Description
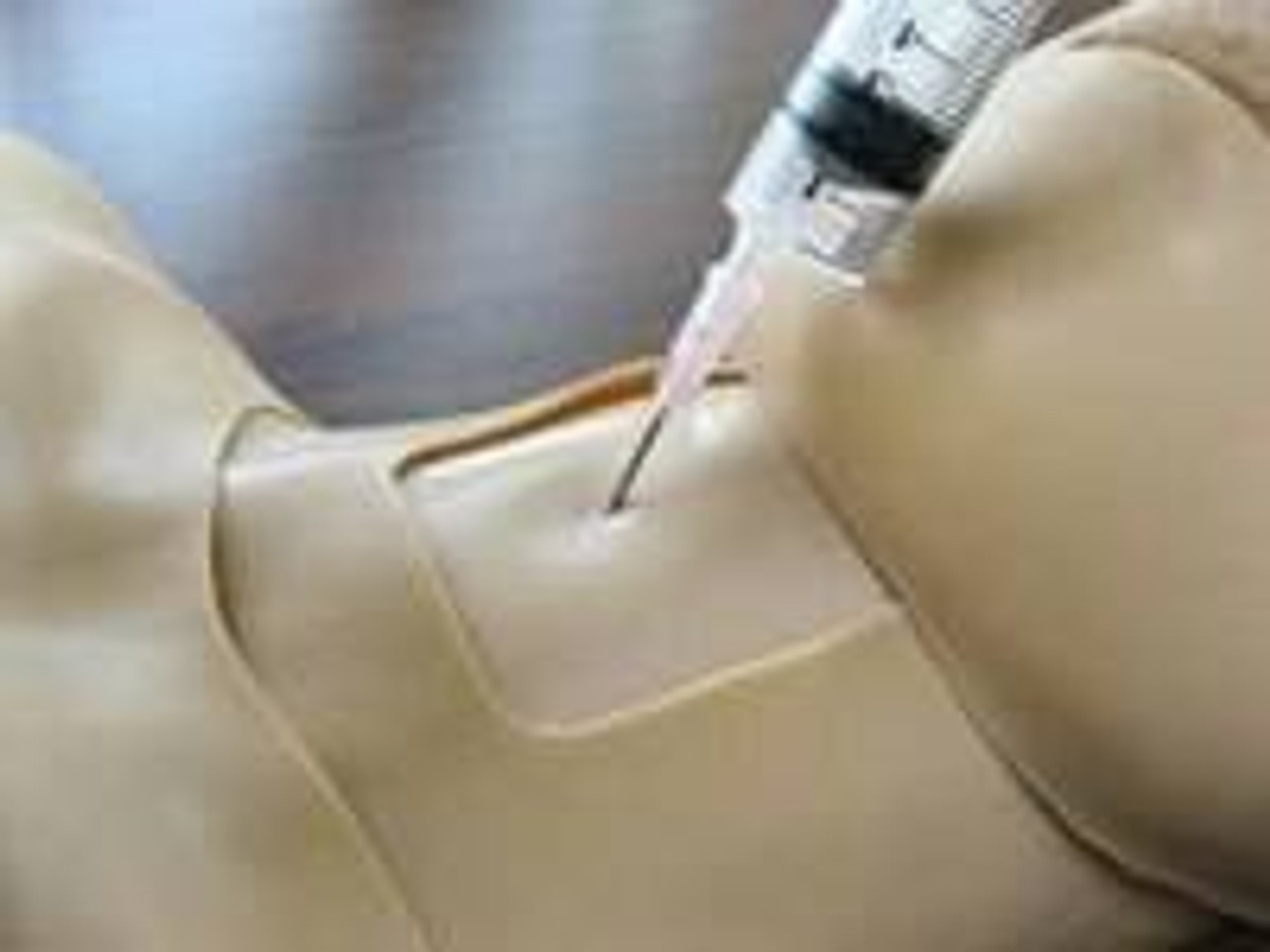
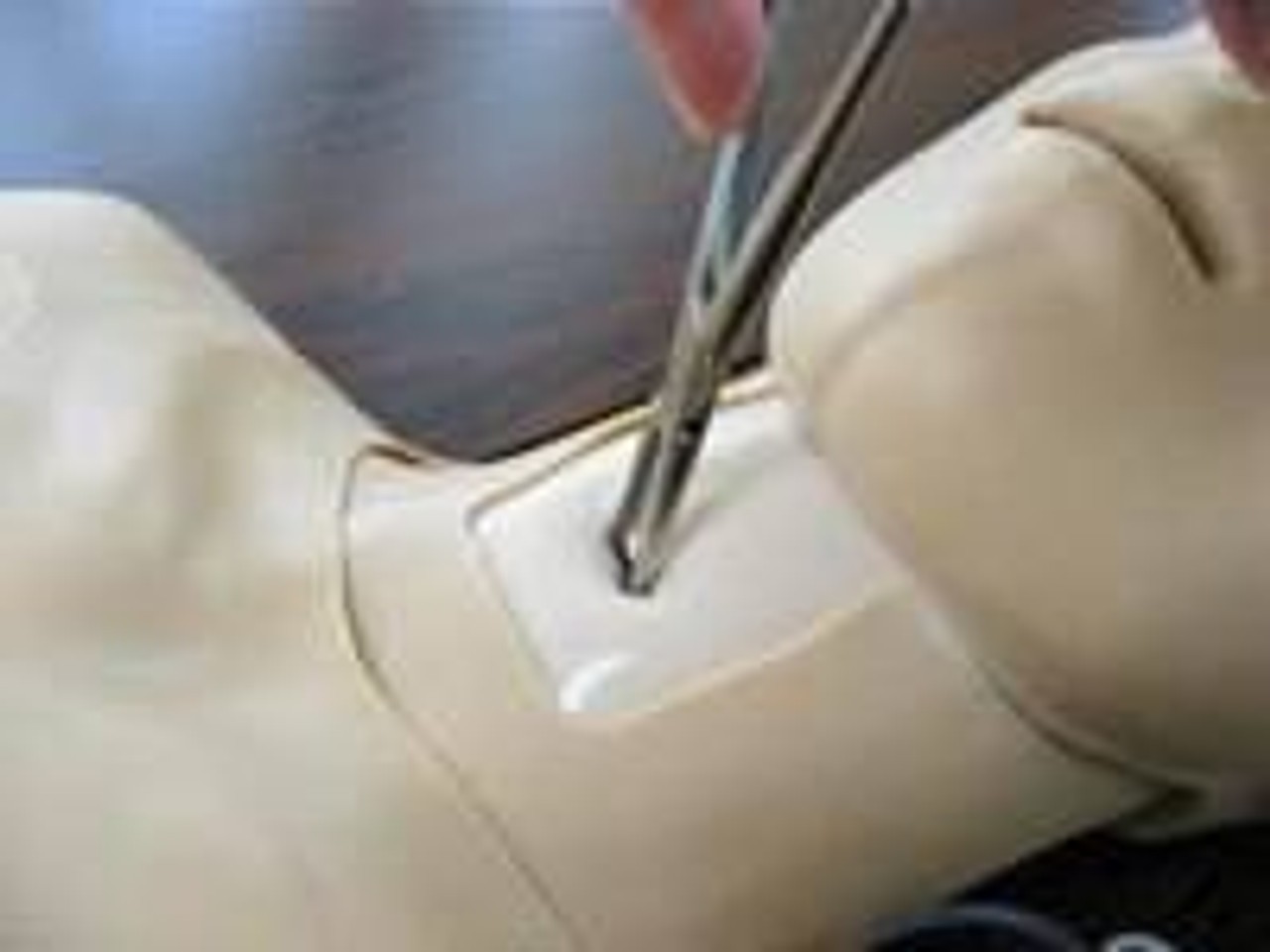
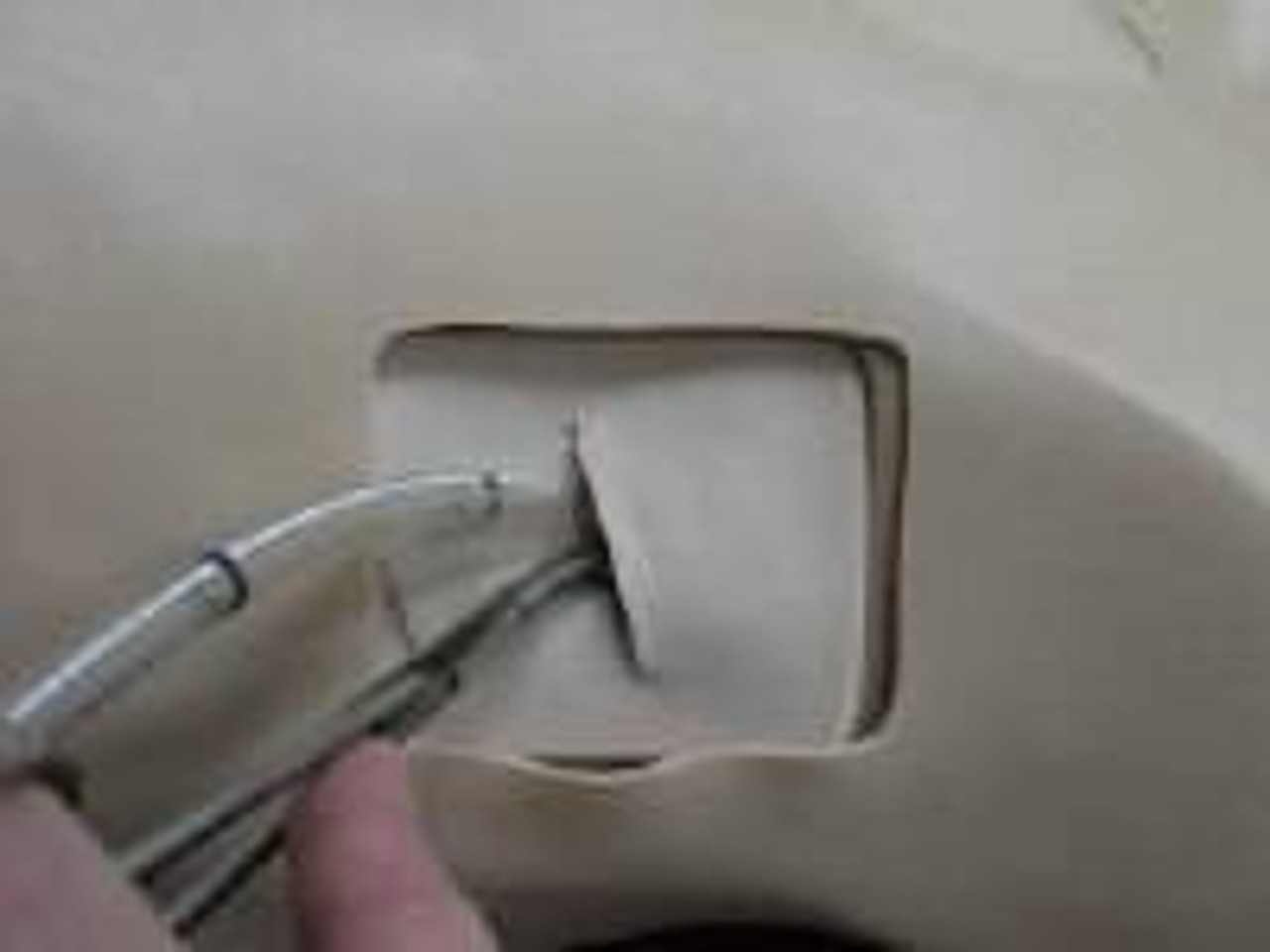
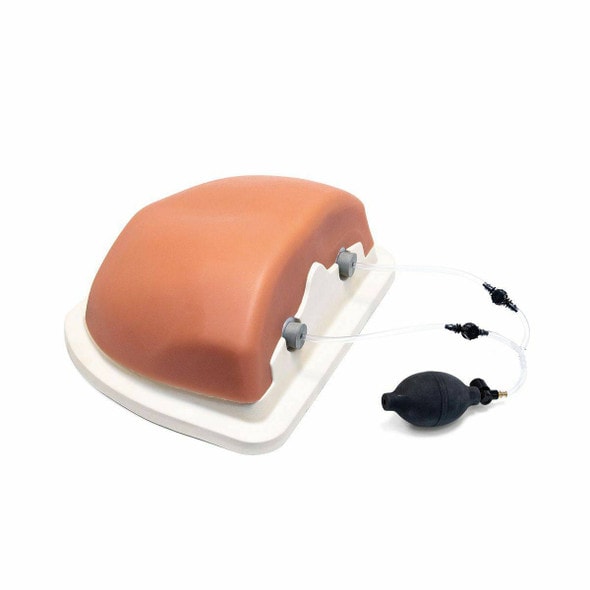
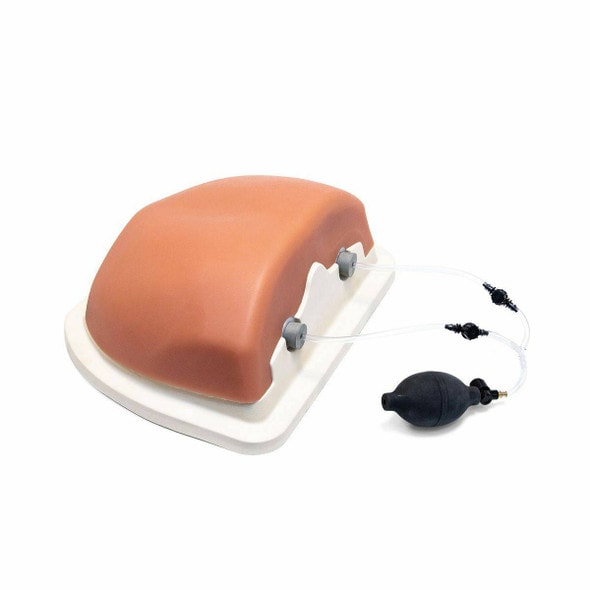
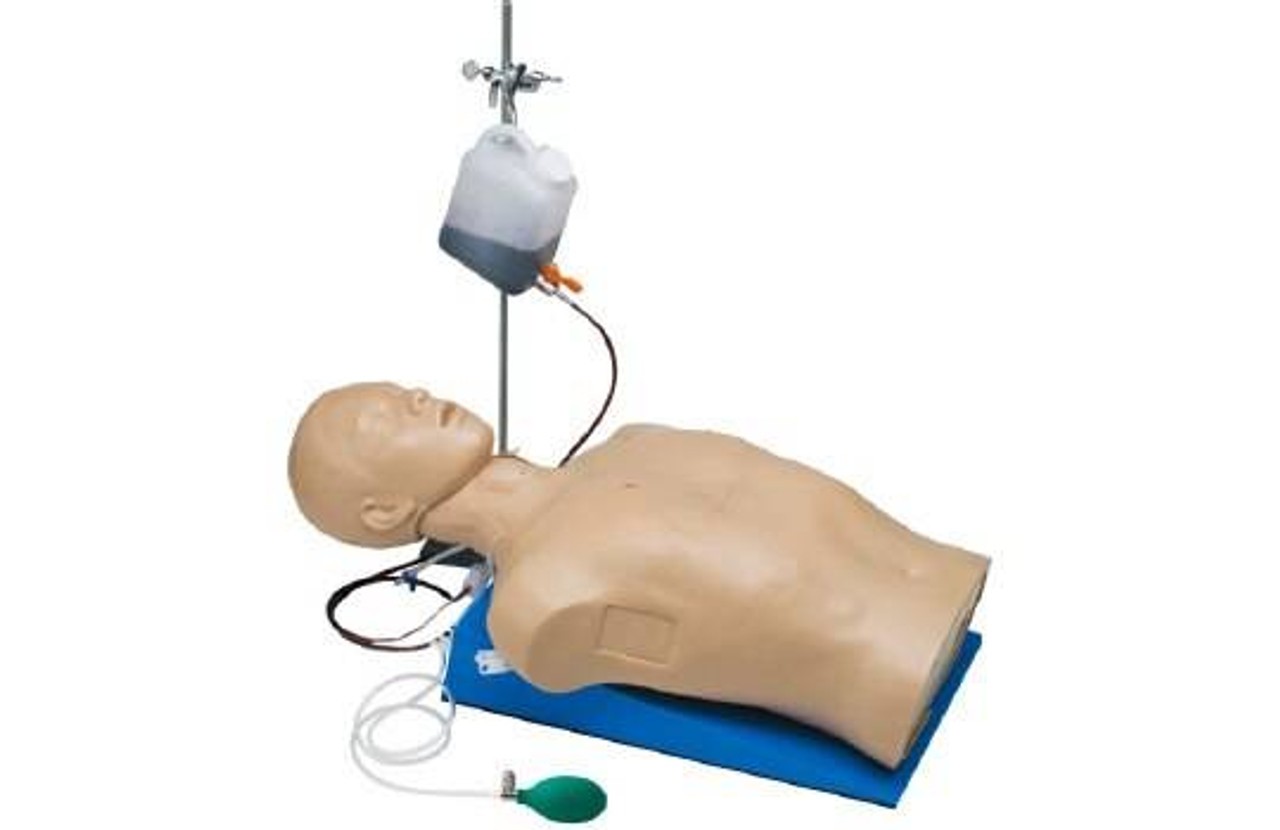
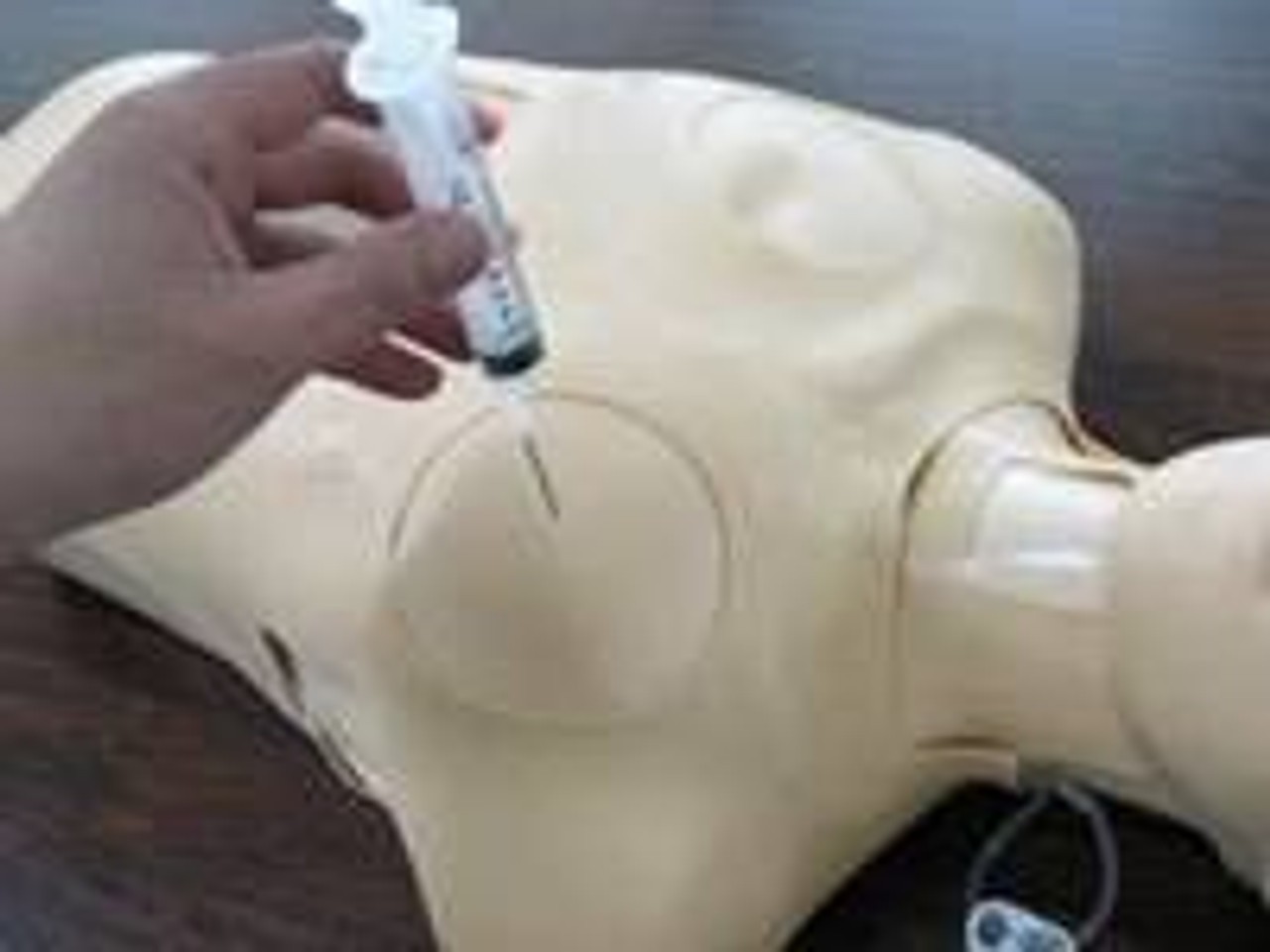
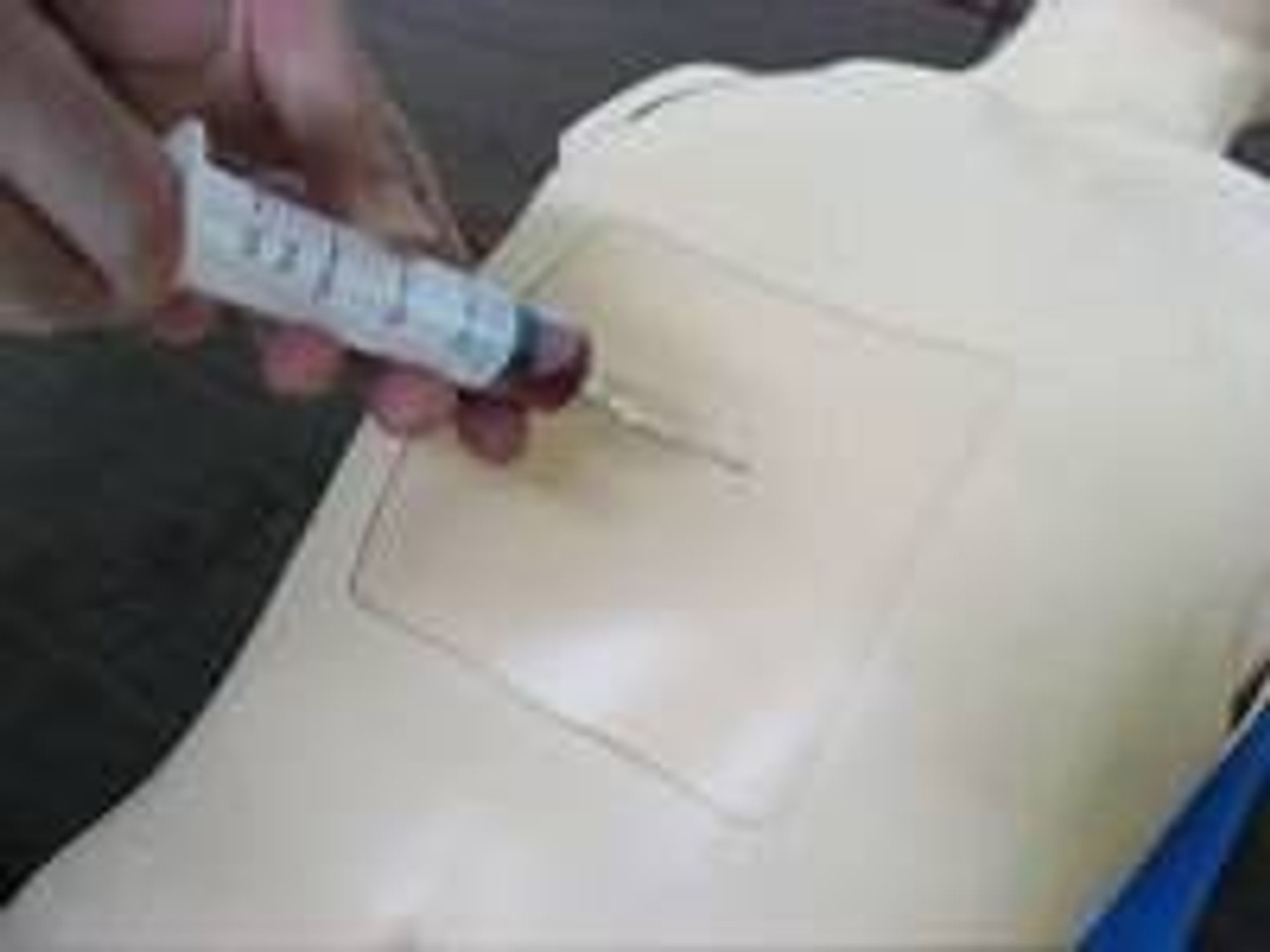
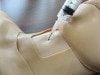
