Description
Developed from real patient case study specimens, the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series introduces an unmatched level of realism in human anatomy models. Each 3D printed anatomy model is a high-fidelity replica of a human cadaveric specimen, focusing on the key morbidity presentations that led to the deceasement of the patient. With advances in 3D printing materials and techniques, these stories can come to life in an ethical, consistently reproduceable, and easy to handle format. Ideal for the most advanced anatomical and pathological study, and backed by authentic case study details, students, instructors, and experts alike will discover a new level of anatomical study with the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series.
Clinical History
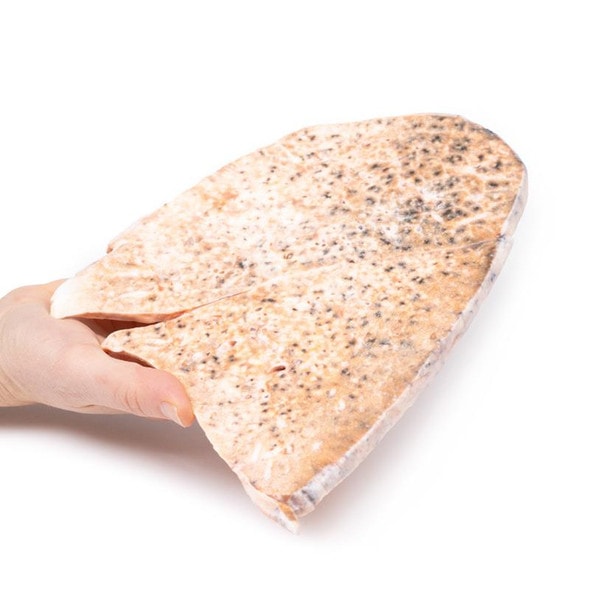
A 6-year old girl was admitted with a productive cough, dyspnoea and fevers. She became increasingly hypotensive and dies soon after admission. She had a previous history of recurrent pneumonia and meconium ileus. The clinical diagnosis was cystic fibrosis (mucoviscidosis). Her sister died aged 3 from the same disease.
Pathology
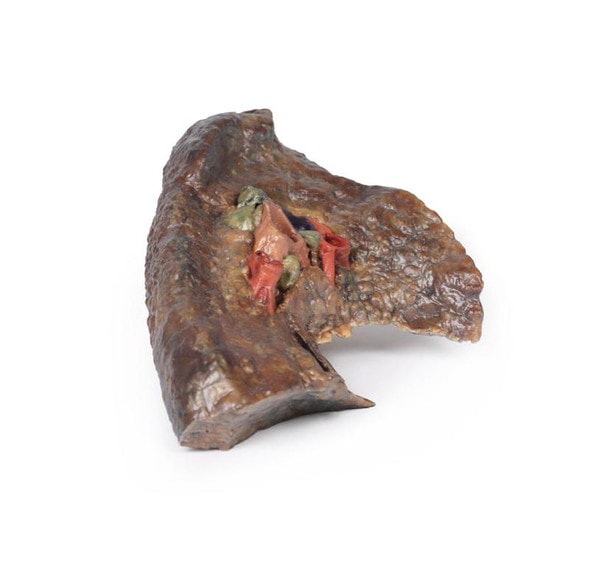
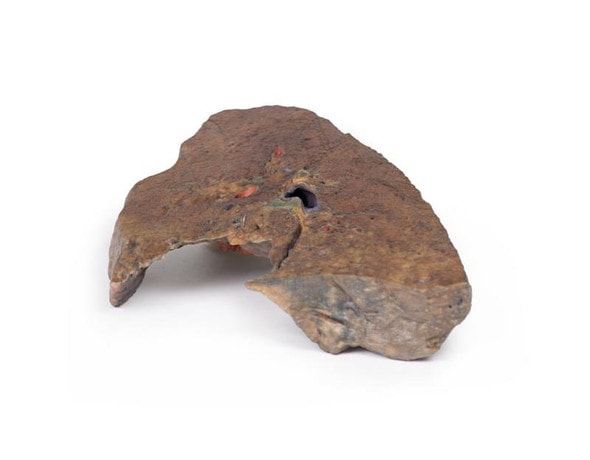
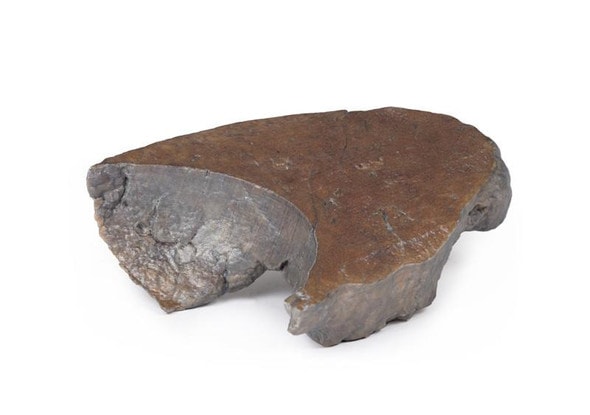
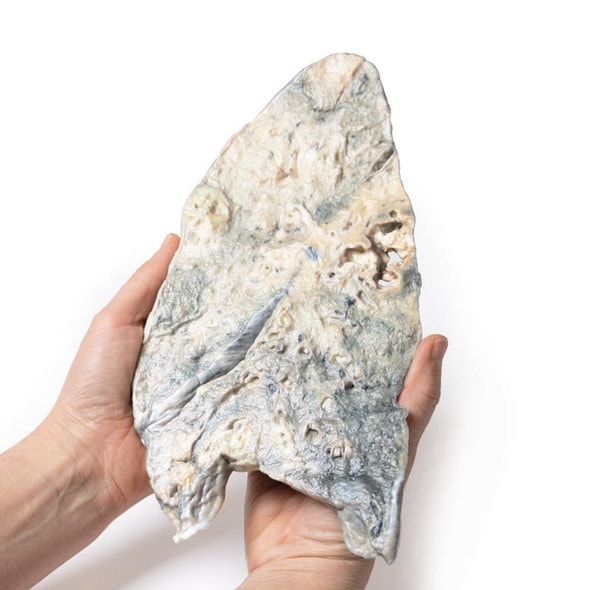
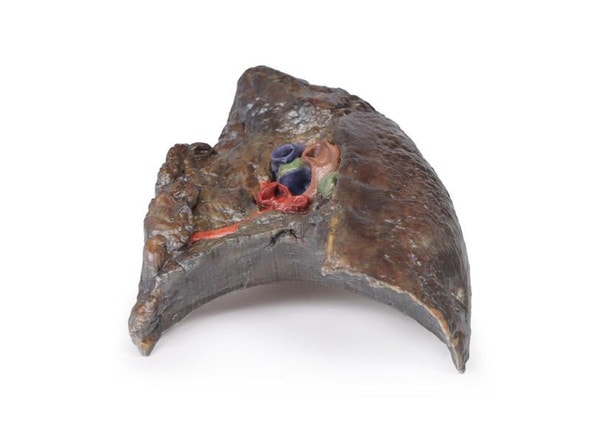
The lung parenchyma shows extensive changes mainly with a bronchial distribution. Many bronchi are dilated (bronchiectasis) and contain thick, yellowish, purulent material. These changes are most marked in the upper lobe, at the apex of which a small focus of honeycomb change is also seen. Multiple abscesses are present, especially in the basal and central parts of the lower lobe. The base of the lower lobe is severely affected with fibrosis and consolidation being evident. There is very little normal lung tissue remaining. These pathological changes are characteristic but not pathognomonic of cystic fibrosis.
Further Information
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited disorder of chloride ion transport. Mutations in the cystic fibrosis conductance regulator (CFTR) gene on chromosome 7 cause defects in the chloride channel protein leading to dysfunction of the chloride channels. This causes increased water absorption in exocrine glands and epithelium of the respiratory, gastrointestinal and reproductive tracts. These dehydrated viscous secretions then obstruct these organ passage causing clinical features including: persistent pulmonary infection, pancreatic insufficiency, liver cirrhosis, intestinal obstruction, male infertility, and elevated sweat chloride levels. In the airway, CF patients have decreased chloride secretion and increased water reabsorption. This causes dehydrated mucous lining the airways leading to defective mucociliary action, mucous obstructing the airway, bronchiole dilatation (bronchiectasis) and secondary infection. Staphylococcus aureus, Haemophilus influenzae and Pseudomonas are the most common bacteria causing CF patients lower respiratory tract infections. Chronic bronchitis and bronchiectasis develops as a result. Pulmonary issues are the highest cause of mortality in CF patients. The average life expectancy is between 40-50 years of age in developed countries.
