- Home
- Anatomy Models
- Reproductive System Anatomy Models
- 3D Printed Nodular Hyperplasia of the Prostate
Description
Developed from real patient case study specimens, the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series introduces an unmatched level of realism in human anatomy models. Each 3D printed anatomy model is a high-fidelity replica of a human cadaveric specimen, focusing on the key morbidity presentations that led to the deceasement of the patient. With advances in 3D printing materials and techniques, these stories can come to life in an ethical, consistently reproduceable, and easy to handle format. Ideal for the most advanced anatomical and pathological study, and backed by authentic case study details, students, instructors, and experts alike will discover a new level of anatomical study with the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series.
Clinical History
A 63-year old male presented to the emergency departed with acute abdominal pain. He has been unable to pass urine for 5 days. Further questioning revealed a 2-year history of urinary frequency, double void, urinary hesitancy, nocturia and a poor urine stream. Abdominal examination showed a tender distended bladder and an enlarged palpable prostate on digital rectal examination. A bedside bladder scan demonstrated a volume of >1L in the bladder. Blood tests shows a severe acute kidney injury. He is diagnosed with acute renal failure due to acute urinary retention. There were multiple failed attempts at catheterizing the patient via the urethra and suprapublically. A total prostatectomy was performed and he made a good recovery.
Pathology
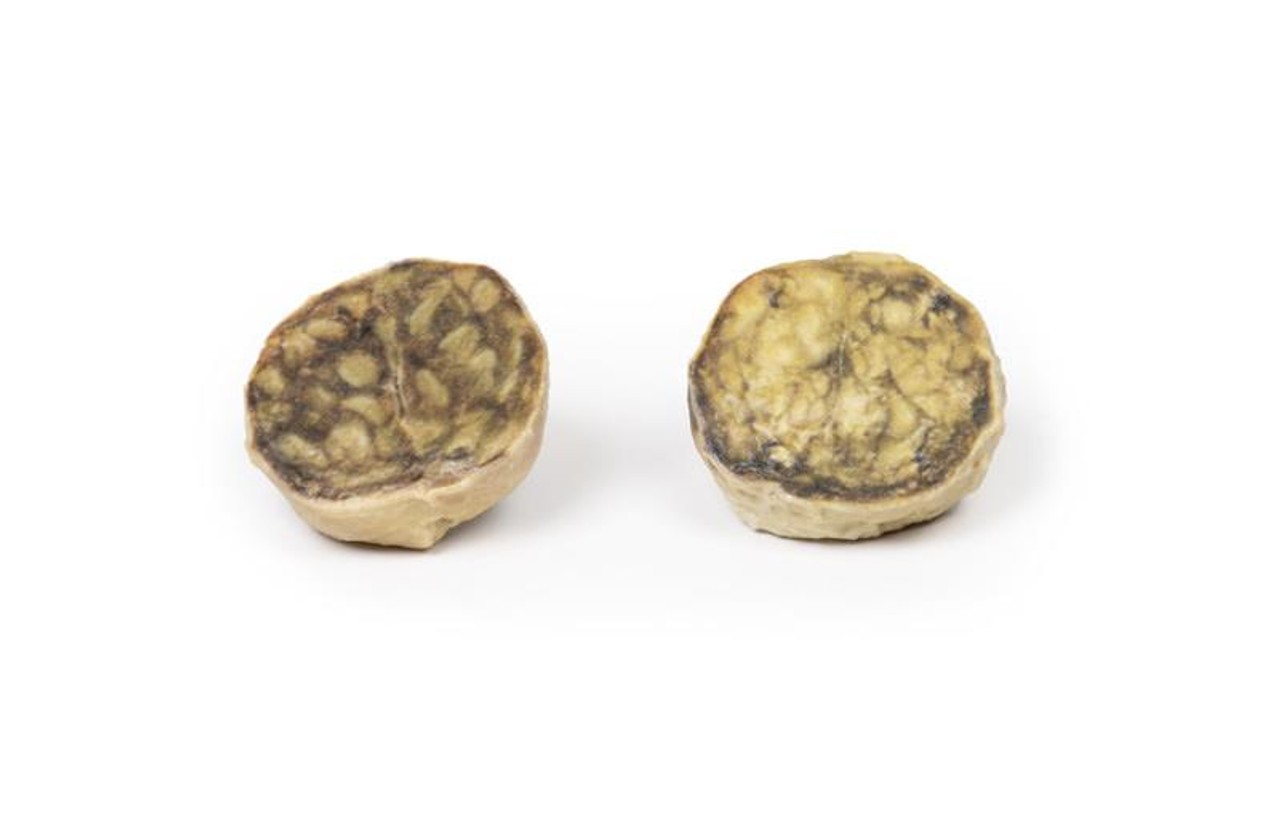
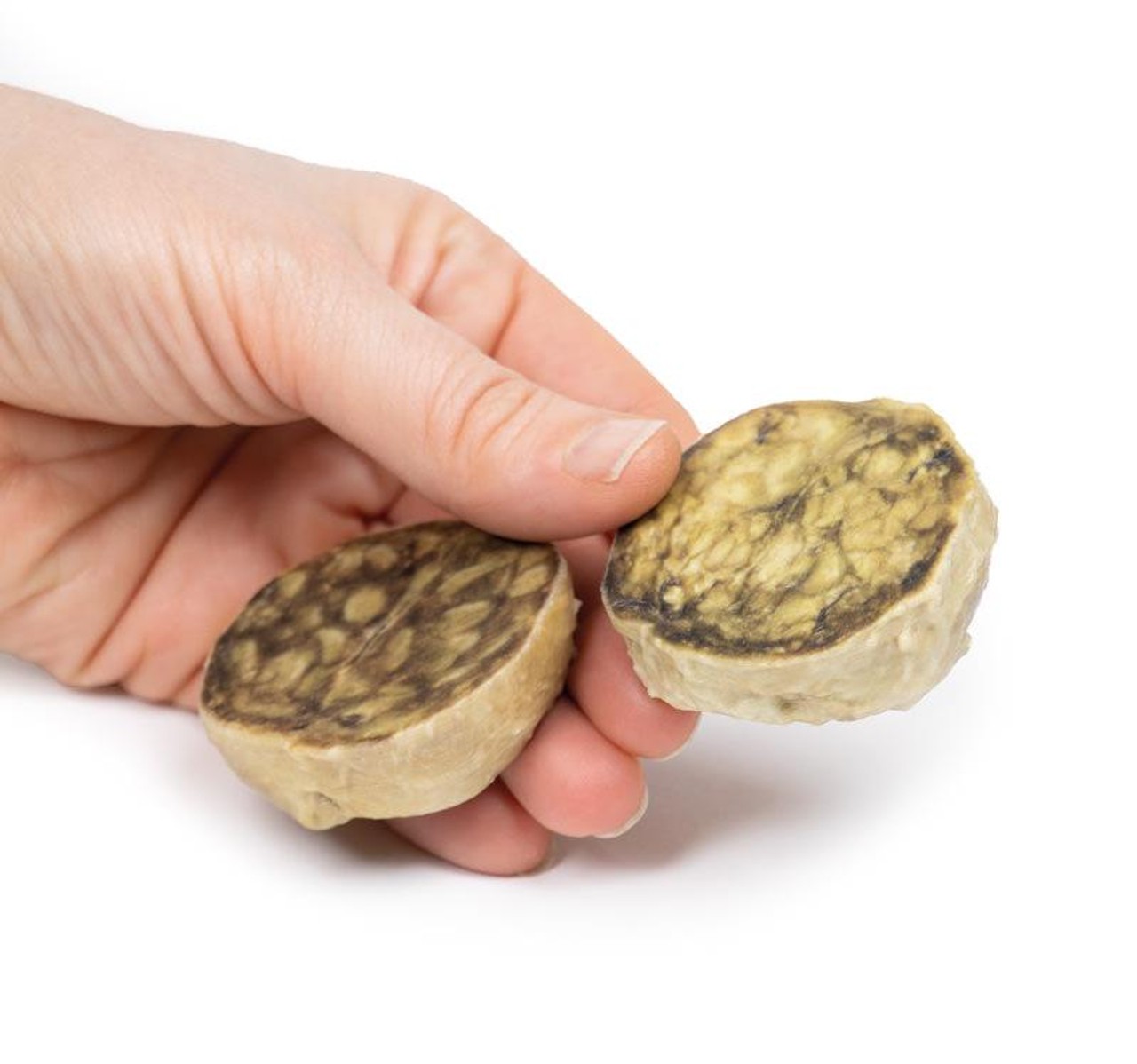
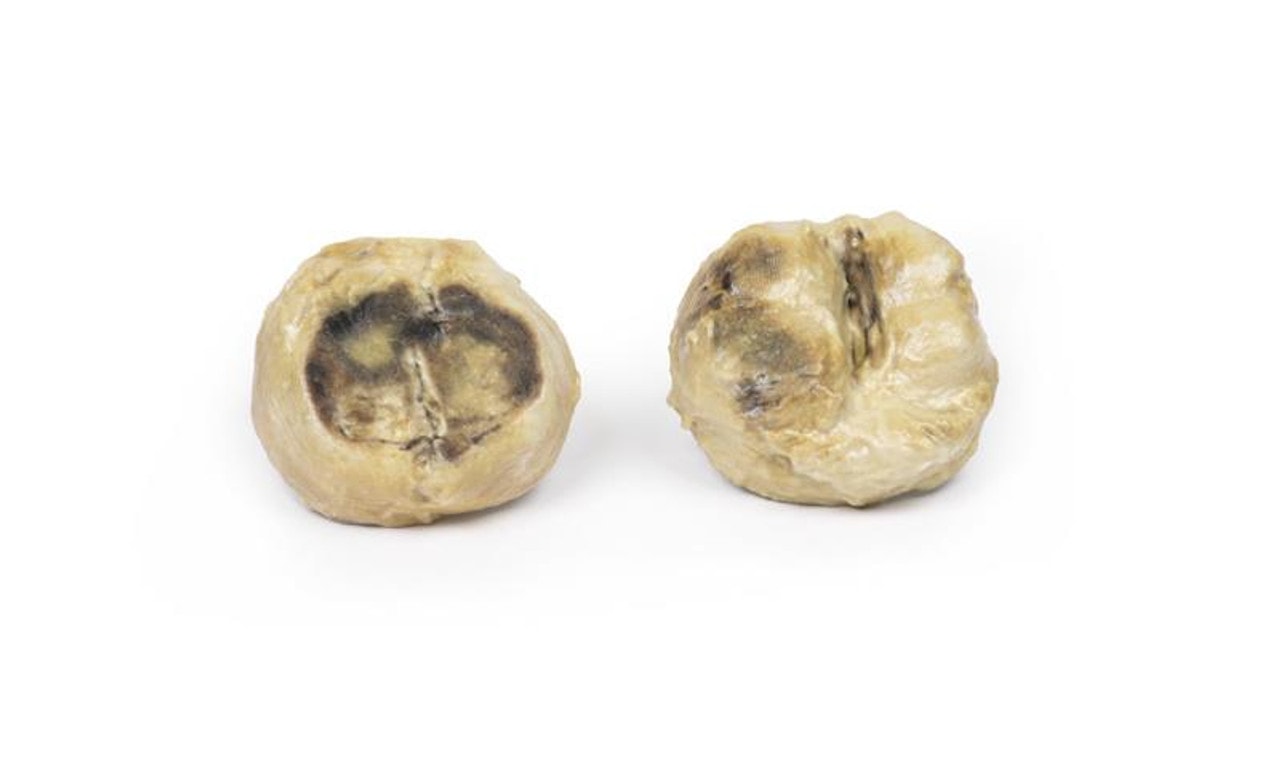
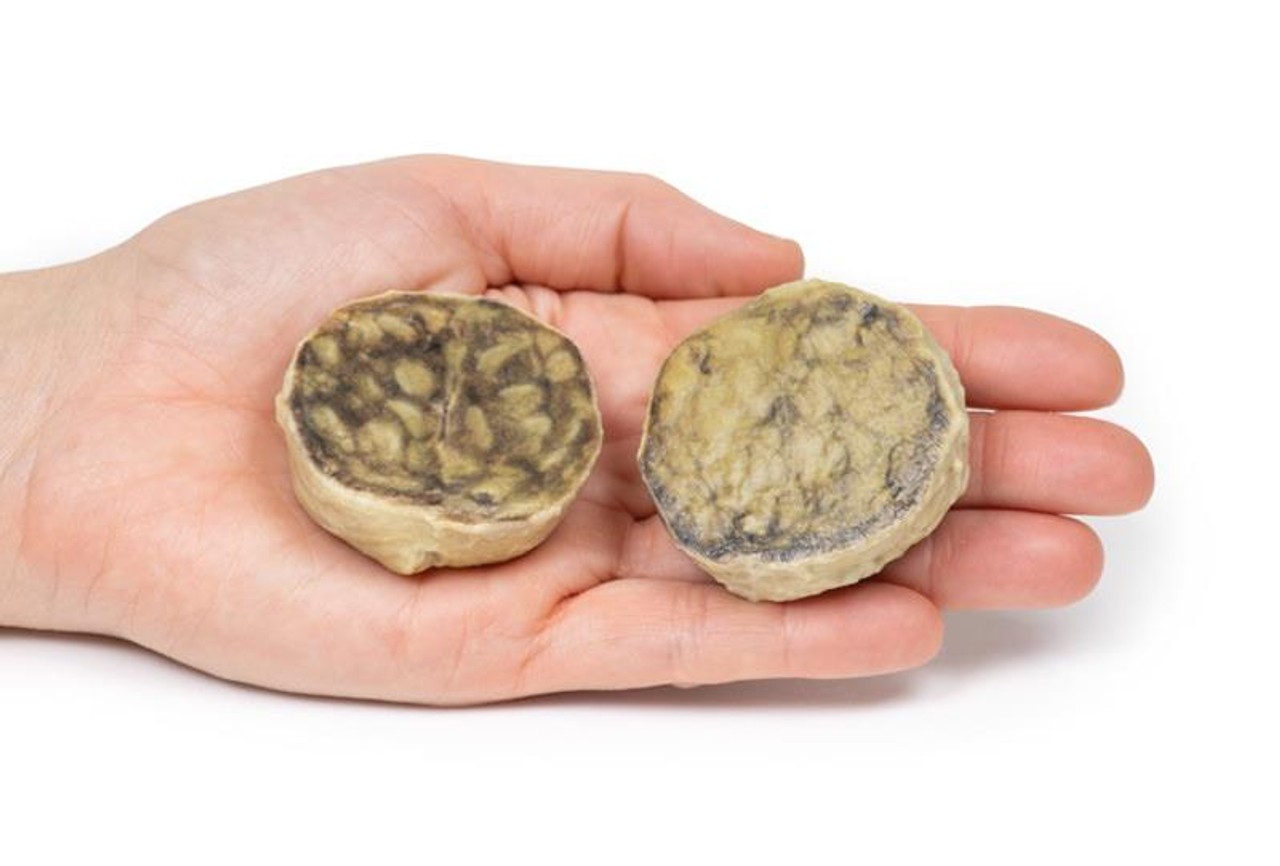
