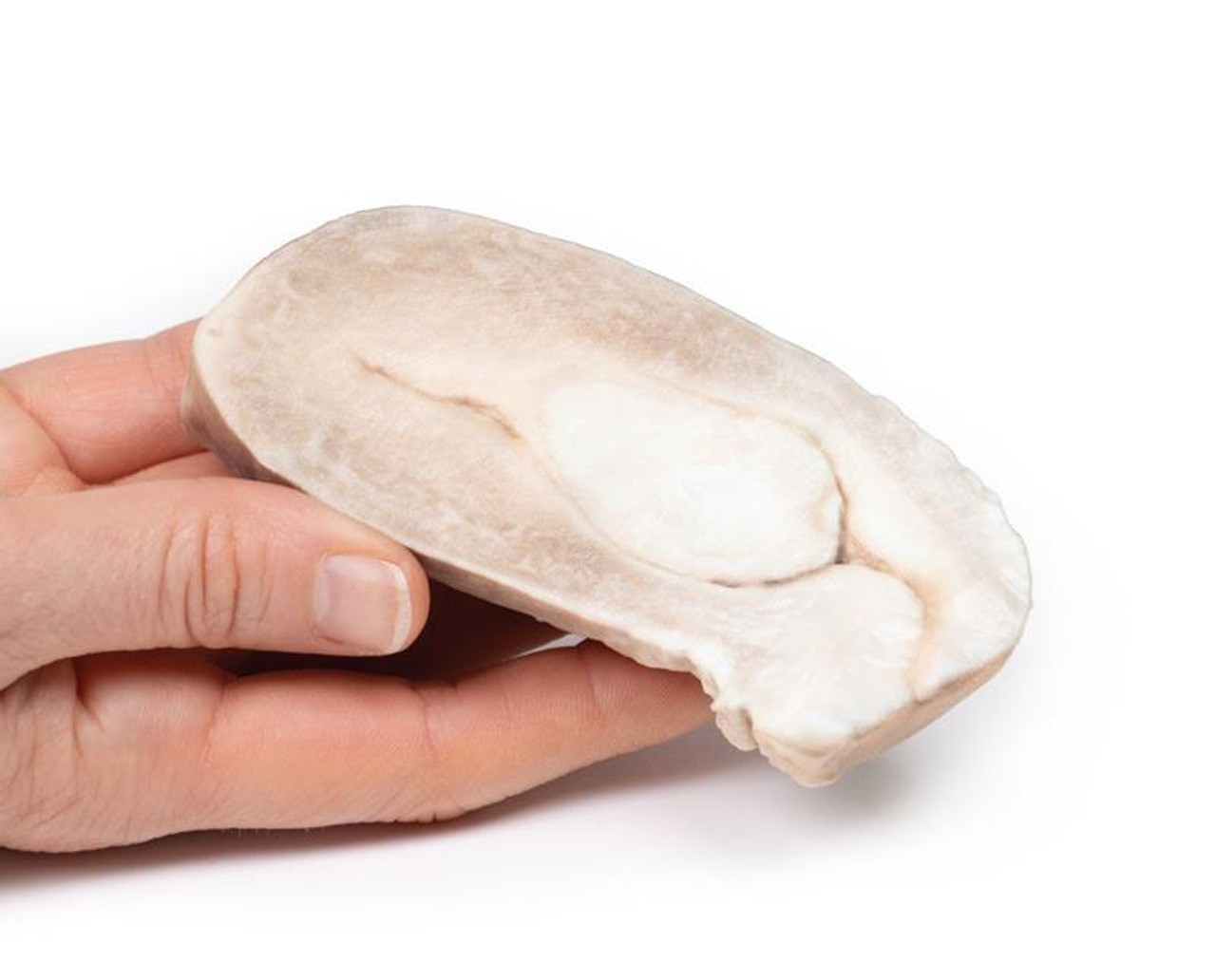
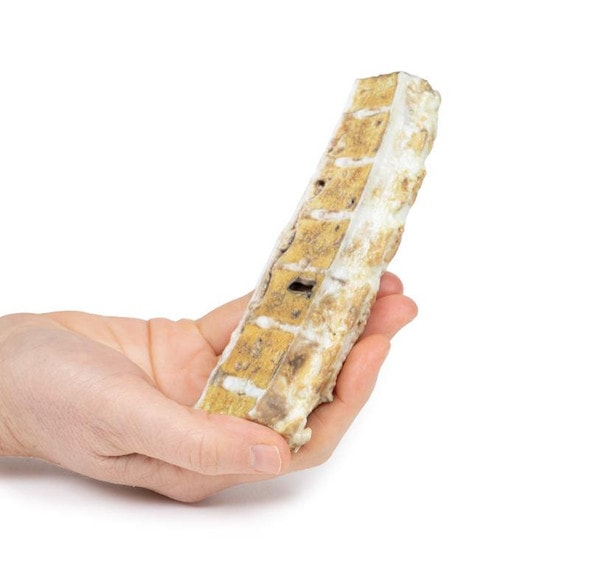
The specimen includes the cervix, body and fundus of the uterus. The uterus, which is of normal size, has been cut in the sagittal plane. A large ovoid mass approximately 4cm x 2cm protrudes into the uterine cavity and extends as far inferiorly as the opening of the cervix. It originates from the posterior aspect of the uterus. The cervical canal is clearly visible.
