Description
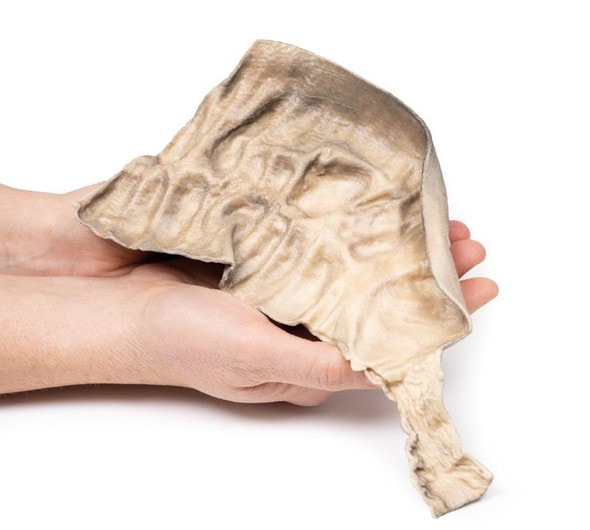
Developed from real patient case study specimens, the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series introduces an unmatched level of realism in human anatomy models. Each 3D printed anatomy model is a high-fidelity replica of a human cadaveric specimen, focusing on the key morbidity presentations that led to the deceasement of the patient. With advances in 3D printing materials and techniques, these stories can come to life in an ethical, consistently reproduceable, and easy to handle format. Ideal for the most advanced anatomical and pathological study, and backed by authentic case study details, students, instructors, and experts alike will