CF occurs in around 1 in 3000 live births. It is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. It is most common in fair-skinned populations: with 1 in 20 being a carrier of the gene. Symptoms can present in-utero or even up to adolescence, depending on the severity of the disease. It is now most commonly diagnosed with the neonatal screening test for immunoreactive trypsinogen (a pancreas enzyme precursor). If this screening test is positive, a formal diagnosis is made with a sweat test showing >60mmol/L of chloride.
Advantages of 3D Printed Anatomical Models
- 3D printed anatomical models are the most anatomically accurate examples of human anatomy because they are based on real human specimens.
- Avoid the ethical complications and complex handling, storage, and documentation requirements with 3D printed models when compared to human cadaveric specimens.
- 3D printed anatomy models are far less expensive than real human cadaveric specimens.
- Reproducibility and consistency allow for standardization of education and faster availability of models when you need them.
- Customization options are available for specific applications or educational needs. Enlargement, highlighting of specific anatomical structures, cutaway views, and more are just some of the customizations available.
Disadvantages of Human Cadavers
- Access to cadavers can be problematic and ethical complications are hard to avoid. Many countries cannot access cadavers for cultural and religious reasons.
- Human cadavers are costly to procure and require expensive storage facilities and dedicated staff to maintain them. Maintenance of the facility alone is costly.
- The cost to develop a cadaver lab or plastination technique is extremely high. Those funds could purchase hundreds of easy to handle, realistic 3D printed anatomical replicas.
- Wet specimens cannot be used in uncertified labs. Certification is expensive and time-consuming.
- Exposure to preservation fluids and chemicals is known to cause long-term health problems for lab workers and students. 3D printed anatomical replicas are safe to handle without any special equipment.
- Lack of reuse and reproducibility. If a dissection mistake is made, a new specimen has to be used and students have to start all over again.
Disadvantages of Plastinated Specimens
- Like real human cadaveric specimens, plastinated models are extremely expensive.
- Plastinated specimens still require real human samples and pose the same ethical issues as real human cadavers.
- The plastination process is extensive and takes months or longer to complete. 3D printed human anatomical models are available in a fraction of the time.
- Plastinated models, like human cadavers, are one of a kind and can only showcase one presentation of human anatomy.
Advanced 3D Printing Techniques for Superior Results
- Vibrant color offering with 10 million colors
- UV-curable inkjet printing
- High quality 3D printing that can create products that are delicate, extremely precise, and incredibly realistic
- To improve durability of fragile, thin, and delicate arteries, veins or vessels, a clear support material is printed in key areas. This makes the models robust so they can be handled by students easily.