Further Information
Uterine leiomyomas , also called fibroids, are the most common pelvic tumors in females. They are present in almost 25% of reproductive females. They are benign tumors arising from smooth muscle and fibroblasts of the myometrium. They usually involve the myometrium of the uterine body. Rarely they can affect the lower uterus or cervix. Leiomyomas can occur as single lesions or multiple and can grow very large. There are rare variants, which can extend and spread distally but are still considered benign: e.g. the benign metastasizing leiomyoma, which commonly spread to the lining; or disseminated peritoneal leiomyomatosis, which appears on the peritoneum covering the uterus
Risk factors for developing fibroid include being of reproductive age, being a black woman and early menarche. Higher parity has been found to be protective. Most leiomyomas have normal karyotypes but there are some which show mutation in the HMG genes. Transformation into malignant leiomyosarcoma is very rare.
Common symptoms of uterine fibroids include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, dyspareunia, dysmenorrhea and symptoms of pelvic structure compression such as urinary symptoms or venous compression symptoms. Leiomyomas can decrease fertility and in pregnant females increase the rate of early pregnancy loss, fetal malpresentation and postpartum hemorrhage. Pelvic ultrasound is usually used to diagnose leiomyomas. CT and MRI scans are rarely used to diagnose.
Leiomyomas can grow but can also regress. Treatment is reserved for persistently or severely symptomatic fibroids. Hormonal treatment may be used to regulate irregular menstrual bleeding symptoms. Surgical treatments include myomectomy (removal of fibroids from myomectomy), hysterectomy, myolysis (thermal ablation of leiomyoma) and uterine artery ablation/embolization.
Advantages of 3D Printed Anatomical Models
- 3D printed anatomical models are the most anatomically accurate examples of human anatomy because they are based on real human specimens.
- Avoid the ethical complications and complex handling, storage, and documentation requirements with 3D printed models when compared to human cadaveric specimens.
- 3D printed anatomy models are far less expensive than real human cadaveric specimens.
- Reproducibility and consistency allow for standardization of education and faster availability of models when you need them.
- Customization options are available for specific applications or educational needs. Enlargement, highlighting of specific anatomical structures, cutaway views, and more are just some of the customizations available.
Disadvantages of Human Cadavers
- Access to cadavers can be problematic and ethical complications are hard to avoid. Many countries cannot access cadavers for cultural and religious reasons.
- Human cadavers are costly to procure and require expensive storage facilities and dedicated staff to maintain them. Maintenance of the facility alone is costly.
- The cost to develop a cadaver lab or plastination technique is extremely high. Those funds could purchase hundreds of easy to handle, realistic 3D printed anatomical replicas.
- Wet specimens cannot be used in uncertified labs. Certification is expensive and time-consuming.
- Exposure to preservation fluids and chemicals is known to cause long-term health problems for lab workers and students. 3D printed anatomical replicas are safe to handle without any special equipment.
- Lack of reuse and reproducibility. If a dissection mistake is made, a new specimen has to be used and students have to start all over again.
Disadvantages of Plastinated Specimens
- Like real human cadaveric specimens, plastinated models are extremely expensive.
- Plastinated specimens still require real human samples and pose the same ethical issues as real human cadavers.
- The plastination process is extensive and takes months or longer to complete. 3D printed human anatomical models are available in a fraction of the time.
- Plastinated models, like human cadavers, are one of a kind and can only showcase one presentation of human anatomy.
Advanced 3D Printing Techniques for Superior Results
- Vibrant color offering with 10 million colors
- UV-curable inkjet printing
- High quality 3D printing that can create products that are delicate, extremely precise, and incredibly realistic
- To improve durability of fragile, thin, and delicate arteries, veins or vessels, a clear support material is printed in key areas. This makes the models robust so they can be handled by students easily.