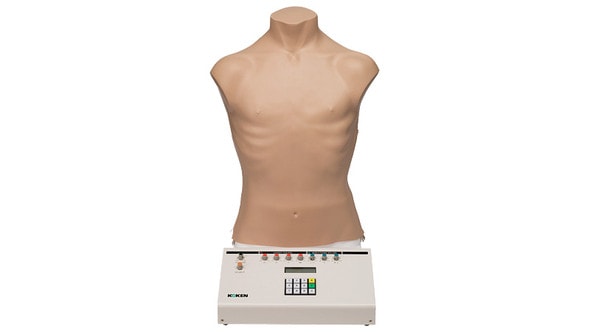
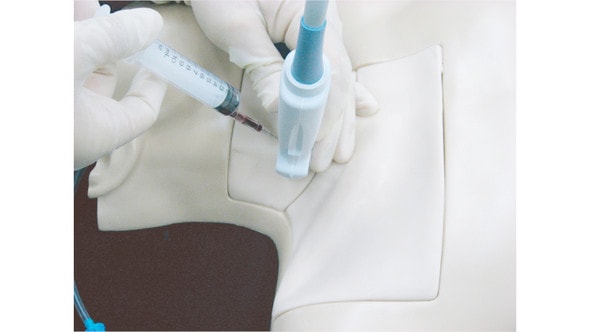
High-energy trauma often consists of multiple injuries, and thoracic trauma can be considered key when determining priority in treatment. This thoracic trauma trainer is a model that combines practice in surgically securing the airway with practice in the treatment of