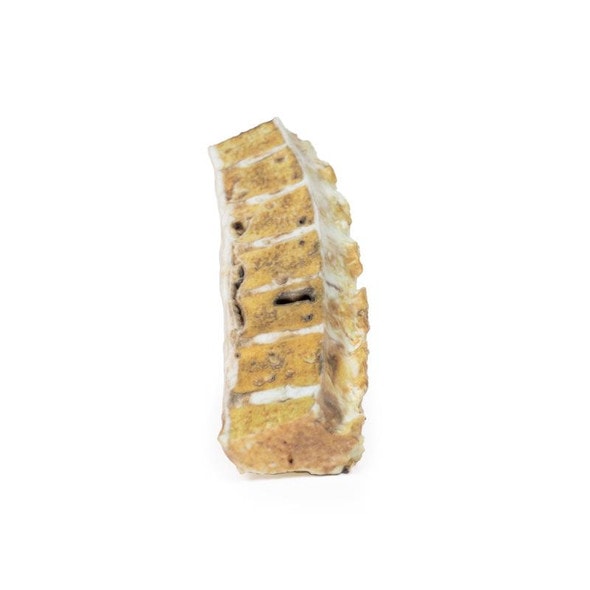
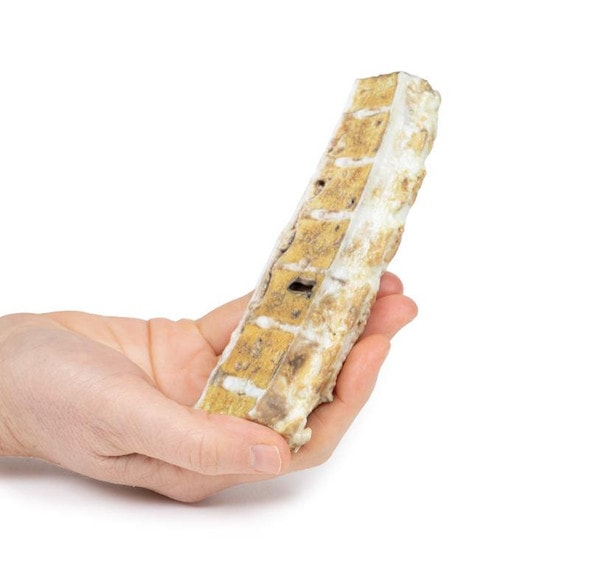
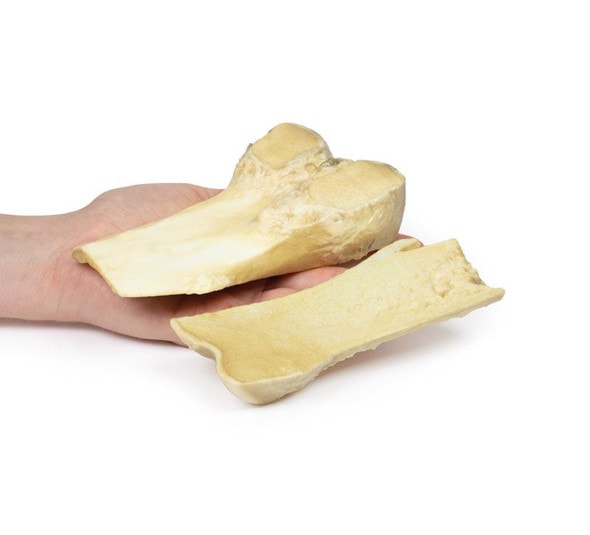
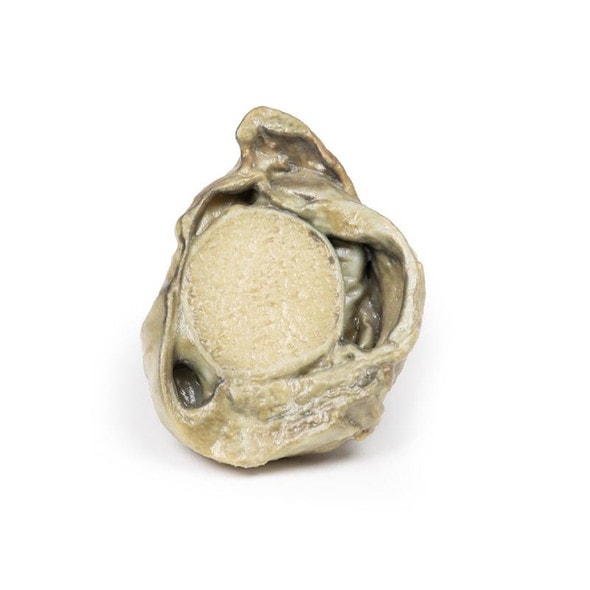
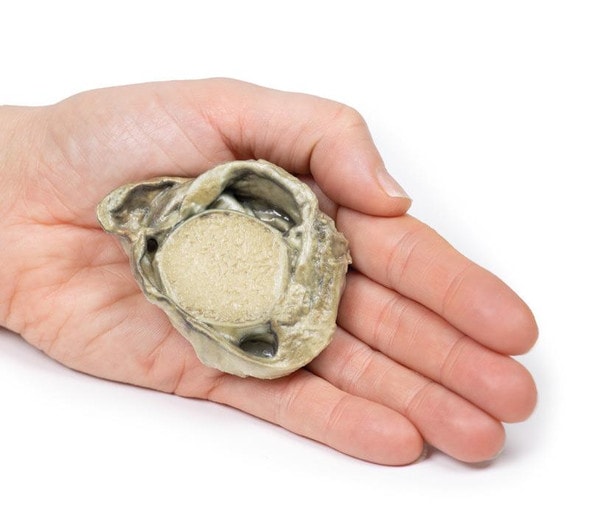
The specimen is an enlarged prostate gland sliced transversely to display the external and cut surfaces, On the cut surface there are numerous nodules varying in size from 2-10mm in diameter. This is an example of benign nodular hyperplasia (BPH) of the prostate gland.