discover a new level of anatomical study with the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series.
Clinical History
A 40-year old male attends his GP complaining of 2 weeks of hematuria and new onset of headache with blurred vision. His GP notes a blood pressure of 260/110 and refers the patient to hospital. The patient collapses on arrival to hospital. A CT brain shows a large subarachnoid hemorrhage from a ruptured berry aneurysm. The patient dies shortly after admission.
Pathology
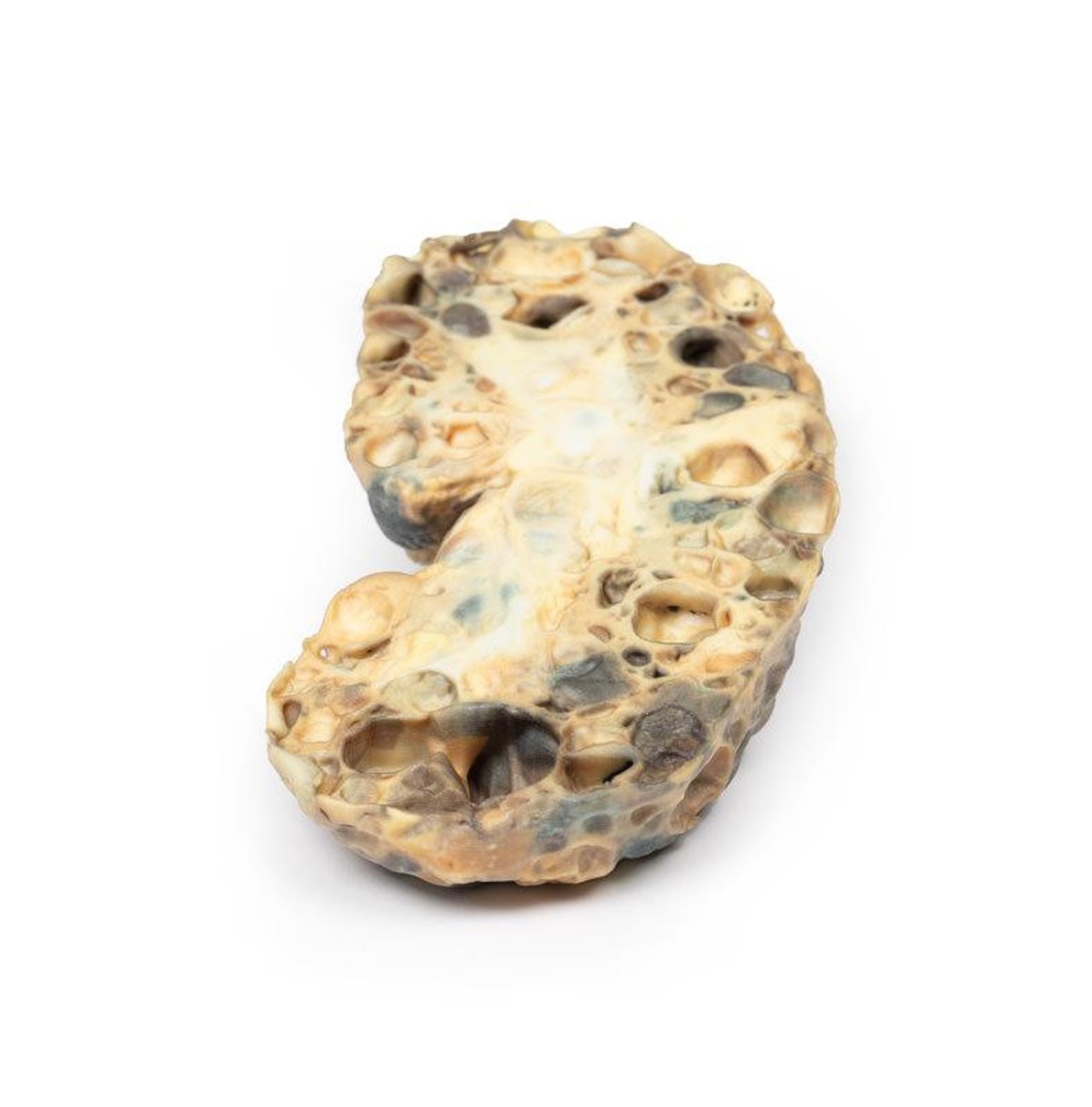
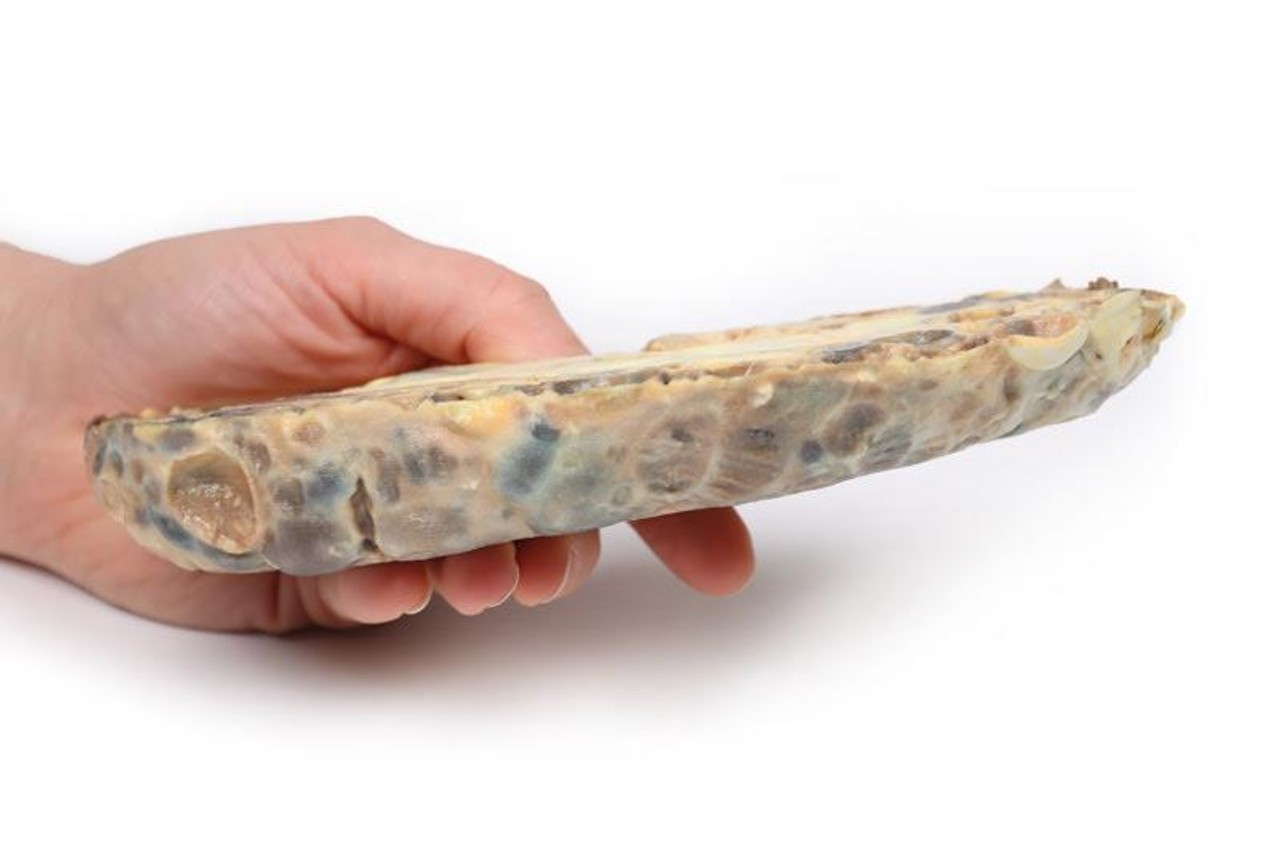
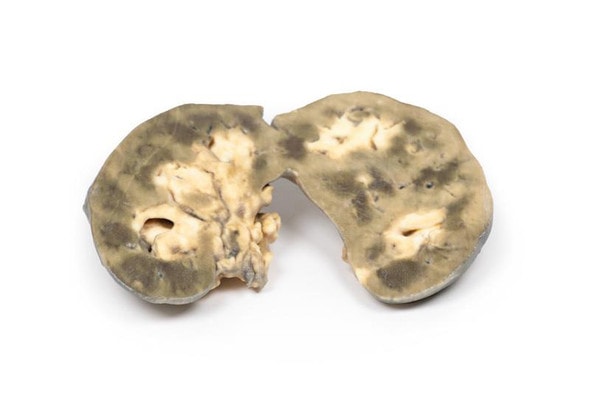
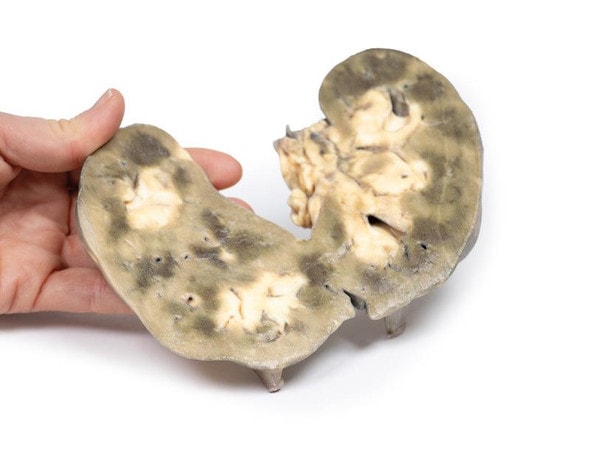
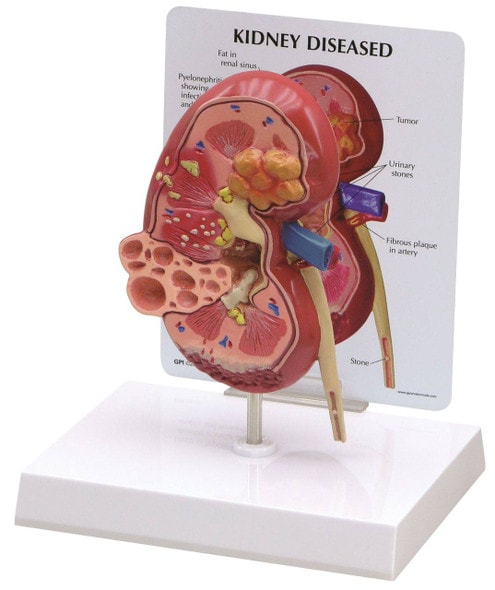