obstructive shock. - Functionality and Features: This model features the ability to puncture and make incisions of the cricothyroid ligament, and through this incision site one can access the airway, cricoid cartilage, and thyroid cartilage. Instructors can attach surgical tape to simulate the cricothyroid ligament. The cricoid cartilage and thyroid cartilage are structured so that they can be opened as a procedure for widening the incision. The skin is made with silicone, giving it a realistic appearance and texture like actual human skin. - Students and instructors can introduce air to create swelling of the left or right side of the chest that could represent tension pneumothorax and subcutaneous emphysema. Distension of the jugular vein can be simulated in conjunction with the swelling of the chest. Sternal angle and second intercostal space are present for use as landmarks for the puncture site. Upon puncture, the air flows out, and the swelling of the chest and distension of the jugular vein subside. When there is a syringe attached to the puncture needle, air pressure will lift the plunger. - Two types of sites are available (one that is uncut, so that an actual incision can be made, and one that is precut for repeated use), and procedures can be carried out on both the left and right sides. Actual insertion of drainage tubes (trocar catheters, etc.) is possible on this model. The fifth and sixth intercostal spaces are present for use as landmarks for the insertion site. - A framework (xiphisternum and costal arch) for identifying the pericardial puncture site is present. Simulated blood can be drawn when a puncture with the correct angle and depth has been made. An error alarm will sound when the angle is incorrect, or the puncture is too deep. Distention of the jugular vein can be simulated.