Description
Developed from real patient case study specimens, the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series introduces an unmatched level of realism in human anatomy models. Each 3D printed anatomy model is a high-fidelity replica of a human cadaveric specimen, focusing on the key morbidity presentations that led to the deceasement of the patient. With advances in 3D printing materials and techniques, these stories can come to life in an ethical, consistently reproduceable, and easy to handle format. Ideal for the most advanced anatomical and pathological study, and backed by authentic case study details, students, instructors, and experts alike will discover a new level of anatomical study with the 3D printed anatomy model pathology series.
Clinical History
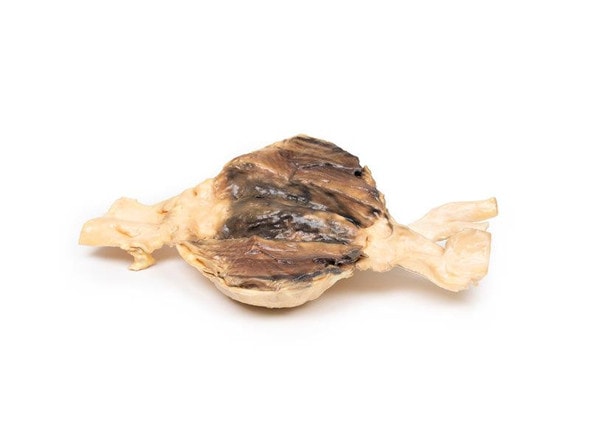
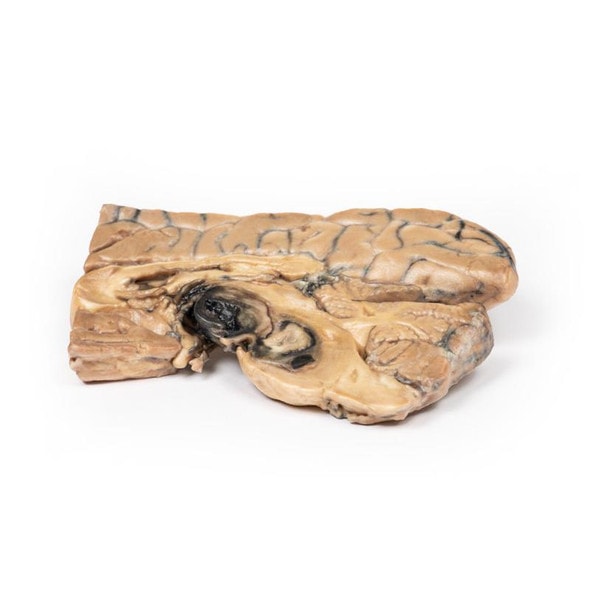
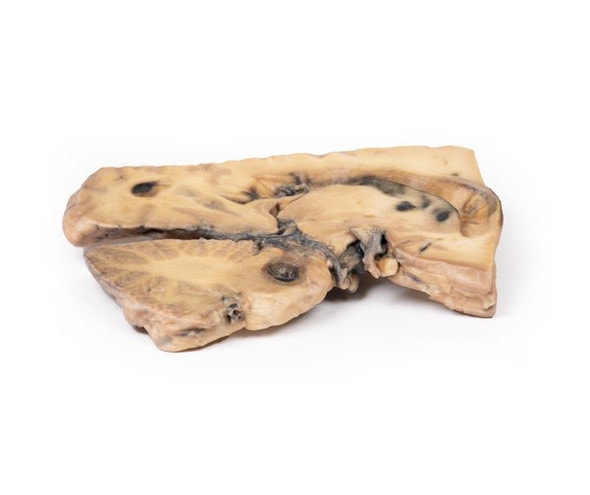
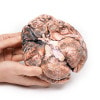
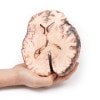
Five days before admission this 38-year old female experienced the sudden onset of pain behind the right eye, associated with a slow development of weakness of the left leg. Examination disclosed left-hemiparesis in a confused hypertensive female. There was also a right homonymous hemianopia and a right VI cranial nerve weakness. Clonus was present at ankle and knee on the left, and the left plantar reflex was upgoing. Lumbar puncture showed a raised pressure and the fluid was blood-stained. Angiography revealed an intracerebral aneurysm. This was clipped at operation but the day following operation the patient died suddenly.