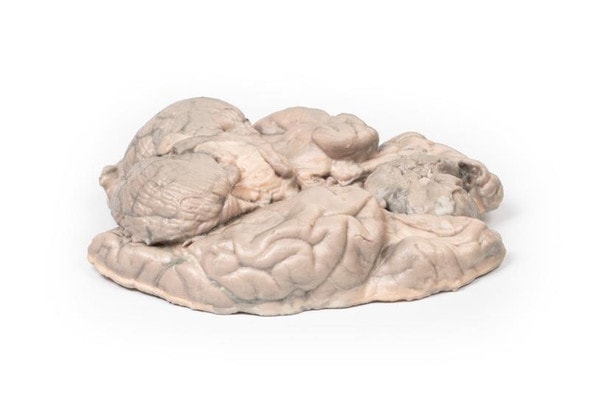
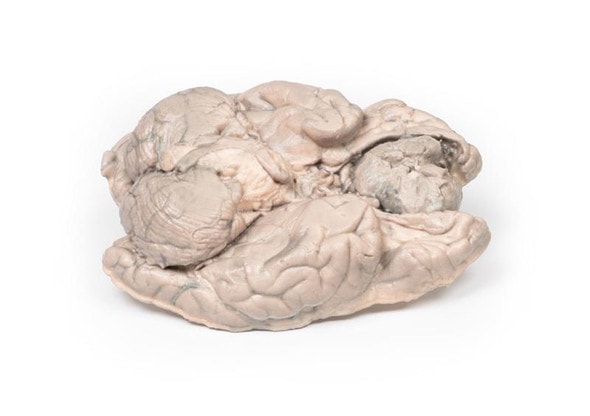
The specimen is an enlarged kidney. The renal parenchyma has been almost completely replaced by numerous dilated cysts varying in size, up to 3cm in diameter. The cysts have thin translucent walls, and some cysts contain material of varying colors, giving a marble-like appearance to the cut surface of the kidney. The varying colors are caused by the secretions within the cysts, which may be admixed with hemorrhage. The external surface appears lobulated as a result of multiple projecting cysts. Any remaining renal parenchyma is severely atrophic caused by the pressure of the numerous cysts. This is an example of adult polycystic kidney disease.
