Description
Developed from real patient case study specimens, the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series introduces an unmatched level of realism in human anatomy models. Each 3D printed anatomy model is a high-fidelity replica of a human cadaveric specimen, focusing on the key morbidity presentations that led to the deceasement of the patient. With advances in 3D printing materials and techniques, these stories can come to life in an ethical, consistently reproduceable, and easy to handle format. Ideal for the most advanced anatomical and pathological study, and backed by authentic case study details, students, instructors, and experts alike will discover a new level of anatomical study with the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series.
Clinical History
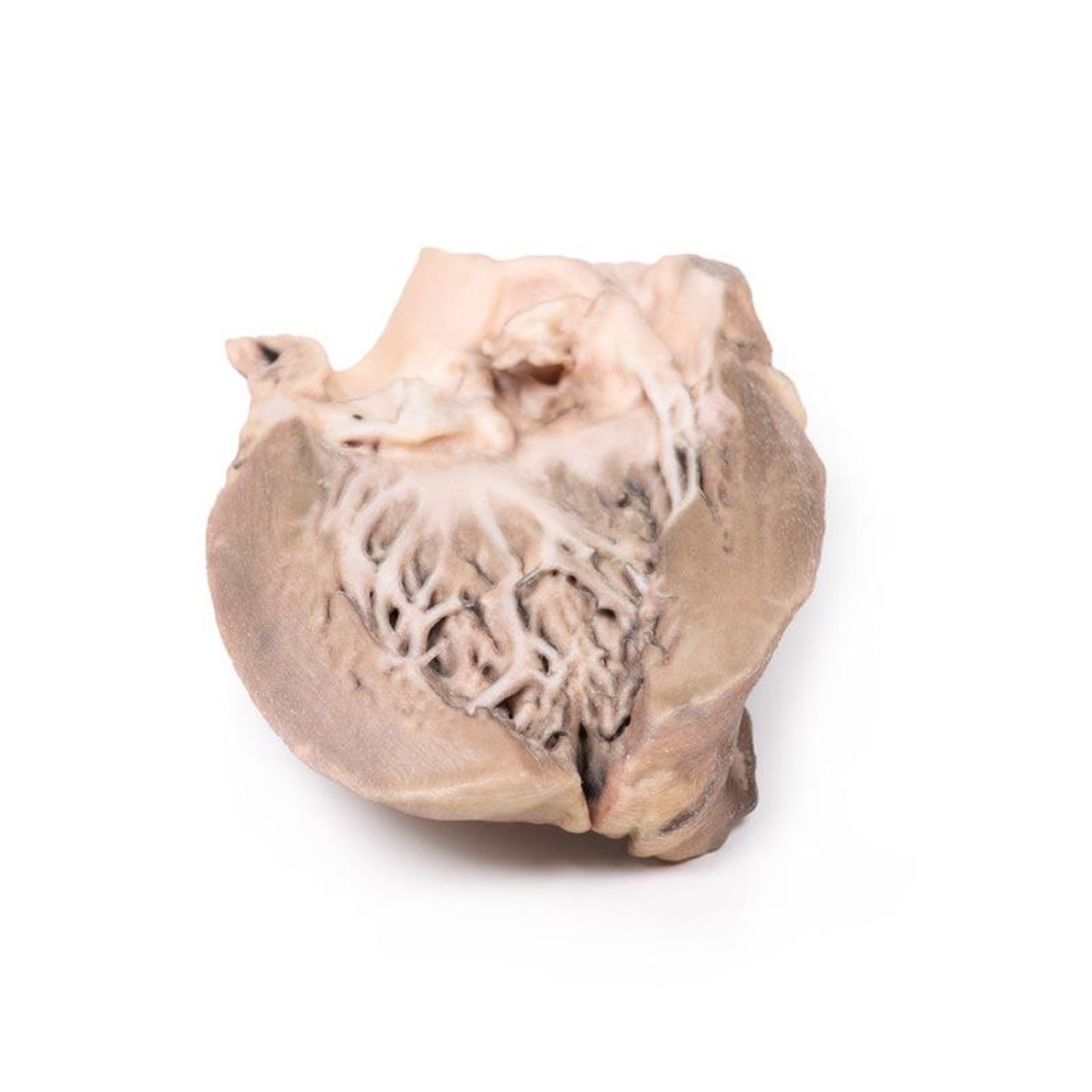
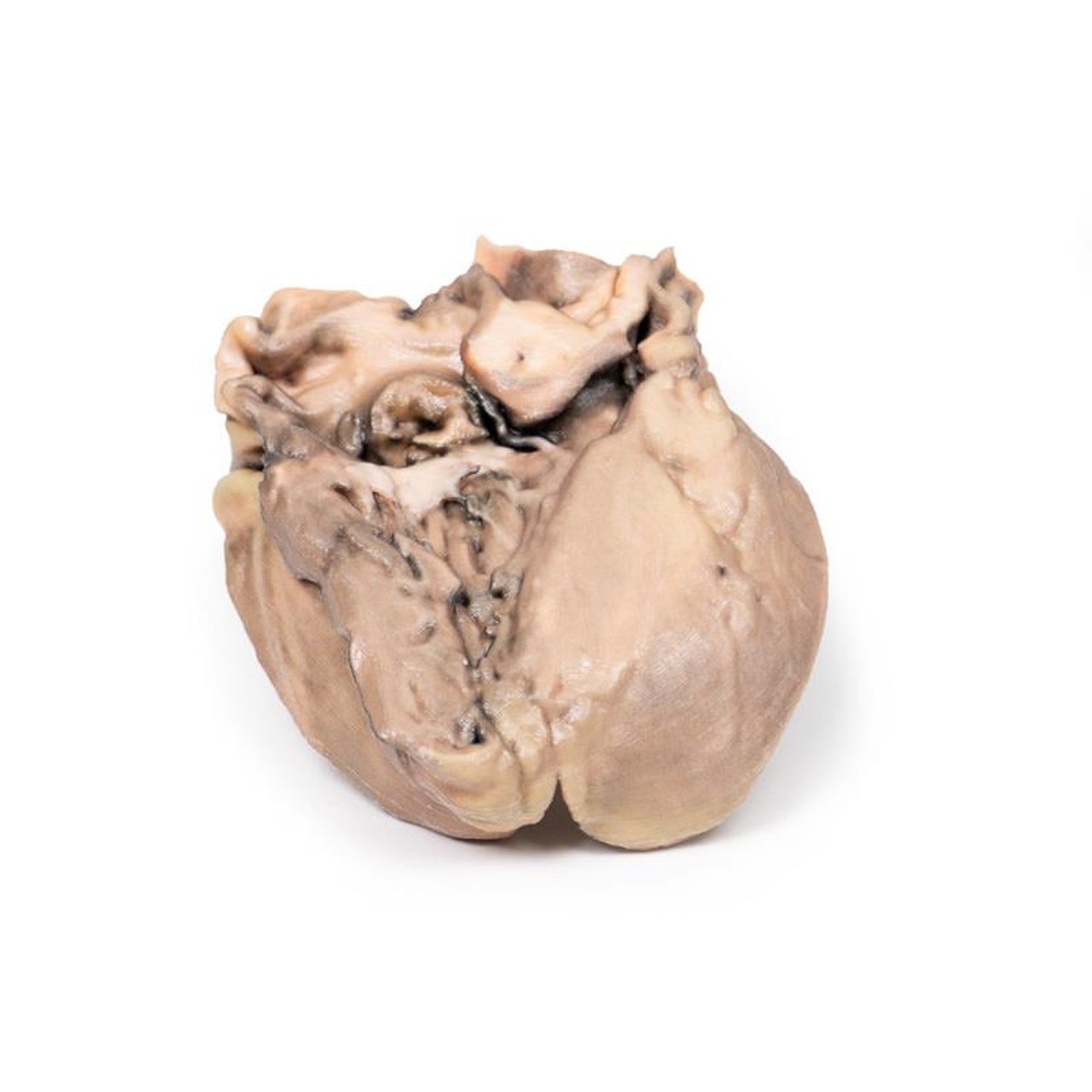
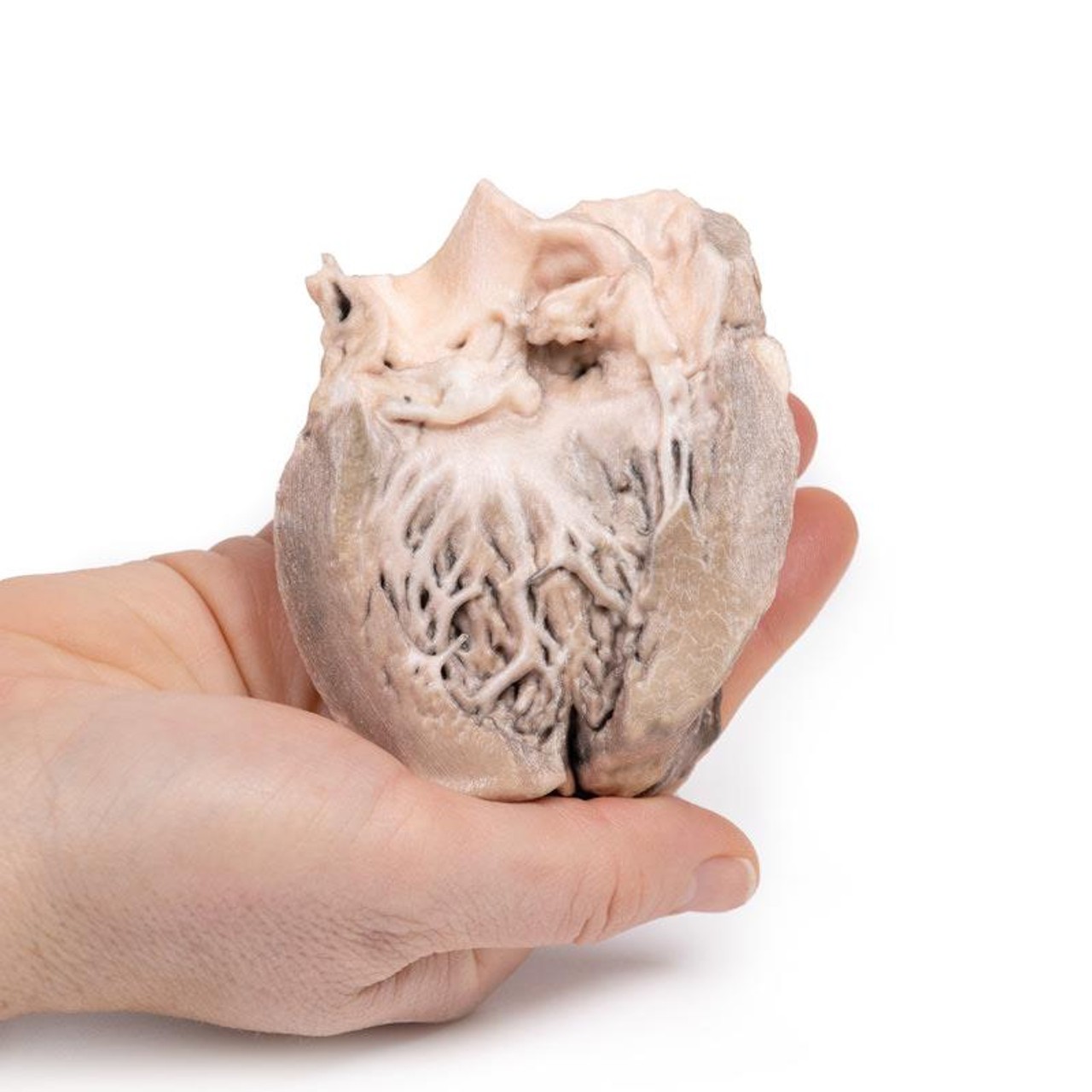