Note
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or nodular hyperplasia of the prostate is a common disease in older men. BPH is caused by nodular hyperplasia of prostatic stromal and glandular epithelial cells primarily in the periurethral prostate. Hyperplasia is a result of accumulation of senescent cells due to impaired cell death and cell proliferation driven by androgens, mainly dihydrotestosterone. Disproportionate enlargement of the median lobe is a common feature of nodular hyperplasia of the prostate. The projecting median lobe may occlude the internal urethral orifice on contraction of the bladder.
Prevalence of BPH increases significantly with age. BPH is present in 20% of males at 40 years of age, 70% of males of 60 year of age and almost 90% of males by the age of 80. There is an increased risk of BPH in men with a positive family history of BPH, in obese males and exposure to exogenous androgenic-anabolic steroids.
Clinical presentation of BPH results from urinary obstructive symptoms. Patients complain of urinary frequency, nocturia, urinary hesitancy, double voiding, poor urinary stream and overflow dribbling. Acute urinary retention may result from complete urinary tract obstruction as in the case discussed above. Post void residual urine results from the obstructing prostate which leads to an increased risk of urinary tract infections.
Diagnosis can be made on clinical history and physical examination of the prostate with a digital rectal exam. Prostate specific antigen may be used to screen for prostate cancer. Ultrasound scan or CT can be used to evaluate the volume of the prostate. Treatment of BPH can be treated medically with Alpha-blockers to relax the prostate smooth muscle tone or 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, which inhibit synthesis of dihydrotesterone. The main surgical treatment for severe cases of BPH is transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). Total prostatectomy is no longer used due to risk of disabling complications.
Advantages of 3D Printed Anatomical Models
- 3D printed anatomical models are the most anatomically accurate examples of human anatomy because they are based on real human specimens.
- Avoid the ethical complications and complex handling, storage, and documentation requirements with 3D printed models when compared to human cadaveric specimens.
- 3D printed anatomy models are far less expensive than real human cadaveric specimens.
- Reproducibility and consistency allow for standardization of education and faster availability of models when you need them.
- Customization options are available for specific applications or educational needs. Enlargement, highlighting of specific anatomical structures, cutaway views, and more are just some of the customizations available.
Disadvantages of Human Cadavers
- Access to cadavers can be problematic and ethical complications are hard to avoid. Many countries cannot access cadavers for cultural and religious reasons.
- Human cadavers are costly to procure and require expensive storage facilities and dedicated staff to maintain them. Maintenance of the facility alone is costly.
- The cost to develop a cadaver lab or plastination technique is extremely high. Those funds could purchase hundreds of easy to handle, realistic 3D printed anatomical replicas.
- Wet specimens cannot be used in uncertified labs. Certification is expensive and time-consuming.
- Exposure to preservation fluids and chemicals is known to cause long-term health problems for lab workers and students. 3D printed anatomical replicas are safe to handle without any special equipment.
- Lack of reuse and reproducibility. If a dissection mistake is made, a new specimen has to be used and students have to start all over again.
Disadvantages of Plastinated Specimens
- Like real human cadaveric specimens, plastinated models are extremely expensive.
- Plastinated specimens still require real human samples and pose the same ethical issues as real human cadavers.
- The plastination process is extensive and takes months or longer to complete. 3D printed human anatomical models are available in a fraction of the time.
- Plastinated models, like human cadavers, are one of a kind and can only showcase one presentation of human anatomy.
Advanced 3D Printing Techniques for Superior Results
- Vibrant color offering with 10 million colors
- UV-curable inkjet printing
- High quality 3D printing that can create products that are delicate, extremely precise, and incredibly realistic
- To improve durability of fragile, thin, and delicate arteries, veins or vessels, a clear support material is printed in key areas. This makes the models robust so they can be handled by students easily.