Further Information
Adult polycystic kidney disease (APKD) is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by the presence of multiple cysts within the renal parenchyma. The cysts develop from altered renal tubule epithelium. The cysts expand destroying the glomeruli, causing ischemia, pressure atrophy, and eventually leading to renal failure.
APKD occurs in 1 in 40 to 1000 live births. Mutations in the PKD1 gene on chromosome 16p13.3 and PKD2 gene on chromosome 4q21 have been described as causal mutations. These code for membrane proteins polycystin 1 and 2, respectively. Patients with PKD1 mutation are more common and have a more severe phenotype. End stage renal disease (ESRD) occurs at a mean age of 74.0 in PKD2 versus 54.3 years in PKD1.
Common symptoms of APKD include hematuria from hemorrhage into cysts and pain or a sensation of dragging from the expansion of cysts and kidney enlargement. Many patients remain asymptomatic until features of renal failure occur such as proteinuria, polyuria, hypertension and uremia. Extrarenal manifestations of the disease include intracranial berry aneurysms, hepatic and pancreatic cysts, as well as mitral valve prolapse and other types of cardiac valve disease. Renal ultrasound is the most common investigation used to diagnose APKD. CT- and MRI scans may also be used as diagnostic tools. Patients with a positive family history of APKD can be offered screening renal US scans and genetic testing in some cases. Treatment involves renal replacement therapy for ESRD and renal transplant (if a donor can be found).
Ultimately, over one-third of patients die from renal failure and one-third from coronary or hypertensive heart disease. Approximately 1% of patients die from subarachnoid hemorrhage, because of berry aneurysm rupture (as in this case). Remaining deaths are due to unrelated causes.
Advantages of 3D Printed Anatomical Models
- 3D printed anatomical models are the most anatomically accurate examples of human anatomy because they are based on real human specimens.
- Avoid the ethical complications and complex handling, storage, and documentation requirements with 3D printed models when compared to human cadaveric specimens.
- 3D printed anatomy models are far less expensive than real human cadaveric specimens.
- Reproducibility and consistency allow for standardization of education and faster availability of models when you need them.
- Customization options are available for specific applications or educational needs. Enlargement, highlighting of specific anatomical structures, cutaway views, and more are just some of the customizations available.
Disadvantages of Human Cadavers
- Access to cadavers can be problematic and ethical complications are hard to avoid. Many countries cannot access cadavers for cultural and religious reasons.
- Human cadavers are costly to procure and require expensive storage facilities and dedicated staff to maintain them. Maintenance of the facility alone is costly.
- The cost to develop a cadaver lab or plastination technique is extremely high. Those funds could purchase hundreds of easy to handle, realistic 3D printed anatomical replicas.
- Wet specimens cannot be used in uncertified labs. Certification is expensive and time-consuming.
- Exposure to preservation fluids and chemicals is known to cause long-term health problems for lab workers and students. 3D printed anatomical replicas are safe to handle without any special equipment.
- Lack of reuse and reproducibility. If a dissection mistake is made, a new specimen has to be used and students have to start all over again.
Disadvantages of Plastinated Specimens
- Like real human cadaveric specimens, plastinated models are extremely expensive.
- Plastinated specimens still require real human samples and pose the same ethical issues as real human cadavers.
- The plastination process is extensive and takes months or longer to complete. 3D printed human anatomical models are available in a fraction of the time.
- Plastinated models, like human cadavers, are one of a kind and can only showcase one presentation of human anatomy.
Advanced 3D Printing Techniques for Superior Results
- Vibrant color offering with 10 million colors
- UV-curable inkjet printing
- High quality 3D printing that can create products that are delicate, extremely precise, and incredibly realistic
- To improve durability of fragile, thin, and delicate arteries, veins or vessels, a clear support material is printed in key areas. This makes the models robust so they can be handled by students easily.