Pathology
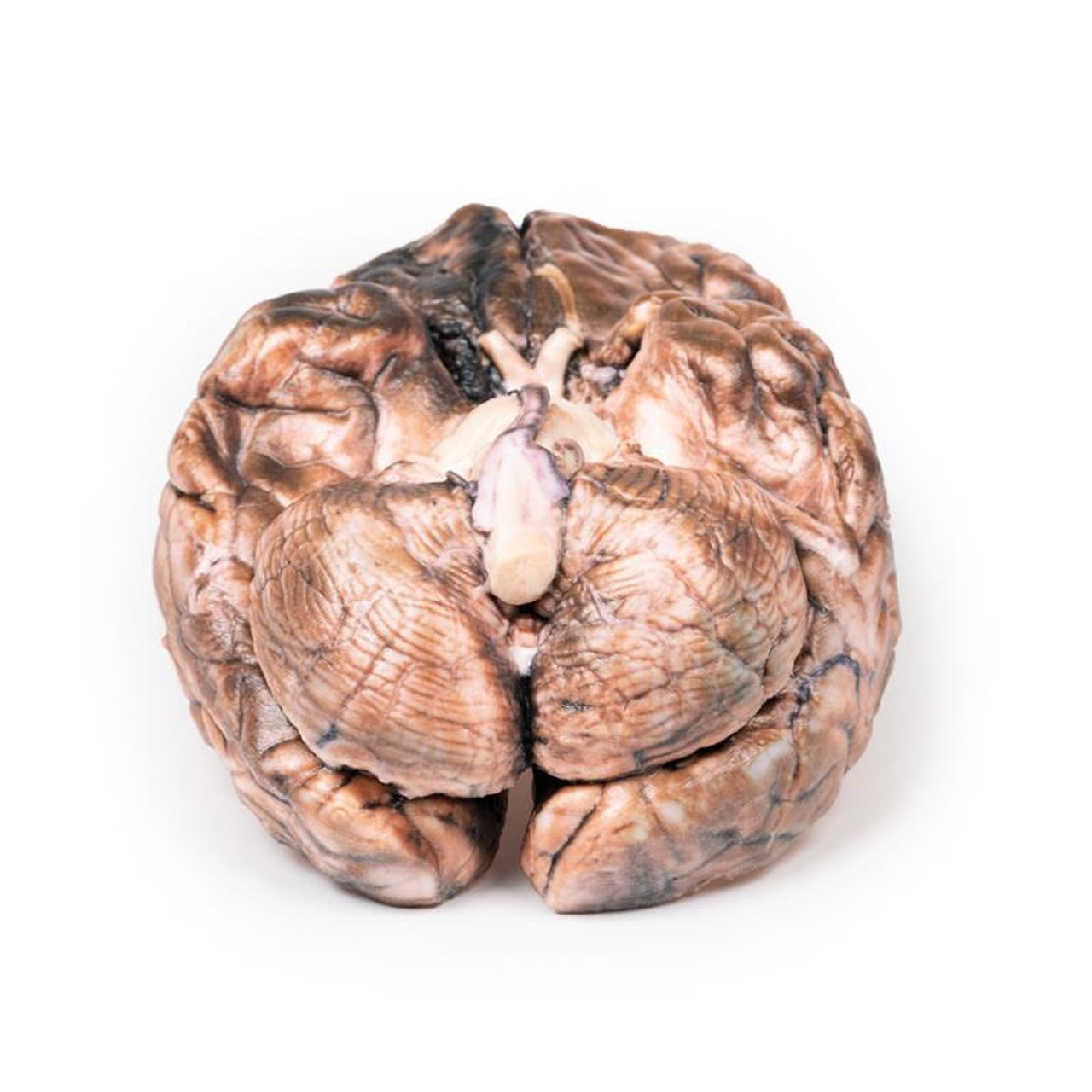
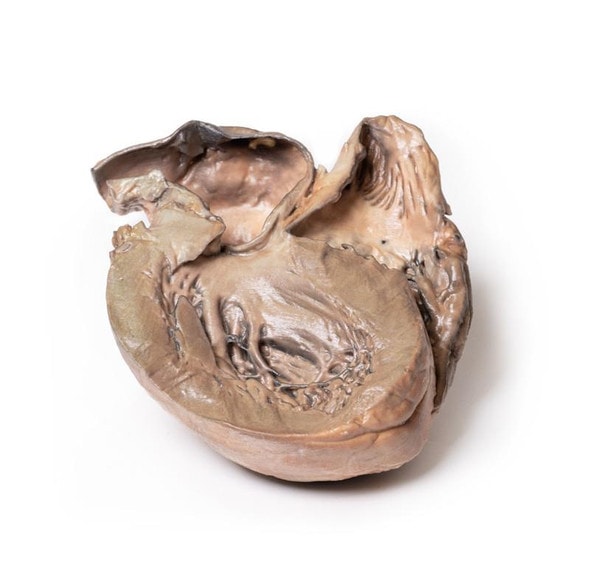
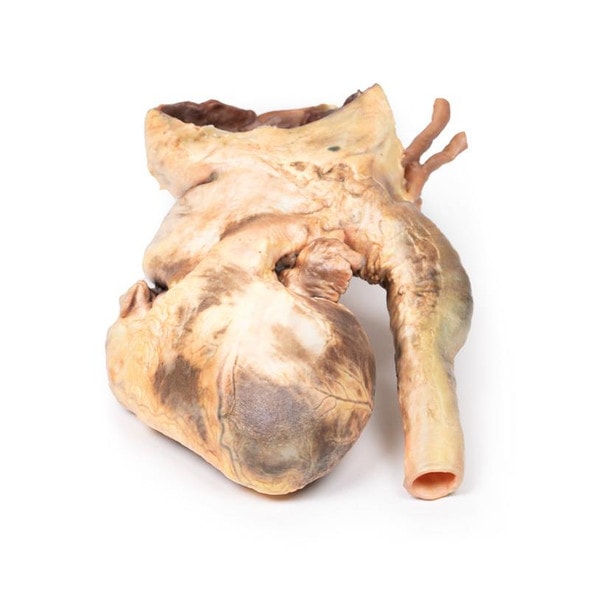
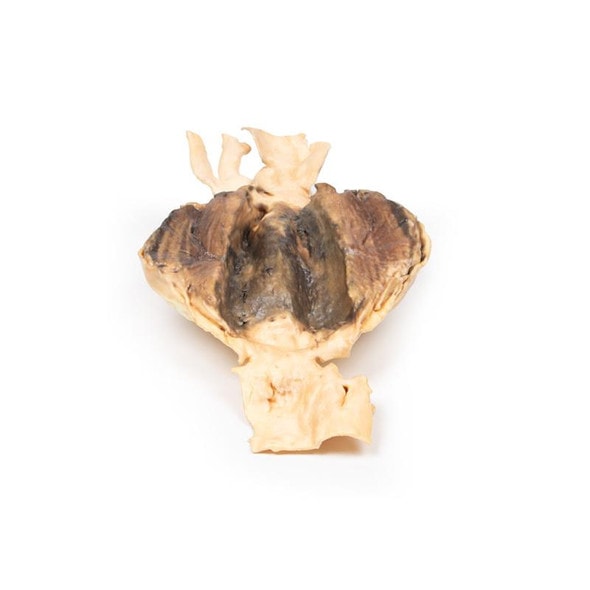
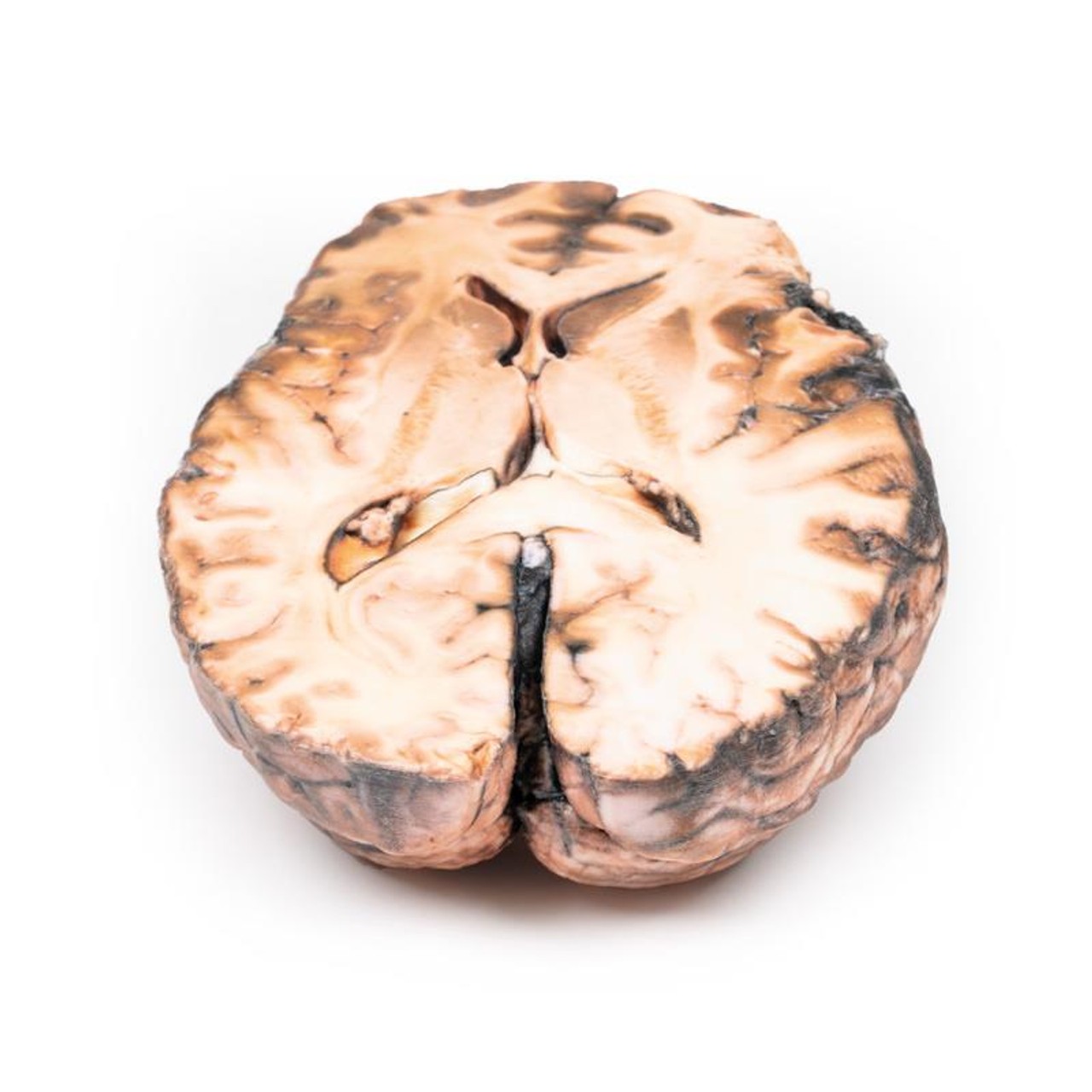
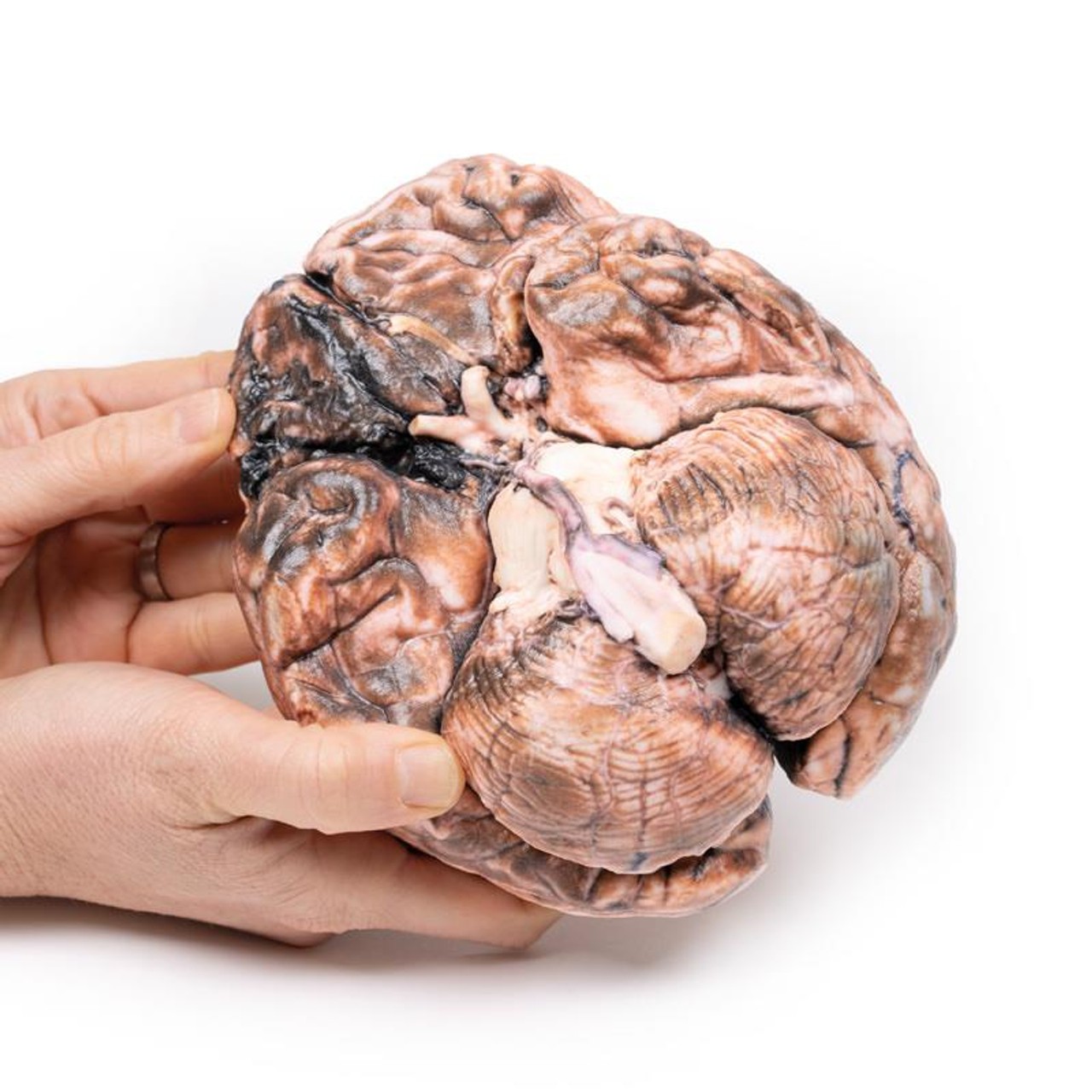
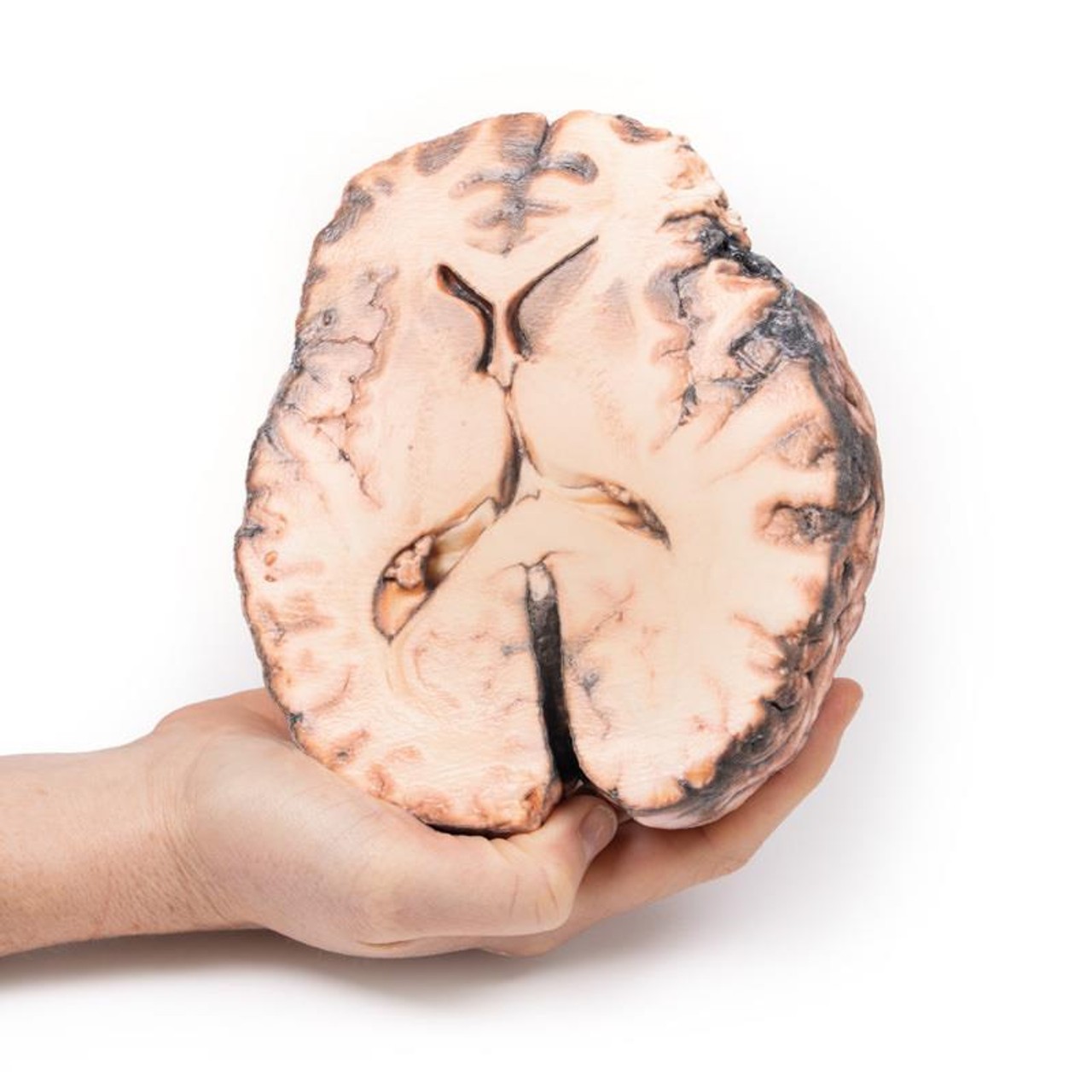
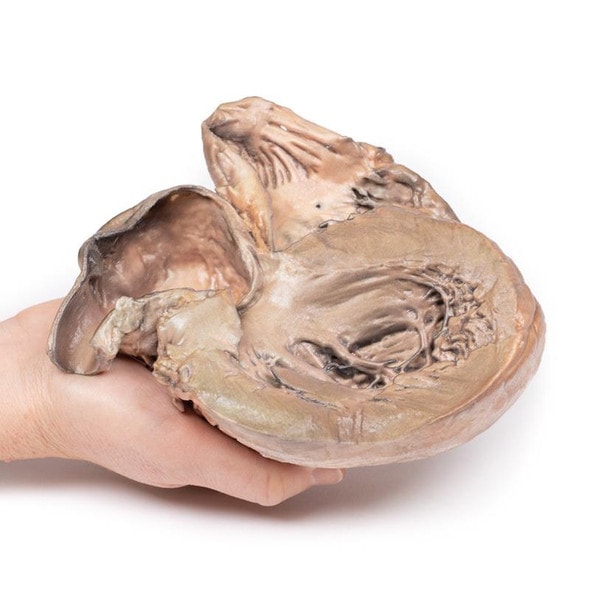
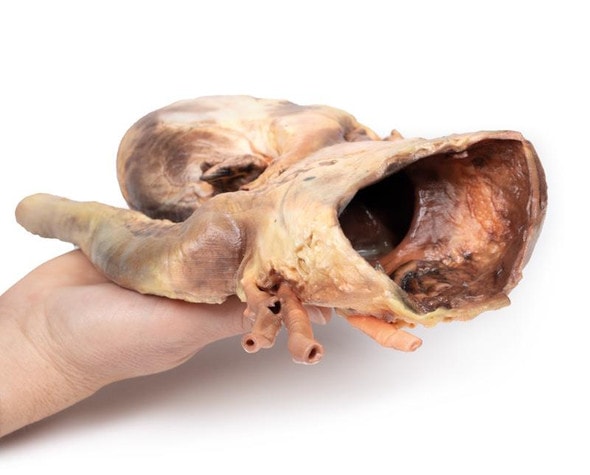
The specimen shows the basal surface of the brain. There is a saccular aneurism 5 mm in diameter at the junction of the right internal carotid and the posterior communicating artery, which has ruptured. There is subarachnoid blood in the immediate area in the cisterna magna and on the inferior surface of the right