- Home
- Anatomy Models
- Respiratory System Anatomy Models
- 3D Printed Metastatic Tumour in Lung from Primary Testicular Cancer
Description
Developed from real patient case study specimens, the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series introduces an unmatched level of realism in human anatomy models. Each 3D printed anatomy model is a high-fidelity replica of a human cadaveric specimen, focusing on the key morbidity presentations that led to the deceasement of the patient. With advances in 3D printing materials and techniques, these stories can come to life in an ethical, consistently reproduceable, and easy to handle format. Ideal for the most advanced anatomical and pathological study, and backed by authentic case study details, students, instructors, and experts alike will discover a new level of anatomical study with the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series.
Clinical History
A 37-year old male patient presents with a 1-month history of lethargy, cough and weight loss. He had a history of an orchiectomy 18 months previous for a testicular tumor. Then 12 months post-op he underwent neck radiotherapy to treat metastasis. On admission, he became acutely dyspnoeic and hypoxic and died.
Pathology
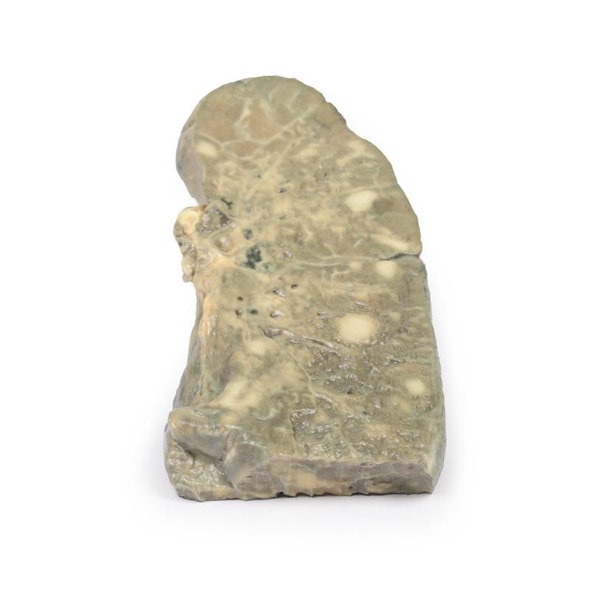
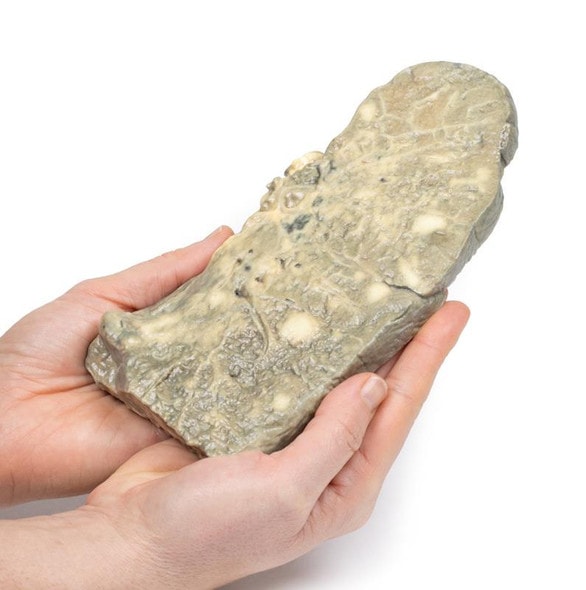
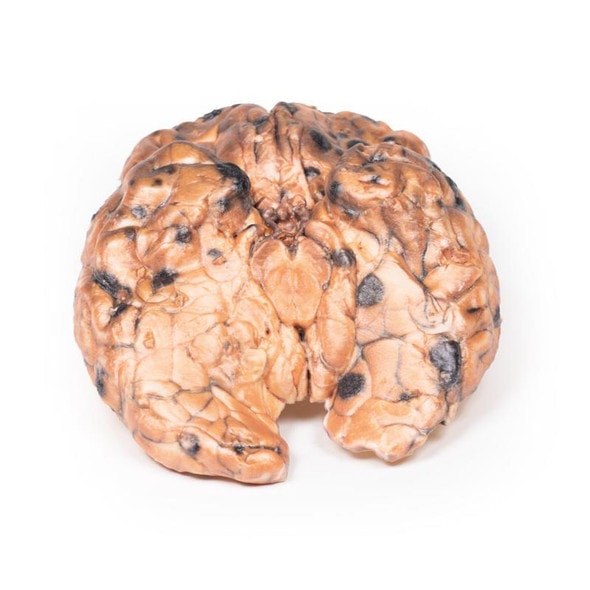
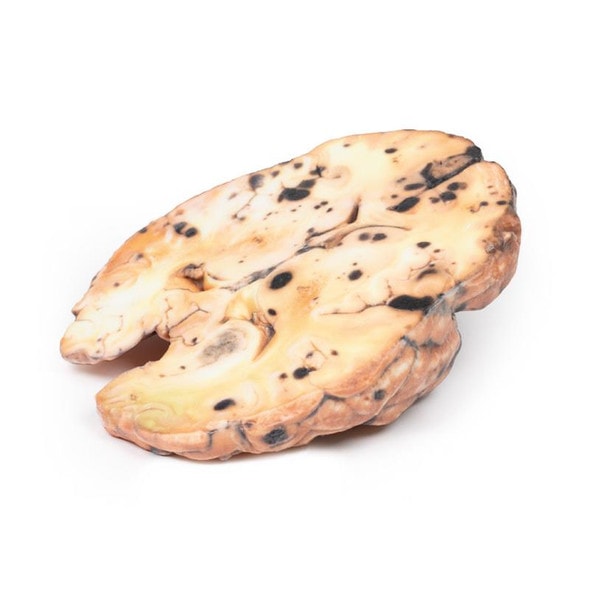
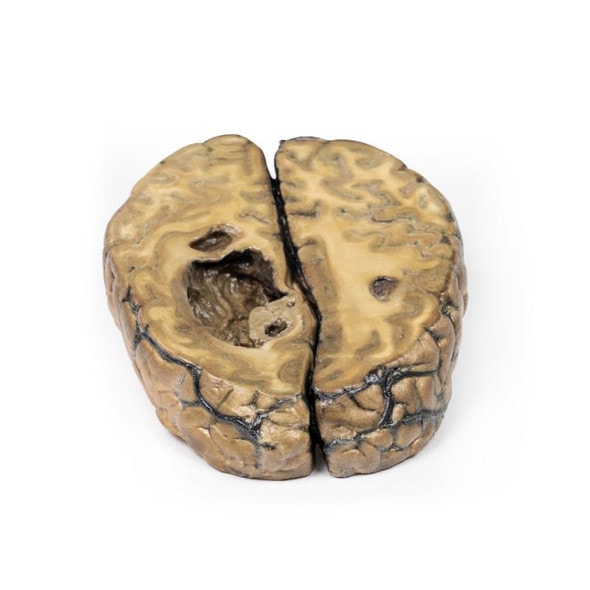
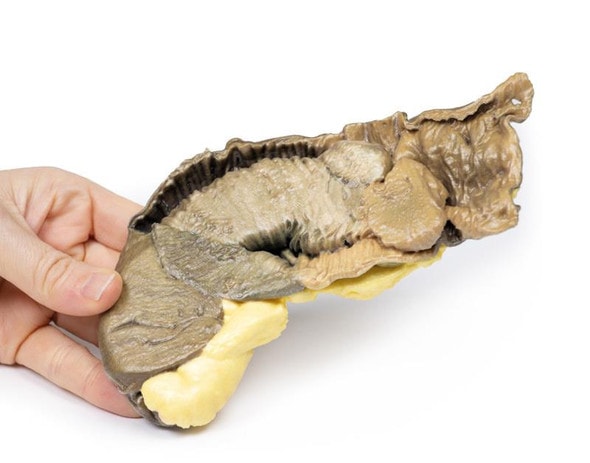
This right lung specimen (and portions of 4 ribs) has been sliced longitudinally. There are numerous rounded tumor nodules evident in the lung parenchyma ranging from 5 to 30mm in diameter. The tumors are variegated in appearance with pale yellow and dark brown cut surfaces. One tumor is extending along the bronchus of the lower lobe forming a cast. Several nodules project from the pleural surface and some show central umbilication from necrosis and hemorrhage. This is an example of pulmonary metastases from a mixed germ cell testicular tumor, most likely choriocarcinoma arising in a malignant teratoma.
