Description
Developed from real patient case study specimens, the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series introduces an unmatched level of realism in human anatomy models. Each 3D printed anatomy model is a high-fidelity replica of a human cadaveric specimen, focusing on the key morbidity presentations that led to the deceasement of the patient. With advances in 3D printing materials and techniques, these stories can come to life in an ethical, consistently reproduceable, and easy to handle format. Ideal for the most advanced anatomical and pathological study, and backed by authentic case study details, students, instructors, and experts alike will discover a new level of anatomical study with the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series.
Clinical History
A 5-year old male presents with a history of constipation since birth. A barium enema showed a constricted rectum with a dilated sigmoid colon. Surgical resection of constricted section of bowl was attempted but the patient died during the surgery.
Pathology
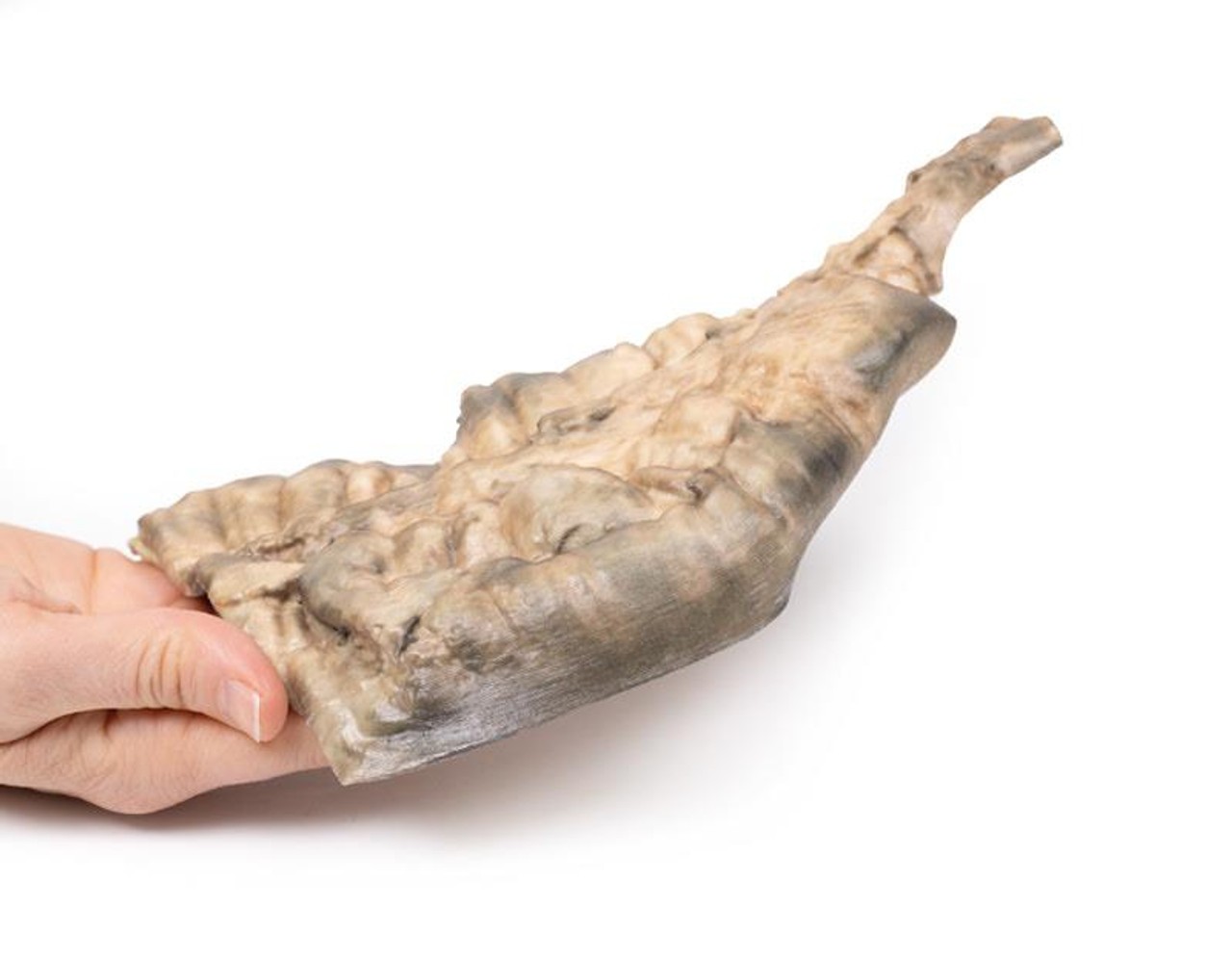
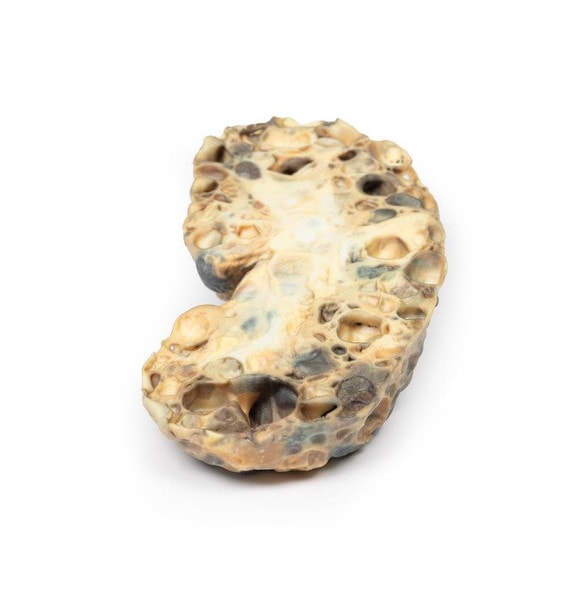
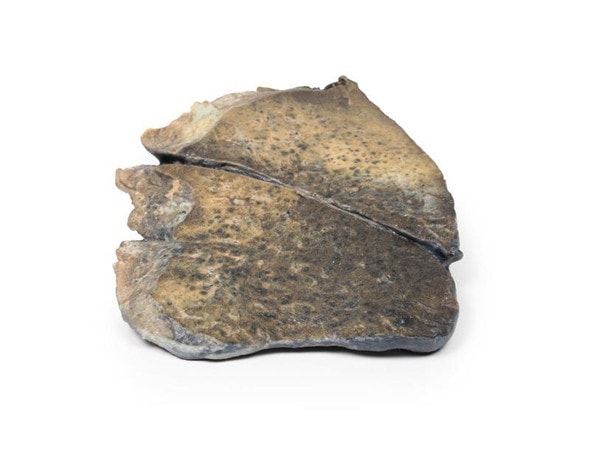
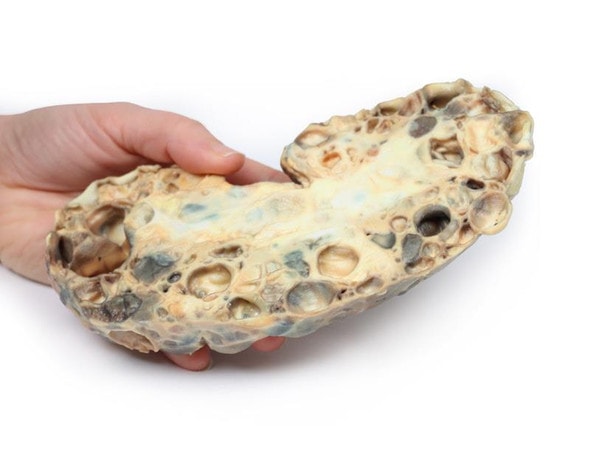
This postmortem section of sigmoid colon has been opened to display the internal surface shown here. There is large dilation of the proximal section of bowel (sigmoid ) with loss of the normal mucosal pattern. The distal section of bowel (rectum) has a normal diameter and a normal mucosal pattern but an absence of ganglion cells in the myenteric plexus. This is an example of Hirschsprung's disease, also known as congenital aganglionic megacolon.
Further Information
Hirschsprung's disease is characterized by lack of coordinated peristaltic contraction in a segment of bowel, due to a lack of parasympathetic ganglia. It mainly affects the rectum but the length of the aganglionic sections vary. It is caused by defective proximal to distal migration of neural crest cells from the caecum to rectum during embryogenesis, which leads to development of a distal bowel segment lacking both a myenteric and submucosal plexus. This causes an obstruction with hypertrophy and dilation of the proximal normally innervated colon, which can lead to perforation, peritonitis, enterocolitis and electrolyte imbalances.
It occurs in 1 in 5000 live births. It is more common in males, those with siblings with Hirschsprung's disease and those with other developmental disorders, such as Down Syndrome. Mutations in the receptor tyrosine kinase RET, which is necessary for neural crest cell migration, account for a majority of the familiar cases and 15% of the sporadic cases.
Patients typically present with failure to pass meconium within 48 hours of birth. Less severe cases present later with chronic constipation, vomiting, abdominal pain and distension. Treatment involves resection of the aganglionic section of bowel with anastomosis of the normal sections of bowel to the rectum.