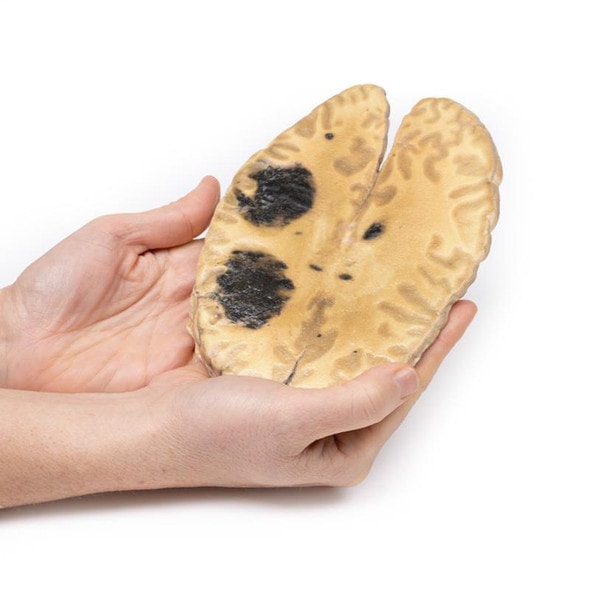
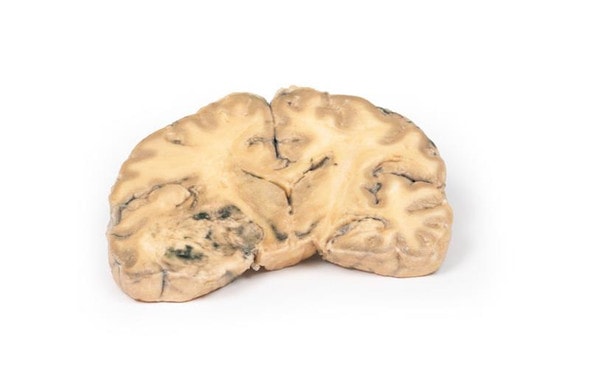
A 15-year old boy with cough and sputum developed a hectic (spiking) fever and chest pain a few days before being admitted in a comatose condition. Examination revealed an early diastolic murmur at the aortic area, which radiated down the left sternal edge. He deteriorated very quickly and died, despite antibiotic chemotherapy. Blood cultures grew Staphylococcus aureus.