Further Information
Germ cell testicular tumors (GCT) are the most common tumors found in men. Average age of diagnosis is 30 year of age and are rarely diagnosed pre-puberty. Risk factors for development include cryptorchidism and a positive family history of GCT. Familial GCT increased risk can be linked to genes encoding for kinases, e.g. KIT and BAK.
They can be divided into two groups: seminomatous (resemble primordial germ cells) and non-seminomatous (resemble embryonic stem cells). Over one third of GCT are mixed GCT, with two or more GCT types in one mass. Many possible combinations of seminoma, teratoma, embryonal carcinoma, yolk sac tumor, and choriocarcinoma can be seen. Teratomas components are found in one third of mixed GCT. Elevated serum Alpha Fetoprotein and beta-HCG are produced by choriocarcinoma. Lymphatic spread involves the retroperitoneal para aortic nodes initially. Mediastinal and supraclavicular nodes may later become involved. The lungs are the most common site for hematogenous spread but the liver, brain or bones may also be affected.
Symptoms may include a painless testicular mass and haematospermia. Later symptoms of distant metastases may occur. Common symptoms of lung metastases include cough, dyspnoea, hemoptysis, recurrent infection
Treatment depends on clinical stage but usually involves radical orchiectomy, chemotherapy and sometimes radiotherapy. More than 95% on early stage GCT can be cured.
Advantages of 3D Printed Anatomical Models
- 3D printed anatomical models are the most anatomically accurate examples of human anatomy because they are based on real human specimens.
- Avoid the ethical complications and complex handling, storage, and documentation requirements with 3D printed models when compared to human cadaveric specimens.
- 3D printed anatomy models are far less expensive than real human cadaveric specimens.
- Reproducibility and consistency allow for standardization of education and faster availability of models when you need them.
- Customization options are available for specific applications or educational needs. Enlargement, highlighting of specific anatomical structures, cutaway views, and more are just some of the customizations available.
Disadvantages of Human Cadavers
- Access to cadavers can be problematic and ethical complications are hard to avoid. Many countries cannot access cadavers for cultural and religious reasons.
- Human cadavers are costly to procure and require expensive storage facilities and dedicated staff to maintain them. Maintenance of the facility alone is costly.
- The cost to develop a cadaver lab or plastination technique is extremely high. Those funds could purchase hundreds of easy to handle, realistic 3D printed anatomical replicas.
- Wet specimens cannot be used in uncertified labs. Certification is expensive and time-consuming.
- Exposure to preservation fluids and chemicals is known to cause long-term health problems for lab workers and students. 3D printed anatomical replicas are safe to handle without any special equipment.
- Lack of reuse and reproducibility. If a dissection mistake is made, a new specimen has to be used and students have to start all over again.
Disadvantages of Plastinated Specimens
- Like real human cadaveric specimens, plastinated models are extremely expensive.
- Plastinated specimens still require real human samples and pose the same ethical issues as real human cadavers.
- The plastination process is extensive and takes months or longer to complete. 3D printed human anatomical models are available in a fraction of the time.
- Plastinated models, like human cadavers, are one of a kind and can only showcase one presentation of human anatomy.
Advanced 3D Printing Techniques for Superior Results
- Vibrant color offering with 10 million colors
- UV-curable inkjet printing
- High quality 3D printing that can create products that are delicate, extremely precise, and incredibly realistic
- To improve durability of fragile, thin, and delicate arteries, veins or vessels, a clear support material is printed in key areas. This makes the models robust so they can be handled by students easily.