frontal lobe. There is a similar unruptured aneurysm on the left side. The right frontal lobe appears softer and more friable anteriorly.
Further Information
Aneurysms of the posterior communicating artery are the third most common Circle of Willis aneurysms, and can lead to compression and palsy of closely-located cranial nerves, such as the VI in this case. The proximity of the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve to the ruptured aneurysm may also in this patient explain the sudden onset of pain behind the eye. The visual field defect is most likely due to compression of the right optic tract. The clinical manifestations of stroke are a consequence of the territory of cerebral cortex whose vascular supply is compromised due to the ruptured aneurysm.
Advantages of 3D Printed Anatomical Models
- 3D printed anatomical models are the most anatomically accurate examples of human anatomy because they are based on real human specimens.
- Avoid the ethical complications and complex handling, storage, and documentation requirements with 3D printed models when compared to human cadaveric specimens.
- 3D printed anatomy models are far less expensive than real human cadaveric specimens.
- Reproducibility and consistency allow for standardization of education and faster availability of models when you need them.
- Customization options are available for specific applications or educational needs. Enlargement, highlighting of specific anatomical structures, cutaway views, and more are just some of the customizations available.
Disadvantages of Human Cadavers
- Access to cadavers can be problematic and ethical complications are hard to avoid. Many countries cannot access cadavers for cultural and religious reasons.
- Human cadavers are costly to procure and require expensive storage facilities and dedicated staff to maintain them. Maintenance of the facility alone is costly.
- The cost to develop a cadaver lab or plastination technique is extremely high. Those funds could purchase hundreds of easy to handle, realistic 3D printed anatomical replicas.
- Wet specimens cannot be used in uncertified labs. Certification is expensive and time-consuming.
- Exposure to preservation fluids and chemicals is known to cause long-term health problems for lab workers and students. 3D printed anatomical replicas are safe to handle without any special equipment.
- Lack of reuse and reproducibility. If a dissection mistake is made, a new specimen has to be used and students have to start all over again.
Disadvantages of Plastinated Specimens
- Like real human cadaveric specimens, plastinated models are extremely expensive.
- Plastinated specimens still require real human samples and pose the same ethical issues as real human cadavers.
- The plastination process is extensive and takes months or longer to complete. 3D printed human anatomical models are available in a fraction of the time.
- Plastinated models, like human cadavers, are one of a kind and can only showcase one presentation of human anatomy.
Advanced 3D Printing Techniques for Superior Results
- Vibrant color offering with 10 million colors
- UV-curable inkjet printing
- High quality 3D printing that can create products that are delicate, extremely precise, and incredibly realistic
- To improve durability of fragile, thin, and delicate arteries, veins or vessels, a clear support material is printed in key areas. This makes the models robust so they can be handled by students easily.