Pathology
This small heart displays the left ventricle and associated valves. The non-coronary cusp of the aortic valve is ulcerated and perforated and has friable vegetations attached. Immediately below this cusp a perforation extends into the right atrium just above the tricuspid valve (see back of specimen. The other aortic cusp is also thickened. This is an acute bacterial endocarditis with aortic cusp and atrioventricular perforations.
Further Information
Acute bacterial endocarditis is a form of infective endocarditis. Endocarditis due to fungal infections can also occur although they are rare.
In normal circumstances, the endothelial lining of the heart and valves is relatively resistant to infection by most bacteria or fungi. Therefore, in order for infective endocarditis to occur, there needs to be initial damage or injury to the endocardial tissue. This often results in aggregation of platelets and fibrin, which then become infected, resulting in vegetation formation (i.e. an infective nidus). Staphylococcus aureus, however, is highly virulent and can sometimes infect normal heart valves.
After the initial platelet-fibrin aggregation, there is further activation of the coagulating system via the extrinsic clotting pathway and initiation of the inflammatory response via monocytes, resulting in further growth of the vegetation/thrombus. The microbial growth tends to occur within the fibrin matrix, which makes it difficult for the immune responses to eradicate the infection. An additional problem is that these infected thombi can also embolize causing distant sites of infection in smaller capillaries (e.g. in the kidney).
Risk factors for developing an infective endocarditis include valvular heart disease, such as previous rheumatic heart disease, congenital heart disease (e.g. ventricular septal defect or bicuspid aortic valve), prosthetic heart valves or any previous invasive cardiac procedures. Anti-thrombotic medications e.g. heparin or aspirin may have to be administered in patients at risk. Diagnosis is initially made by clinical examination followed by pathology (blood cultures) and diagnostic imaging. Transthoracic echocardiogram is often first line, followed by transoesophageal echocardiogram. Treatment includes antimicrobial therapy, anti-coagulants, and in some complicated cases, surgical intervention such as valve surgery.
Advantages of 3D Printed Anatomical Models
- 3D printed anatomical models are the most anatomically accurate examples of human anatomy because they are based on real human specimens.
- Avoid the ethical complications and complex handling, storage, and documentation requirements with 3D printed models when compared to human cadaveric specimens.
- 3D printed anatomy models are far less expensive than real human cadaveric specimens.
- Reproducibility and consistency allow for standardization of education and faster availability of models when you need them.
- Customization options are available for specific applications or educational needs. Enlargement, highlighting of specific anatomical structures, cutaway views, and more are just some of the customizations available.
Disadvantages of Human Cadavers
- Access to cadavers can be problematic and ethical complications are hard to avoid. Many countries cannot access cadavers for cultural and religious reasons.
- Human cadavers are costly to procure and require expensive storage facilities and dedicated staff to maintain them. Maintenance of the facility alone is costly.
- The cost to develop a cadaver lab or plastination technique is extremely high. Those funds could purchase hundreds of easy to handle, realistic 3D printed anatomical replicas.
- Wet specimens cannot be used in uncertified labs. Certification is expensive and time-consuming.
- Exposure to preservation fluids and chemicals is known to cause long-term health problems for lab workers and students. 3D printed anatomical replicas are safe to handle without any special equipment.
- Lack of reuse and reproducibility. If a dissection mistake is made, a new specimen has to be used and students have to start all over again.
Disadvantages of Plastinated Specimens
- Like real human cadaveric specimens, plastinated models are extremely expensive.
- Plastinated specimens still require real human samples and pose the same ethical issues as real human cadavers.
- The plastination process is extensive and takes months or longer to complete. 3D printed human anatomical models are available in a fraction of the time.
- Plastinated models, like human cadavers, are one of a kind and can only showcase one presentation of human anatomy.
Advanced 3D Printing Techniques for Superior Results
- Vibrant color offering with 10 million colors
- UV-curable inkjet printing
- High quality 3D printing that can create products that are delicate, extremely precise, and incredibly realistic
- To improve durability of fragile, thin, and delicate arteries, veins or vessels, a clear support material is printed in key areas. This makes the models robust so they can be handled by students easily.