Advantages of 3D Printed Anatomical Models
- 3D printed anatomical models are the most anatomically accurate examples of human anatomy because they are based on real human specimens.
- Avoid the ethical complications and complex handling, storage, and documentation requirements with 3D printed models when compared to human cadaveric specimens.
- 3D printed anatomy models are far less expensive than real human cadaveric specimens.
- Reproducibility and consistency allow for standardization of education and faster availability of models when you need them.
- Customization options are available for specific applications or educational needs. Enlargement, highlighting of specific anatomical structures, cutaway views, and more are just some of the customizations available.
Disadvantages of Human Cadavers
- Access to cadavers can be problematic and ethical complications are hard to avoid. Many countries cannot access cadavers for cultural and religious reasons.
- Human cadavers are costly to procure and require expensive storage facilities and dedicated staff to maintain them. Maintenance of the facility alone is costly.
- The cost to develop a cadaver lab or plastination technique is extremely high. Those funds could purchase hundreds of easy to handle, realistic 3D printed anatomical replicas.
- Wet specimens cannot be used in uncertified labs. Certification is expensive and time-consuming.
- Exposure to preservation fluids and chemicals is known to cause long-term health problems for lab workers and students. 3D printed anatomical replicas are safe to handle without any special equipment.
- Lack of reuse and reproducibility. If a dissection mistake is made, a new specimen has to be used and students have to start all over again.
Disadvantages of Plastinated Specimens
- Like real human cadaveric specimens, plastinated models are extremely expensive.
- Plastinated specimens still require real human samples and pose the same ethical issues as real human cadavers.
- The plastination process is extensive and takes months or longer to complete. 3D printed human anatomical models are available in a fraction of the time.
- Plastinated models, like human cadavers, are one of a kind and can only showcase one presentation of human anatomy.
Advanced 3D Printing Techniques for Superior Results
- Vibrant color offering with 10 million colors
- UV-curable inkjet printing
- High quality 3D printing that can create products that are delicate, extremely precise, and incredibly realistic
- To improve durability of fragile, thin, and delicate arteries, veins or vessels, a clear support material is printed in key areas. This makes the models robust so they can be handled by students easily.